Overview
This article explores the important role of ketones in managing Type 2 diabetes, offering insights into their potential as an alternative energy source when glucose levels are low. It's understandable to feel concerned about the risks associated with high ketone levels, particularly diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). By explaining the metabolic process of ketogenesis, we aim to shed light on this complex topic and help you feel more informed.
Monitoring ketone levels is crucial, and various methods are available to assist you in this process. We want to emphasize the clinical implications of elevated ketones and the importance of staying vigilant. Remember, knowledge is power, and being educated about your condition can help prevent serious health complications.
You're not alone in this journey. We encourage you to seek support and resources that can guide you through managing your diabetes effectively. Together, we can navigate the challenges and celebrate the successes along the way.
Introduction
Understanding the role of ketones in managing Type 2 diabetes is becoming increasingly vital for those seeking effective strategies for blood sugar control. These organic compounds, produced during fat metabolism, can provide an alternative energy source when glucose is limited. However, it's crucial to manage their levels to avoid potential complications like diabetic ketoacidosis. How can you harness the benefits of ketones while minimizing the risks associated with elevated levels?
This exploration delves into the mechanisms of ketone production and monitoring methods, along with their implications for diabetes management. We aim to offer insights that could transform your approach to living with this condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Define Ketones and Their Role in Diabetes
Ketones are organic compounds that your liver produces when breaking down fats for energy, especially when glucose is scarce. For those managing blood sugar conditions, ketones type 2 diabetes can provide a vital alternative energy source, especially when insulin levels are low due to fasting, prolonged exercise, or insufficient insulin delivery. However, it's important to be aware that while these compounds can provide energy, high concentrations may indicate a state of ketosis. If not monitored, this can escalate into diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which can be life-threatening.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to providing extensive resources and support for individuals navigating their condition. Understanding how ketones type 2 diabetes are generated is essential for effectively managing blood sugar levels. For instance, during times of illness or stress, individuals with high blood sugar may produce more acids, making it crucial to monitor acid concentrations, particularly when blood glucose exceeds 240 mg/dl. Recent studies indicate that even moderate levels of these compounds can suggest inadequate insulin, underscoring the need for prompt medical consultation to prevent complications.
