Overview
This article is dedicated to helping you understand new onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). We will explore its key concepts, the underlying mechanisms, how it is diagnosed, and the treatment strategies available for ongoing management. It’s important to recognize that insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction play significant roles in T2DM.
As you navigate this journey, we provide guidelines for diagnosis through specific tests. You might be feeling overwhelmed, but please know that a comprehensive approach can truly make a difference. This approach combines lifestyle modifications with pharmacological treatments, empowering you to effectively manage your condition. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; support is available every step of the way.
If you have any questions or need further guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out. We are here to support you and ensure you have the resources you need.
Introduction
Understanding the complexities of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is crucial, especially as its prevalence continues to rise globally. This chronic metabolic condition not only poses significant health challenges but also demands a multifaceted approach to management. As you read, you will explore essential concepts—from the mechanisms behind insulin resistance to the latest treatment strategies—empowering you to take control of your health.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed with so much information available. How can you effectively navigate your diabetes journey and implement the right strategies for your unique situation? You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Define Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Key Concepts and Terminology
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic condition that can be challenging to understand. It is characterized by resistance to a key hormone and a relative deficiency of this hormone. Essentially, it occurs when the body struggles to use hormones that help regulate sugar, leading to increased glucose levels in the blood. Let's explore some key terms that can help clarify this condition:
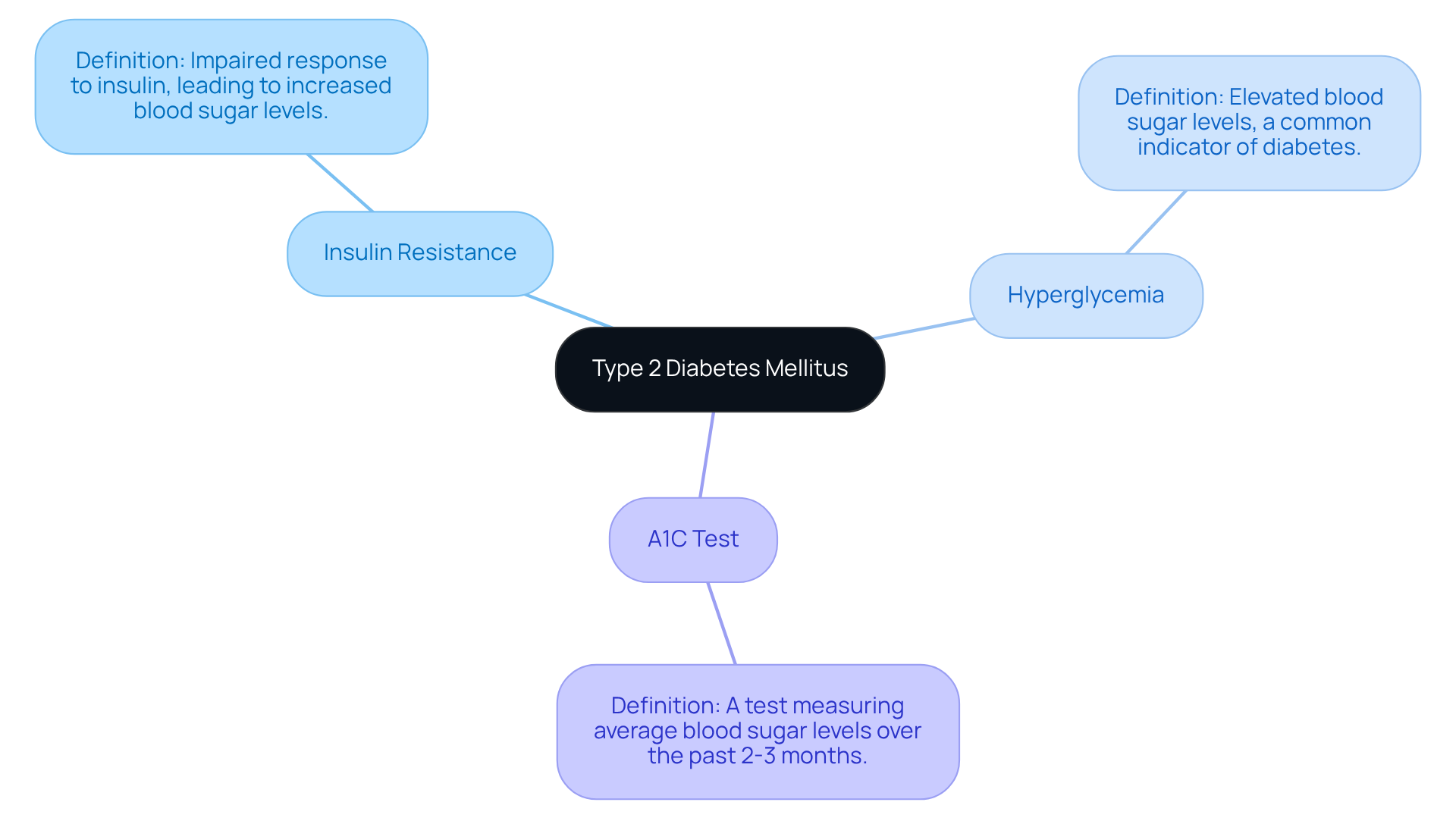
- Insulin Resistance: This is when your body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, which is crucial for managing blood sugar levels.
