Overview
The article focuses on the importance of achieving LDL cholesterol goals in individuals with diabetes, highlighting the critical link between elevated LDL levels and increased cardiovascular risk. It supports this by detailing guidelines from the American Diabetes Association on target LDL levels, the significance of lifestyle modifications, and the necessity of regular monitoring to mitigate cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes.
Introduction
Understanding the intricate relationship between LDL cholesterol and diabetes is crucial for effective health management. Low-Density Lipoprotein, often labeled as 'bad' cholesterol, poses significant risks, particularly for individuals with diabetes who are already predisposed to cardiovascular complications.
With alarming statistics indicating that a substantial percentage of adults with diabetes also suffer from elevated blood pressure, the need for comprehensive LDL management becomes even more pressing. This article delves into the latest guidelines and strategies for maintaining optimal LDL levels, the profound impact of lifestyle modifications, and the importance of regular monitoring.
By equipping readers with essential knowledge and practical tools, it aims to empower individuals to take charge of their health and mitigate the risks associated with diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
The Critical Link Between LDL Cholesterol and Diabetes
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new resource hub for comprehensive education and community support tailored for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 conditions. As we prepare to launch, we recognize the significance of understanding wellness metrics, particularly the LDL goal diabetes in relation to Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, commonly known as 'bad' cholesterol. Elevated LDL levels play a crucial role in plaque accumulation within arteries, significantly increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, particularly among those diagnosed with the condition.
Recent statistics show that 70.8% of U.S. adults with high blood sugar face increased blood pressure, further complicating their cardiovascular condition. Research, including insights from the Framingham Heart Study, underscores the need for vigilant LDL management to achieve the LDL goal for diabetes and mitigate these risks. We are dedicated to offering a range of resources, including:
- Personalized strategies for managing LDL levels effectively to achieve the LDL goal diabetes
- Educational articles
- Community support forums
To stay informed and receive updates on our latest resources, we encourage you to subscribe to our newsletter. By joining our community, you'll be empowered to enhance your long-term health outcomes as we launch T2DSolutions, dedicated to supporting your journey in managing blood sugar levels. Our team at T2DSolutions Content Team is here to assist you every step of the way.
Current Guidelines for LDL Targets in Diabetes Management
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the American College of Cardiology (ACC) established particular recommendations for managing the LDL goal diabetes in individuals with high blood sugar. For patients with a history of cardiovascular disease, the target LDL cholesterol level is less than 70 mg/dL. This is supported by findings from the FOURIER trial, which demonstrated that evolocumab reduced the primary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or coronary revascularization by 15% at the relative rate.
Conversely, for those without such a history, while the thresholds may be less stringent, it remains essential to evaluate individual risk factors to determine suitable targets. As Dr. Itamar Raz, MD, states, "It appears that based on current available data, all individuals with blood sugar issues should be treated with a statin to achieve their ldl goal diabetes unless they apply to very specific exclusion criteria." Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential to ensure alignment with these guidelines and to tailor wellness goals to the unique circumstances of each patient.
Additionally, case studies indicate that dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and a P2Y12 receptor antagonist can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent ischemic events in individuals with glucose metabolism disorders and prior myocardial infarction, underscoring the importance of individualized treatment approaches. This comprehensive and personalized method is essential for effective management of blood sugar levels and cardiovascular health.
Impact of LDL Management on Cardiovascular Health in Diabetic Patients
Controlling LDL levels is crucial for achieving the LDL goal in diabetes, as it helps reduce the increased risks of heart attacks and strokes that are common among individuals with high blood sugar. Research indicates that effective management of LDL levels can reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events by as much as 30%. This significant reduction underscores the necessity of addressing LDL cholesterol through a combination of:
- Pharmacological treatments
- Lifestyle modifications
- Consistent monitoring
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that individuals with diabetes have their metrics closely monitored, particularly to achieve their LDL goal diabetes levels. Additionally, the ORION-1 trial revealed that 26% of individuals were not taking statins, highlighting the prevalence of alternative treatments and the critical need for effective LDL management. Recent studies, including the AMPLITUDE-O trial, have reinforced the importance of LDL management, illustrating that efpeglenatide can reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, thereby optimizing overall well-being in this high-risk population.