Statistics show that while DKA is more common in Type 1 diabetes, it can also occur in Type 2 diabetes, particularly among those who are obese or have other risk factors related to ketones type 2 diabetes. This emphasizes the importance of education and awareness regarding acid management in glucose care. By fostering a deeper understanding of ketones type 2 diabetes and their implications, individuals can better navigate their diabetes journey, thereby reducing the risk of serious health emergencies associated with unmanaged diabetes. As Nicole Glaser, a professor and pediatric endocrinologist, notes, "With diabetic ketoacidosis, blood sugar rises significantly, and acidic compounds accumulate to perilous amounts in the body."
You're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way.
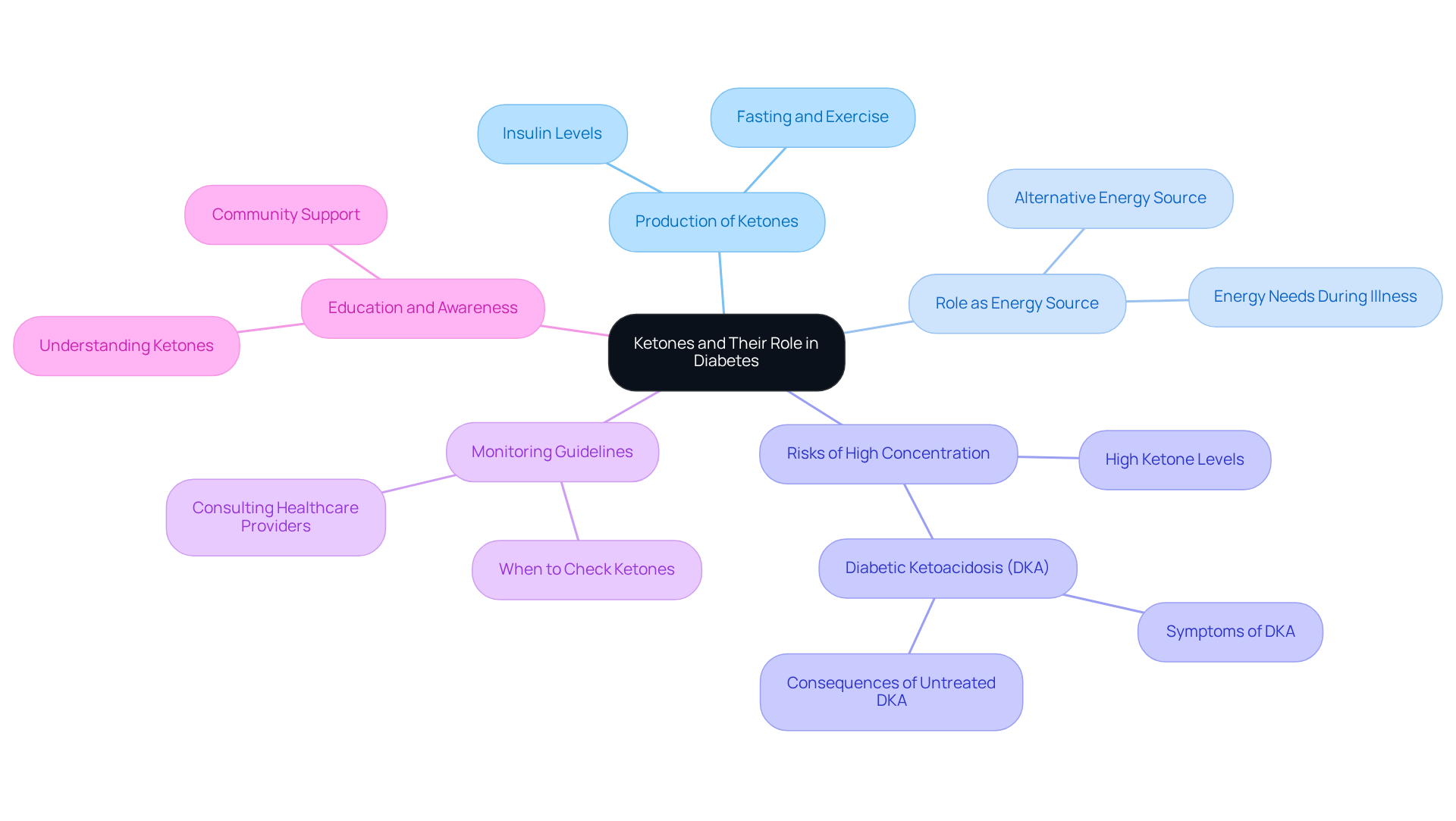
Explain Ketone Production and Physiology
Ketone production, an essential metabolic process known as ketogenesis, primarily takes place in the liver. When carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, insulin levels drop, prompting the body to draw on fat stores for energy. During this process, fatty acids are transformed into ketone-like compounds, mainly acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate (β-OHB), and acetone. These compounds are then released into the bloodstream, serving as an alternative energy source for various tissues, including the brain.
This metabolic adjustment can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes by promoting ketones in type 2 diabetes, which helps maintain energy during times of low glucose availability. However, it's important to monitor levels of these compounds, as excessive production may lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, a serious condition characterized by acidosis.
Recent studies have shown that certain drinks can improve heart efficiency in those with Type 2 Diabetes, suggesting a promising path for enhancing overall health outcomes. For instance, a study involving 13 participants revealed that the consumption of specific fatty acids improved cardiac efficiency both at rest and during moderate exercise compared to a placebo.
Understanding the production of these compounds and their implications for the management of ketones in type 2 diabetes is crucial. You're not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you navigate these changes. We are here to support you every step of the way.