- Hyperglycemia: This term refers to elevated sugar concentrations, which is a common indicator of diabetes.
- A1C Test: This test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, serving as a vital tool for diagnosis and ongoing monitoring.
Understanding these terms is essential for effective communication with your healthcare provider and for managing your condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; seeking support and resources can make a significant difference in your experience. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Explore the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes: Mechanisms and Implications
Explore the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes: Mechanisms and Implications
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes can feel overwhelming, but it’s important to know you’re not alone in this journey. The pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes involves several key mechanisms that are crucial to grasp:
-
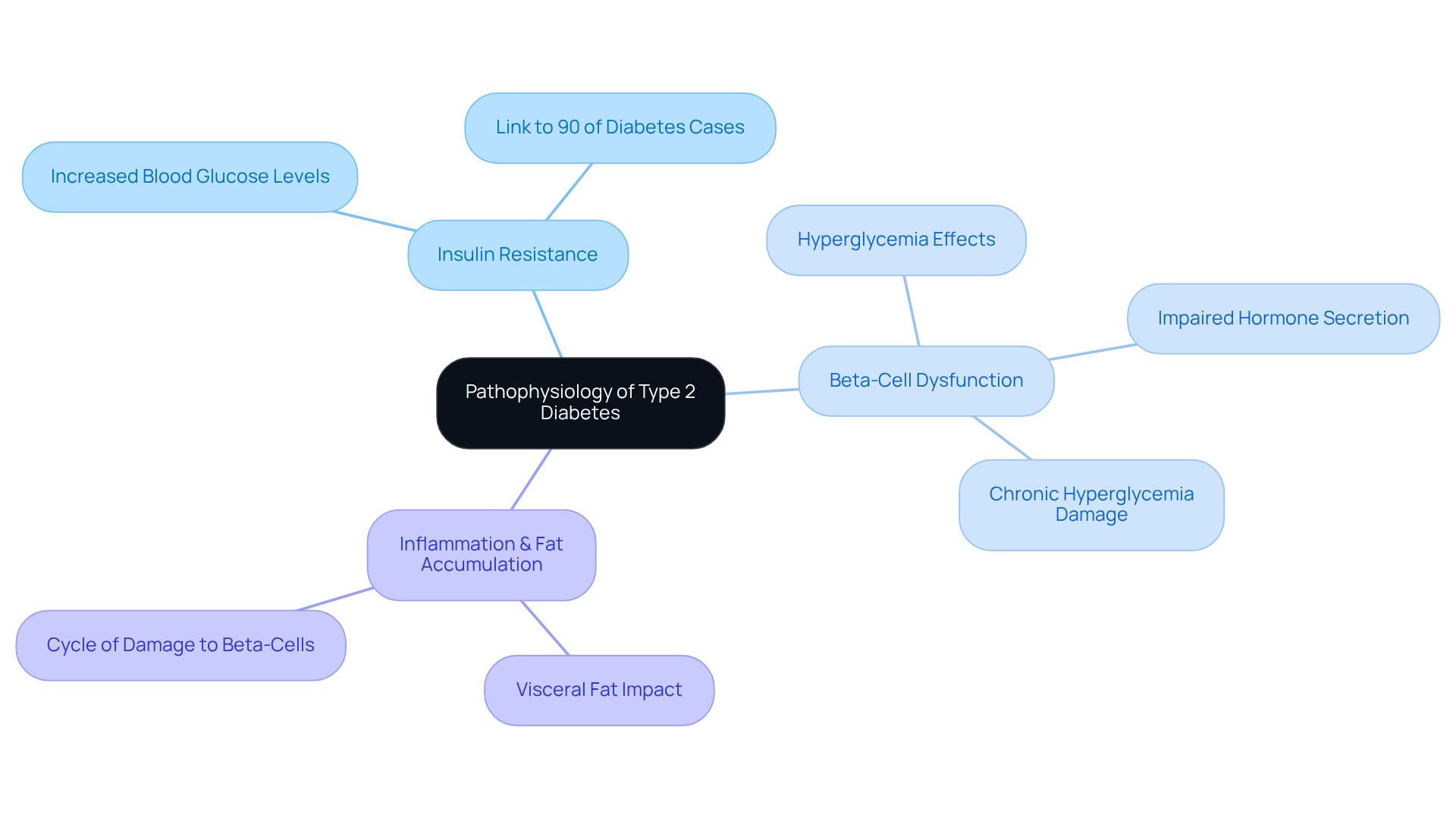
Insulin Resistance: Many people experience insulin resistance, where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin. This leads to increased blood glucose levels. Almost 90% of diabetes instances are linked to new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus, highlighting how significant this resistance is in the overall diabetes context.
-
Beta-Cell Dysfunction: Over time, the pancreas may struggle to produce enough insulin to overcome resistance, resulting in hyperglycemia. Research indicates that persistent high blood sugar can harm pancreatic beta-cells, hindering their ability to release hormones effectively. It’s understandable to feel concerned about how this affects your health.
-