By adopting these strategies, diabetic patients can substantially improve their cardiovascular health, achieve their LDL goal diabetes, and enhance their longevity. Furthermore, T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource hub for newly diagnosed patients, offering educational materials and community support to help manage LDL levels effectively and navigate their diabetes journey.
Lifestyle Modifications for Achieving Optimal LDL Levels
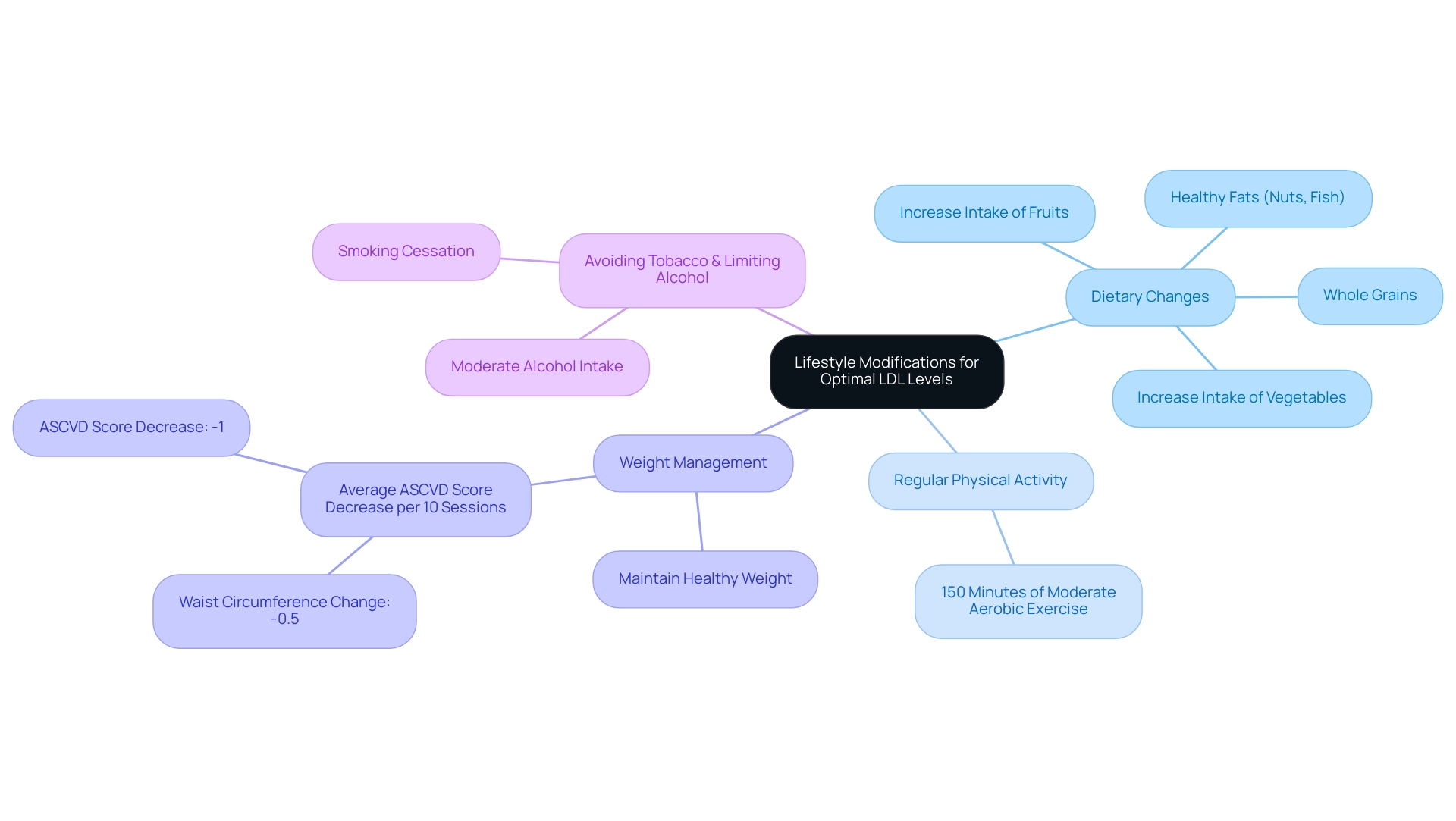
To achieve the LDL goal diabetes, it is crucial for patients to adopt specific lifestyle modifications:
-
Dietary Changes: Increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats—such as those found in nuts and fish—can significantly help in reaching optimal LDL levels. Recent evidence emphasizes that dietary adjustments are essential elements of achieving the LDL goal diabetes management.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Participating in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week is advised, as regular physical activity not only improves lipid levels but also boosts overall well-being.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is vital, as even modest weight loss can lead to significant improvements in LDL levels. A study showed that per ten intervention sessions attended, participants experienced an average decrease of -1 in their ASCVD score, alongside a reduction in waist circumference (-0.5), underscoring the benefits of lifestyle changes.
