Overview
This article seeks to understand the nursing diagnoses for type 2 diabetes, highlighting their vital role in guiding patient care. By categorizing these diagnoses into actual, risk, and health promotion diagnoses, we can see how these classifications inform tailored interventions and education. This approach ultimately leads to improved health outcomes for individuals managing this condition.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed when navigating a new diagnosis. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. The insights provided here aim to empower you with knowledge, enabling you to take an active role in your health. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
In the realm of healthcare, managing Type 2 Diabetes can feel overwhelming, presenting a unique set of challenges. It's essential to have a comprehensive understanding of nursing diagnoses, as these critical clinical judgments guide healthcare professionals in meeting the specific needs of patients, families, and communities affected by diabetes. By categorizing these diagnoses into actual, risk, and health promotion types, nurses can tailor interventions that not only address existing health issues but also empower patients on their journey toward better health.
As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, particularly among vulnerable populations, the importance of effective nursing diagnoses becomes increasingly clear. You're not alone in this journey; many are facing similar challenges. This article delves into the intricacies of nursing diagnoses in Type 2 Diabetes, exploring their vital role in enhancing patient education, promoting lifestyle modifications, and ultimately improving health outcomes. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Defining Nursing Diagnoses in Type 2 Diabetes
The nursing diagnosis for type 2 diabetes is a vital aspect of understanding how individuals, families, or communities respond to both actual and potential medical concerns. These diagnoses are crucial for guiding the nursing process and can be classified into three primary categories:
-
Actual Diagnoses: These reflect current health challenges, such as 'Ineffective Health Management' or 'Imbalanced Nutrition: More than Body Requirements.' Such diagnoses indicate that the patient is facing difficulties that require prompt attention and intervention.
-
Risk Diagnoses: These highlight potential medical issues that may emerge, like 'Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose Levels.' Recognizing these risks allows healthcare professionals to implement preventive measures, reducing the likelihood of complications related to the condition.
-
Health Promotion Diagnoses: These emphasize the individual's readiness to enhance their health, exemplified by 'Readiness for Enhanced Self-Management.' This category underscores the importance of empowering individuals to take an active role in managing their health.
Understanding these categories is essential for nurses as they develop nursing diagnoses for type 2 diabetes and create tailored care plans and interventions. The prevalence of nursing diagnoses in glucose management is significant, with research indicating that effective individual education and self-management techniques can lead to improved health outcomes. For example, a case study titled "Patient Education and Self-Management in Diabetes" highlighted the role of nurses in educating patients about dietary choices, exercise, and medication adherence, demonstrating that proactive management can enhance overall well-being.
Recent statistics reveal a concerning trend: from 2002 to 2018, the incidence of this condition among children and adolescents has notably risen, especially among non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic Black groups. This emphasizes the urgent need for healthcare professionals to effectively utilize nursing diagnoses for type 2 diabetes, addressing the evolving landscape of diabetes care.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of these nursing diagnoses and strive to provide a comprehensive resource hub for those newly diagnosed. By integrating the nursing diagnosis for type 2 diabetes into our educational materials, we empower individuals to better understand their health and engage in effective self-management strategies. Experts agree that maintaining consistent blood glucose levels is crucial for promoting healing and preventing complications.
As noted by Sapra A., "Patients should also strive to maintain consistent blood glucose levels to promote healing." As healthcare providers enhance their strategies for managing blood sugar conditions, the incorporation of nursing diagnoses for type 2 diabetes will remain a cornerstone of effective care, ensuring that individuals receive comprehensive support tailored to their unique needs. Furthermore, lifestyle modification programs have been shown to improve outcomes for individuals with type 2 diabetes, highlighting the importance of lifestyle changes within nursing assessments.