Inflammation and Fat Accumulation: Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat, can lead to inflammation that worsens glucose sensitivity. This inflammation creates a harmful cycle where elevated blood glucose further damages beta-cells, decreasing hormone secretion.
Recognizing these mechanisms is vital for developing effective treatment strategies and lifestyle modifications. At T2DSolutions, we aim to be a comprehensive resource hub for patients with new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus like you, providing education and support to help navigate these challenges. By understanding the interplay between insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction, you can adopt lifestyle changes and treatment plans that address these underlying issues, ultimately improving your health outcomes.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Understand Diagnosis: Criteria and Screening for Type 2 Diabetes
Understanding the diagnosis of new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus can feel overwhelming, but it's essential to know that specific criteria established by health organizations guide this process. Let's explore the key tests that help in this diagnosis:
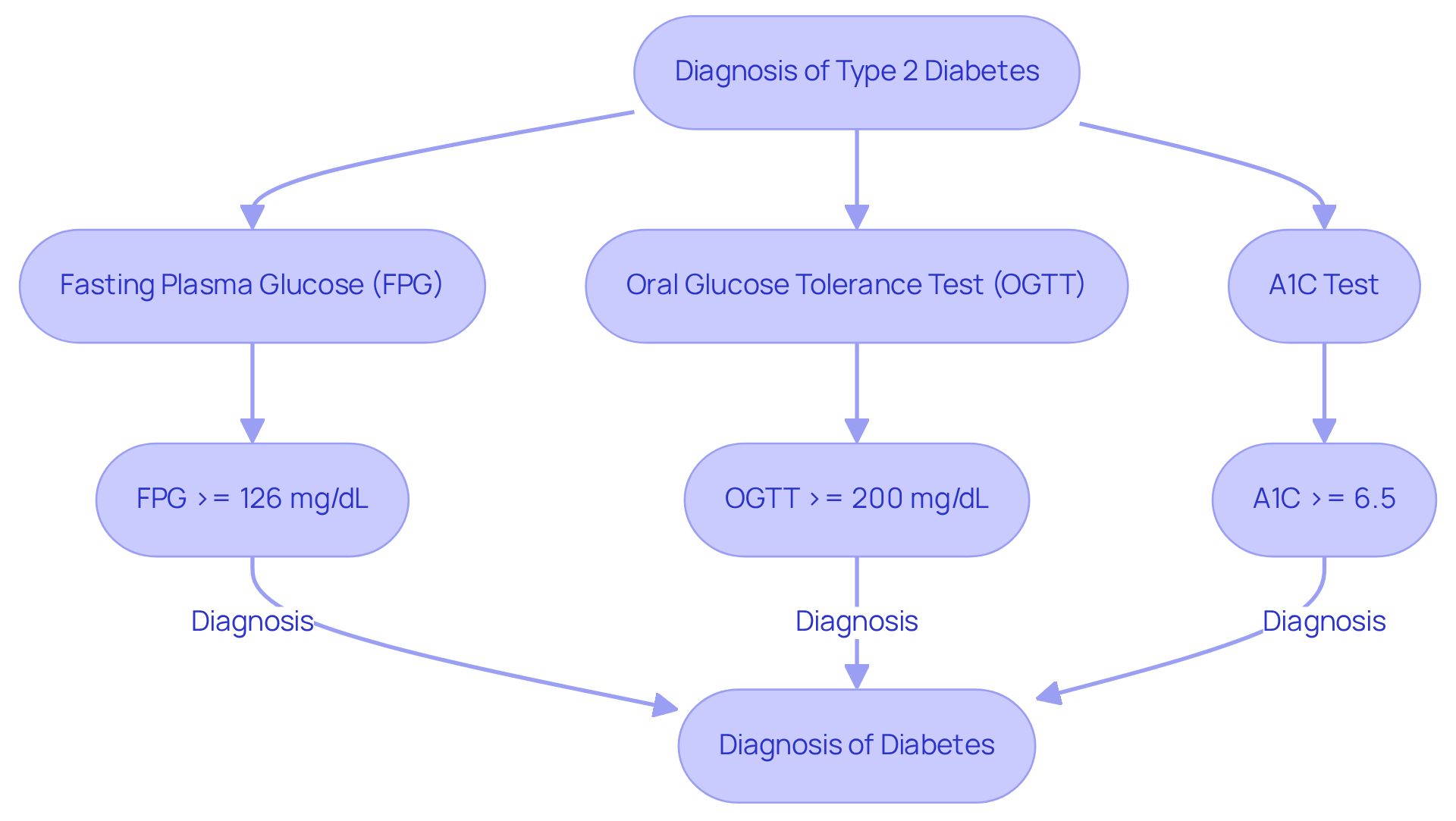
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG): A level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher indicates diabetes. This test is crucial as it shows how well your body manages blood sugar levels after fasting.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): A 2-hour plasma concentration of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or above signals diabetes. This test assesses how effectively your body handles sugar, which is particularly important for identifying insulin resistance.
- A1C Test: An A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes. This test provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months, giving a broader perspective on your sugar management.
Regular screening is vital, especially for those aged 45 and older or individuals with risk factors like obesity or a family history of new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. Did you know that approximately 29.1 million people in the U.S. have diabetes, many of whom remain undiagnosed? Early detection through these screening methods can significantly influence management strategies for individuals with new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and improve health outcomes.
For example, if a patient has a fasting plasma sugar level of 130 mg/dL and an A1C of 6.8%, they would be diagnosed with diabetes. This emphasizes the importance of consistent monitoring. Additionally, the OGTT can reveal how your body responds to glucose intake, providing critical insights for tailored management plans.
It's understandable to feel uncertain about these processes, but remember that regular screening and a clear understanding of diagnostic criteria are essential for effective diabetes management. You can take proactive steps in your health journey, and you’re not alone in this. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Review Treatment Strategies: Lifestyle Modifications and Pharmacological Approaches
Effectively managing new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus requires a multifaceted approach that combines lifestyle changes with medications. At T2DSolutions, we understand how overwhelming this journey can be for patients newly diagnosed with new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus, and we are here to provide the guidance and support you need.