-
Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol: Smoking cessation and moderating alcohol intake are equally important, as both factors contribute to better cardiovascular health.
As Gómez-Pardo et al. noted, 'comprehensive lifestyle interventions can positively affect cardiovascular risk factors,' reinforcing the significance of these modifications in managing LDL levels effectively. Additionally, the Management Change Package (CMCP) has been developed to assist outpatient clinical settings in implementing evidence-based enhancements for optimal lipid management, emphasizing the importance of such interventions.
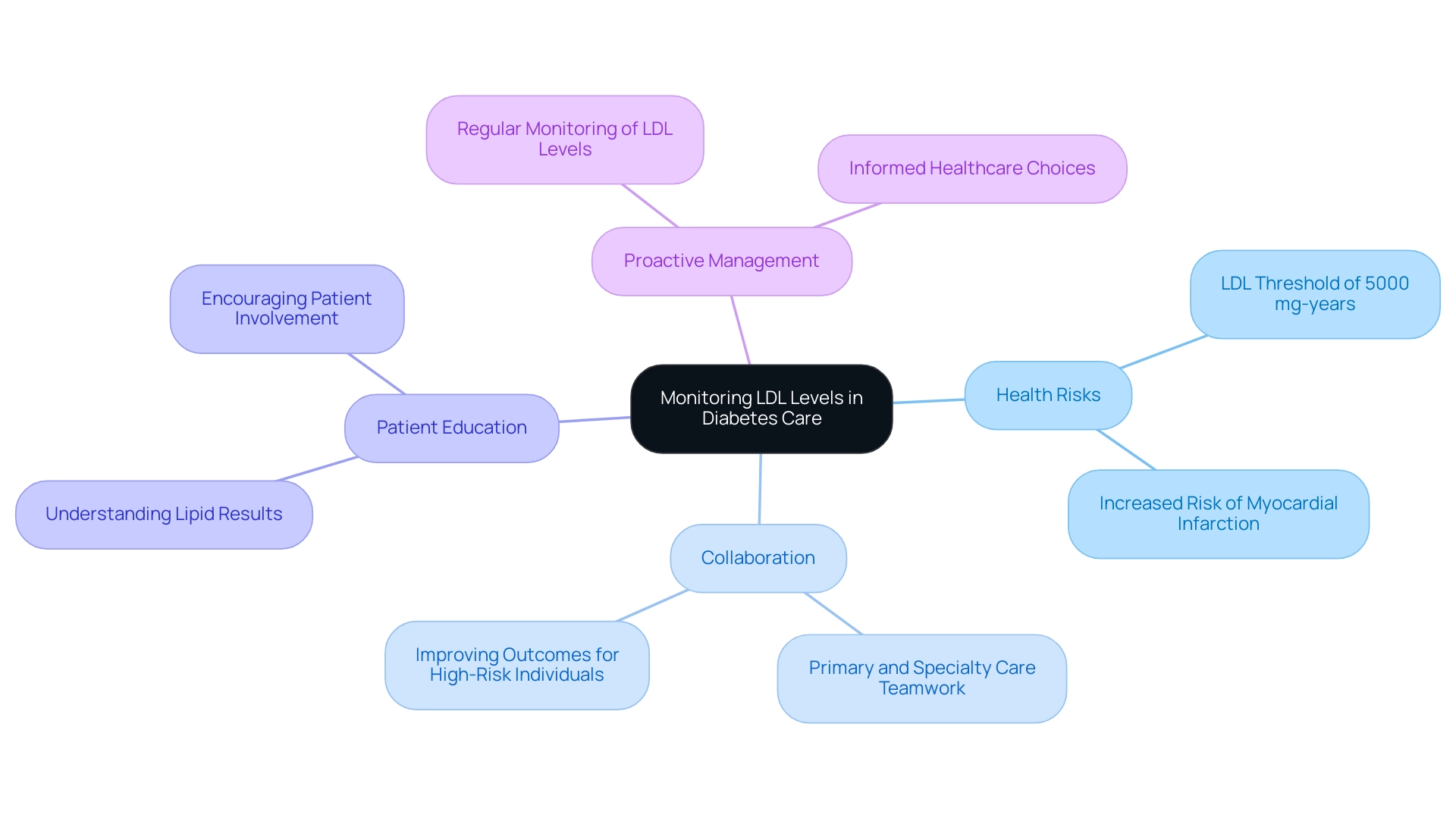
The Importance of Monitoring LDL Levels in Diabetes Care
Regular monitoring of LDL levels is crucial for individuals living with diabetes to achieve their LDL goal diabetes, as it directly impacts the effectiveness of their management strategies. Current recommendations support regular blood tests to assess lipid levels at least once annually, allowing healthcare providers and patients to detect any variations from target ranges quickly. An LDL cholesterol threshold of 5000 mg-years has been linked to a substantial increase in the risk of acute myocardial infarction, underscoring the necessity of vigilant monitoring.
Furthermore, the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee states, 'Close collaboration between primary and specialty care professionals can help to facilitate these transitions in clinical care and, in turn, improve outcomes for high-risk individuals with type 2 conditions.' This emphasizes the significance of collaboration in managing the condition effectively.
Furthermore, a case study titled 'Diabetes Risk With Statin Use' indicates that while statins may elevate the risk of developing the condition, the cardiovascular advantages considerably surpass this risk, with one additional occurrence for every 255 individuals treated over four years, while preventing 5.4 vascular events.