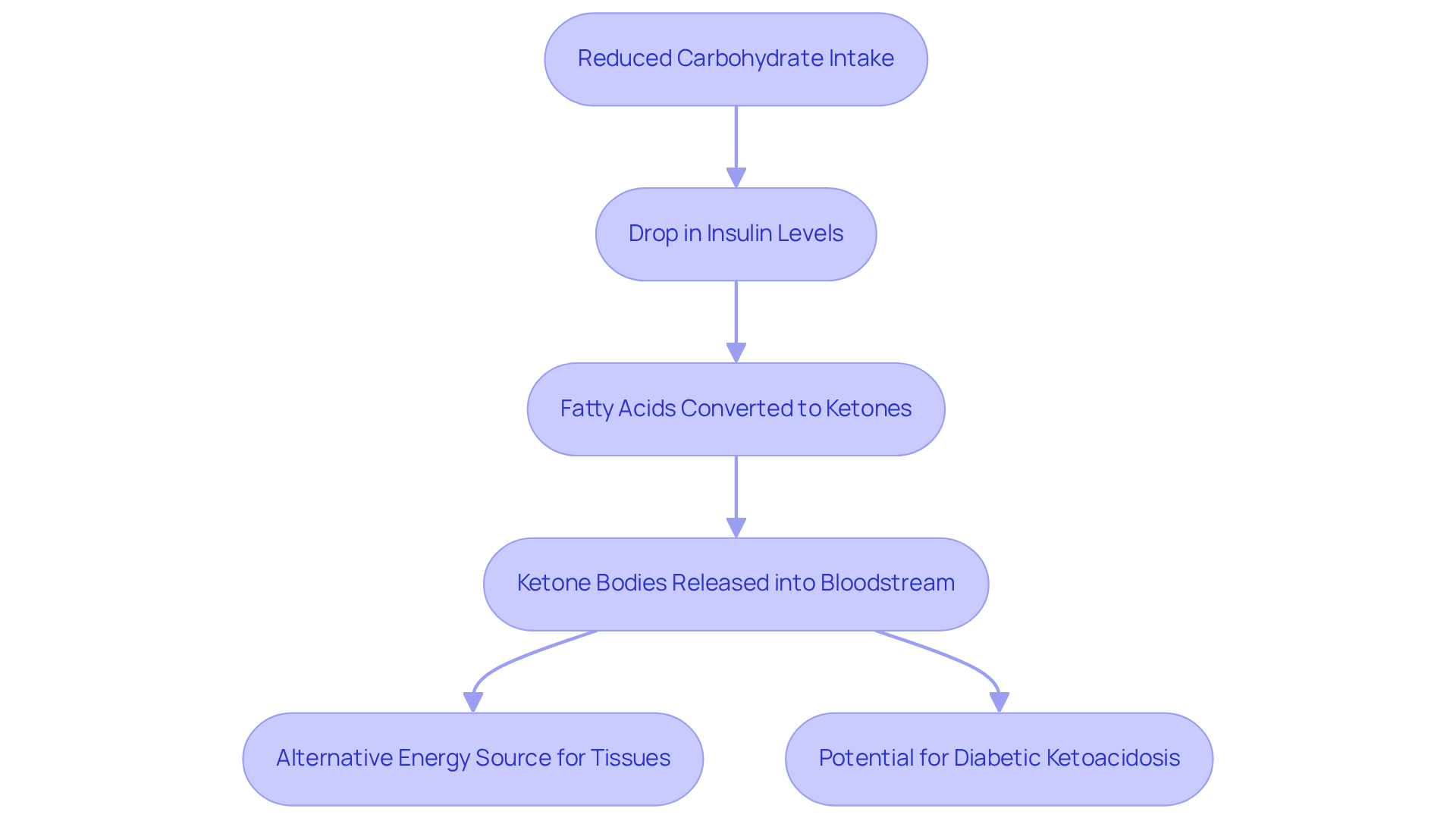
Outline Methods for Measuring Ketones
When it comes to measuring ketones, there are several methods available, each with its own advantages and limitations. Understanding these can help you make informed choices about your health.
-
Blood Ketone Meters: These devices measure beta-hydroxybutyrate levels in the blood, offering a quick and accurate assessment of ketosis. They are considered the gold standard for monitoring ketones type 2 diabetes, with studies showing a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 89% for diagnosing diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Blood testing has been proven to improve outcomes in DKA, especially in critical care settings like ICUs.
-
Urine Ketone Strips: These strips are designed to detect acetoacetate in urine and are very user-friendly, making them a great option for home monitoring. However, it’s important to note that they may not provide reliable results during the early stages of ketosis, as they primarily reflect past production rather than current levels. While urine testing is the most cost-effective method for assessing ketones type 2 diabetes levels, it may not be suitable for long-term monitoring.
-
Breath Acetone Meters: These devices measure acetone levels in your breath, providing a non-invasive way to track ketones. Although convenient, their accuracy can vary, and they may not be as dependable as blood tests for diagnosing DKA.
-
Continuous Ketone Monitoring (CKM): This emerging technology holds promise for preventing DKA by offering real-time insights into your body’s chemical levels.
It’s essential to consistently monitor these substances, especially when you’re feeling unwell or if your blood glucose levels exceed 240 mg/dL. This vigilance can help prevent the onset of DKA. The current recommendation is to check for related compounds every 4-6 hours during these times, ensuring that you can take prompt action and manage your blood sugar effectively.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way.