-
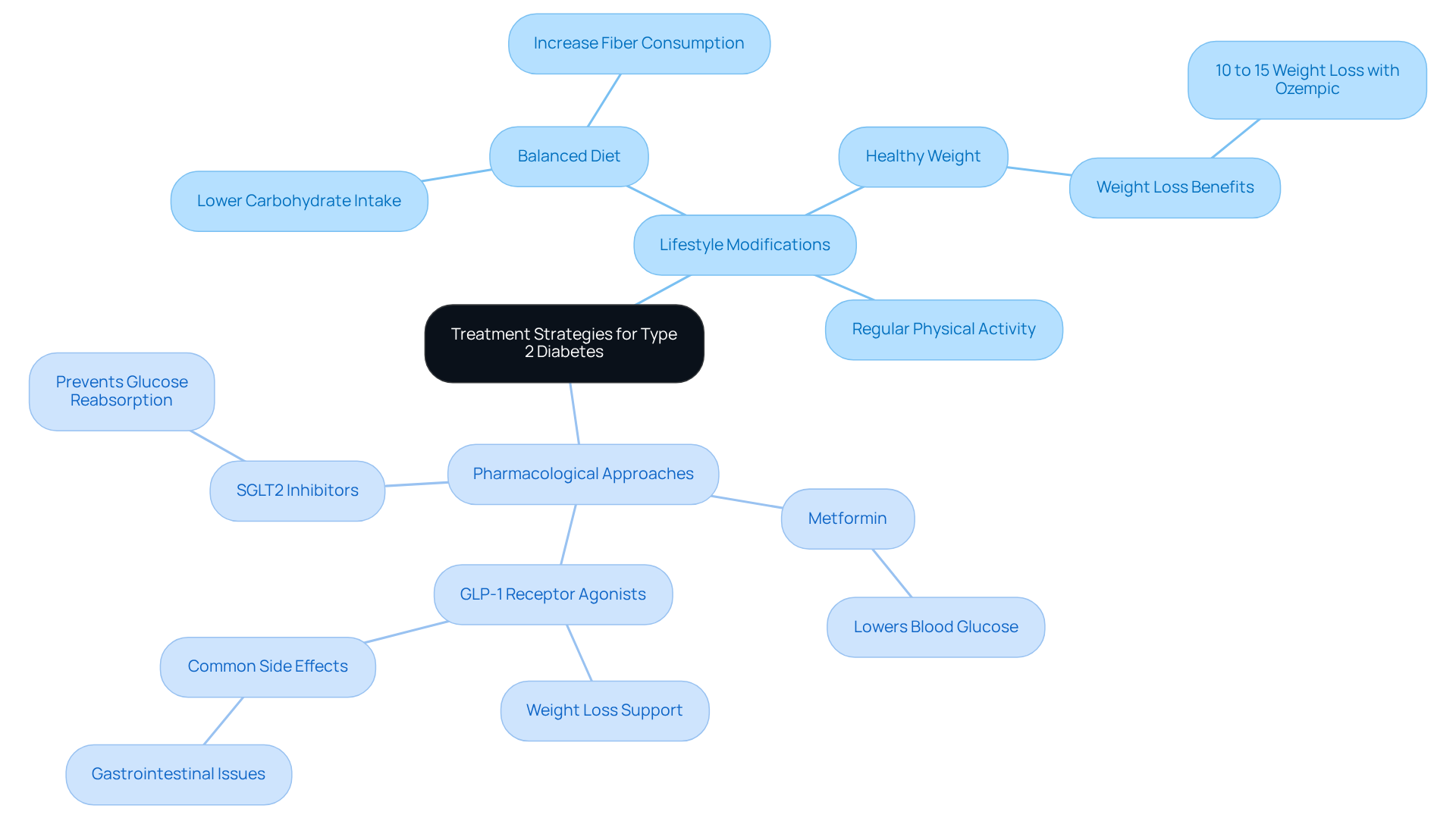
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and achieving a healthy weight are key strategies that can make a real difference. Dietary guidelines often emphasize lowering carbohydrate intake while increasing fiber consumption, which can significantly help in regulating blood sugar levels. Many patients have experienced improved glucose readings and better weight management through these changes, and T2DSolutions offers educational resources to help you implement these lifestyle modifications effectively. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
-
Pharmacological Approaches: Medications such as Metformin are commonly recommended to help control glucose levels. Recently, newer classes of medications, including GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, have proven effective for many patients. These medications not only assist in lowering glucose levels but also support weight loss and heart health. For example, GLP-1 receptor agonists can lead to weight reductions of about 10% to 15% over a year when paired with lifestyle changes. However, it’s important to be aware that medications like Ozempic may have potential side effects, including gastrointestinal issues like nausea and constipation.