Instructing patients on understanding their lipid results is equally vital, as it encourages increased involvement in their healthcare choices and enhances a sense of responsibility for their condition management. By adopting a proactive approach to LDL monitoring, patients can significantly influence their cardiovascular results while achieving their LDL goal diabetes.
To further support your journey in managing diabetes, we invite you to subscribe to Td Solutions for updates and resources that will empower you in understanding your cholesterol management and overall health.
Conclusion
Understanding the critical connection between LDL cholesterol and diabetes is fundamental for effective health management. Elevated LDL levels pose significant risks, particularly for individuals with diabetes, who are already at a higher risk for cardiovascular complications. The guidelines established by the American Diabetes Association and American College of Cardiology emphasize the importance of targeted LDL management, especially for those with a history of cardiovascular disease.
Implementing lifestyle modifications plays a crucial role in achieving optimal LDL levels. By adopting dietary changes, engaging in regular physical activity, managing weight, and avoiding tobacco, individuals can significantly lower their LDL cholesterol and improve their overall health. Coupled with pharmacological treatments and regular monitoring, these strategies can lead to a marked reduction in cardiovascular events, enhancing longevity and quality of life for those living with diabetes.
Regular monitoring of LDL levels is essential to ensure that management strategies are effective. With proactive engagement in their health care, individuals can better understand their cholesterol levels and take necessary actions to mitigate risks. The importance of education and community support cannot be overstated, as they empower patients to take charge of their diabetes management.
In conclusion, prioritizing LDL cholesterol management is vital for individuals with diabetes to reduce their risk of cardiovascular diseases. By combining medical guidelines, lifestyle changes, and consistent monitoring, patients can significantly improve their health outcomes and navigate their diabetes journey with confidence.