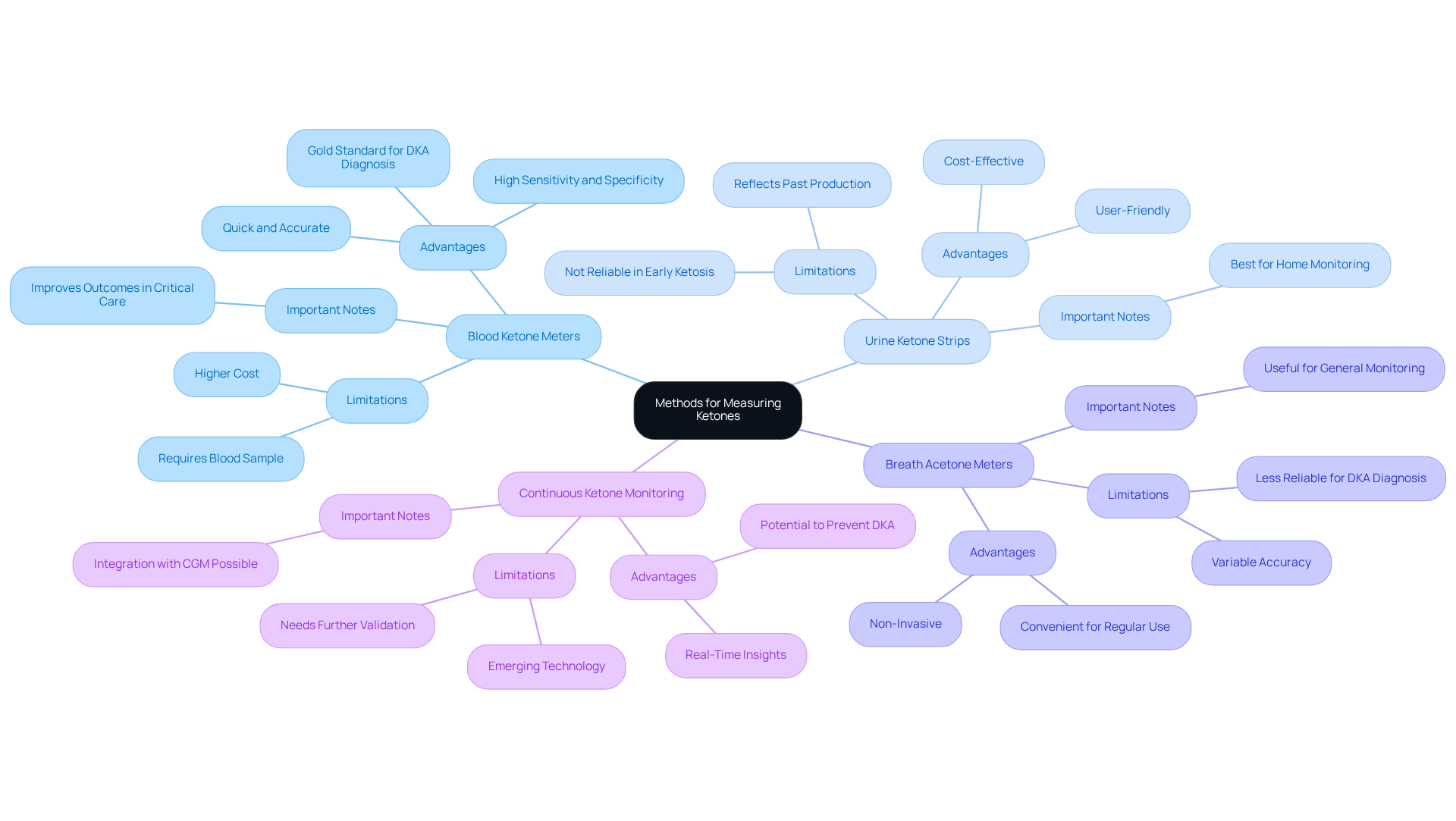
Discuss Clinical Implications of Ketone Levels
Increased concentrations of ketones type 2 diabetes can have significant clinical implications for individuals managing diabetes. While low to moderate levels of these compounds may occur naturally during fasting or low carbohydrate intake, elevated concentrations of ketones type 2 diabetes—typically exceeding 1.5 mmol/L—signal an increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is a serious condition that presents with hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketonuria, and is particularly common in individuals with ketones type 2 diabetes, leading to 14% of diabetes-related hospital admissions and 16% of diabetes-related fatalities.