A comprehensive approach that integrates both lifestyle changes and pharmacological treatments is vital for effective management of new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. At T2DSolutions, we empower you to take control of your health and enhance your quality of life through accessible information and community support. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Implement Ongoing Management: Monitoring and Support for Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Type 2 Diabetes effectively requires consistent monitoring and a strong support system.
-
Sugar Monitoring: Regularly checking your sugar levels is essential for understanding how your diet, physical activity, and medications impact your glucose. This practice empowers you to make informed choices about your health, helping you feel more in control.
-
A1C Testing: It’s important to have A1C testing done at least twice a year. This test provides a comprehensive view of your long-term sugar control, helping you to identify patterns and necessary adjustments in your management approach. Remember, it’s a step toward understanding your body better.
-
Support Systems: Connecting with healthcare providers, diabetes educators, and support groups is crucial for both emotional and practical support. These resources can offer personalized guidance, creating a sense of community and shared experience. Additionally, using technology like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can enhance your self-management by providing real-time insights into your sugar levels.
Establishing a routine for monitoring your blood glucose and seeking support is vital for effective diabetes management. You're not alone in this journey; reaching out can lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus is crucial for effective management and improved health outcomes. This condition, characterized by insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction, requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, pharmacological treatments, and ongoing monitoring. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but by familiarizing yourself with key concepts and terminology, you can better navigate your health journey and engage in meaningful conversations with healthcare providers.
The article delves into the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes, emphasizing the significance of insulin resistance and the implications of inflammation and fat accumulation. It outlines essential diagnostic criteria and screening methods, highlighting the importance of early detection. You may wonder how to take the next steps; effective management strategies—including dietary changes, exercise, and medication options—are vital components in controlling blood sugar levels and enhancing your overall well-being.
Ultimately, managing type 2 diabetes is an ongoing process that requires dedication and support. By actively monitoring your blood glucose levels and seeking assistance from healthcare professionals and support groups, you can take charge of your health and improve your quality of life. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Embracing these strategies not only fosters a better understanding of the condition but also empowers you to live a healthier, more fulfilling life. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)?
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic condition characterized by resistance to insulin and a relative deficiency of insulin, leading to increased glucose levels in the blood.
What does insulin resistance mean?
Insulin resistance refers to the body's cells not responding effectively to insulin, which is crucial for managing blood sugar levels.
What is hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia is the term used to describe elevated sugar concentrations in the blood, which is a common indicator of diabetes.
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test measures the average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months and is an important tool for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes.
What role does beta-cell dysfunction play in Type 2 Diabetes?
Beta-cell dysfunction occurs when the pancreas struggles to produce enough insulin to overcome insulin resistance, resulting in hyperglycemia. Persistent high blood sugar can harm pancreatic beta-cells, affecting their ability to release hormones.
How does inflammation and fat accumulation affect Type 2 Diabetes?
Excess body fat, especially visceral fat, can lead to inflammation that worsens glucose sensitivity. This inflammation creates a cycle where elevated blood glucose further damages beta-cells, decreasing hormone secretion.
Why is understanding the pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes important?
Understanding the pathophysiology is vital for developing effective treatment strategies and lifestyle modifications that can improve health outcomes for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes.
What support is available for those with Type 2 Diabetes?
Support and resources are available through organizations like T2DSolutions, which aim to provide education and assistance for individuals navigating the challenges of new onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.