If blood sugar levels rise above 250 mg/dL, it is a clear indication of DKA, and immediate attention is necessary. Common symptoms include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Confusion
It’s crucial to identify and monitor the concentration of these substances, particularly ketones type 2 diabetes, to prevent DKA and manage blood sugar effectively. Risk factors such as infections, missed insulin treatments, and newly diagnosed diabetes highlight the importance of vigilant monitoring and education.
Recent studies emphasize the value of tracking these substances as a preventive measure. Real-life examples demonstrate that proactive management can effectively prevent DKA. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; seeking support and resources can make a significant difference in your health management.
Explore Future Trends in Ketone Monitoring
The future of monitoring these compounds is bright and full of promise, largely thanks to technological innovations. Ongoing monitoring systems for acid bodies are evolving, enabling real-time observation of concentrations, much like continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. These devices are designed to provide timely alerts for rising levels of acid metabolites, helping you manage your health proactively and significantly reducing the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) associated with ketones type 2 diabetes.
Moreover, researchers are exploring the combination of monitoring with insulin delivery systems, which could allow for automated insulin adjustments based on real-time data. As research progresses, these advancements are set to enhance the quality of life for those managing blood sugar challenges, making effective care more accessible and responsive.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to harnessing these advancements by offering educational materials and support for those who have recently been diagnosed. We aim to help you understand how to monitor your levels effectively and manage your condition. Professor Ketan Dhatariya has highlighted the clinical benefits of a dual-analyte glucose and ketone monitoring system, emphasizing the vital role these innovations play in the management of ketones type 2 diabetes.
You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of ketones in managing type 2 diabetes is crucial for anyone navigating this complex condition. Ketones can serve as an alternative energy source when glucose levels are low, but monitoring their levels is vital to prevent serious complications like diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). By being aware of how ketones are produced and their physiological implications, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your health.
It's important to measure ketones through various methods, such as:
- Blood ketone meters
- Urine strips
- Emerging continuous monitoring technologies
Each method has its own advantages and limitations, but the goal remains clear: effectively managing ketone levels to reduce the risk of DKA. Understanding the clinical implications of elevated ketone levels reinforces the necessity of vigilance in your diabetes management journey.
As technology continues to advance, the future of ketone monitoring looks promising. Innovations like dual-analyte glucose and ketone monitoring systems could revolutionize how you manage your diabetes. Embracing these developments, alongside ongoing education and support, can significantly enhance your quality of life. Taking proactive steps in monitoring and understanding ketones can lead to better health outcomes and a more empowered approach to managing your diabetes.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way as you navigate your health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are ketones and their role in diabetes?
Ketones are organic compounds produced by the liver when breaking down fats for energy, especially when glucose is scarce. For individuals managing blood sugar conditions like type 2 diabetes, ketones can serve as an alternative energy source, particularly when insulin levels are low.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and why is it a concern?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious condition that can occur when high concentrations of ketones accumulate in the body, leading to acidosis. It is more common in Type 1 diabetes but can also occur in Type 2 diabetes, especially in individuals who are obese or have other risk factors.
How can ketone levels affect blood sugar management?
During illness or stress, individuals with high blood sugar may produce more ketones. Monitoring acid concentrations is crucial, particularly when blood glucose exceeds 240 mg/dl, as even moderate levels of ketones can indicate inadequate insulin and the need for medical consultation.
How is ketone production triggered in the body?
Ketone production, known as ketogenesis, occurs primarily in the liver when carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, leading to lower insulin levels. The body then uses fat stores for energy, transforming fatty acids into ketone-like compounds.
What are the main types of ketone compounds produced?
The main ketone compounds produced during ketogenesis are acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate (β-OHB), and acetone. These compounds are released into the bloodstream and serve as an alternative energy source for various tissues, including the brain.
How can certain dietary changes impact heart health in individuals with Type 2 diabetes?
Recent studies suggest that certain drinks containing specific fatty acids can improve heart efficiency in individuals with Type 2 diabetes, enhancing overall health outcomes during both rest and moderate exercise.
What resources are available for individuals managing their diabetes?
T2DSolutions provides extensive resources and support for individuals navigating diabetes, including information on ketones and their implications for blood sugar management.