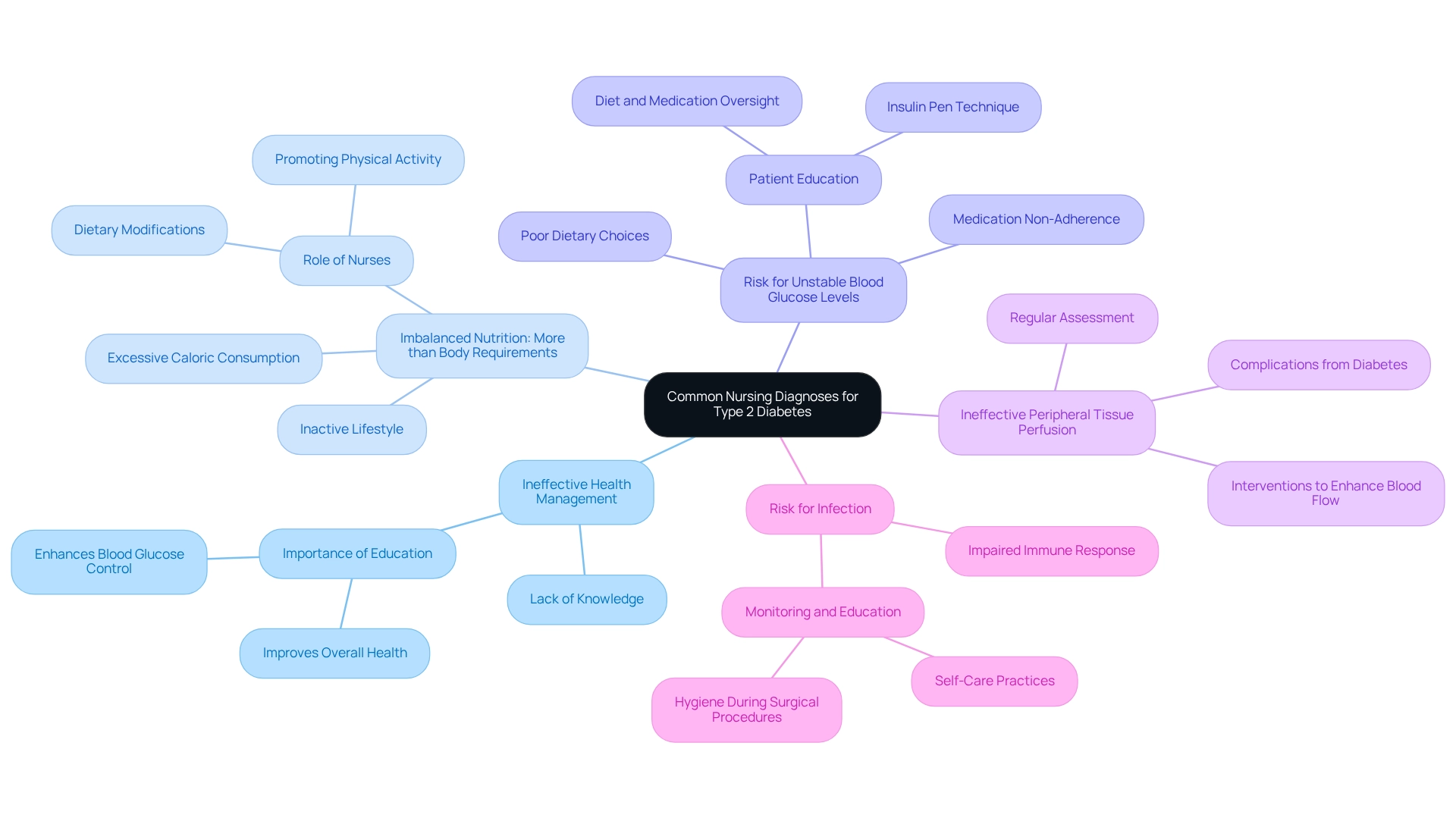
Common Nursing Diagnoses for Type 2 Diabetes
Common nursing diagnoses for patients with Type 2 Diabetes encompass several critical areas that guide effective care and intervention strategies.
-
Ineffective Health Management: It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed when managing diabetes. This diagnosis often arises from a lack of knowledge regarding diabetes management. Patients may struggle to understand their condition, leading to poor adherence to treatment plans. Education is crucial; research shows that effective health education significantly enhances blood glucose control and overall health results.
-
Imbalanced Nutrition: More than Body Requirements: Many individuals face challenges related to excessive caloric consumption and an inactive lifestyle. This diagnosis highlights the need for dietary modifications and increased physical activity. Nurses play a vital role in informing individuals about balanced nutrition and the significance of sustaining a healthy weight. Remember, small changes can lead to significant improvements.
-
Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose Levels: Poor dietary choices and medication non-adherence contribute to this diagnosis. It’s essential for healthcare practitioners to observe individuals closely and offer advice on maintaining stable blood glucose levels through appropriate diet and medication oversight. Patients should also be instructed on proper insulin pen technique and safety measures for effective use.
-
Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion: Diabetes can lead to complications such as poor circulation. Nurses must assess peripheral circulation regularly and implement interventions to enhance blood flow, thus reducing the risk of complications.
-
Risk for Infection: Elevated blood sugar levels can impair the immune response, increasing susceptibility to infections. This diagnosis necessitates vigilant monitoring and education on self-care practices to minimize infection risks.
Statistics reveal that a significant percentage of individuals with Type 2 Diabetes experience nursing diagnoses, underscoring the importance of targeted interventions. For instance, individuals aged 40 years or older should be screened for diabetes, emphasizing the importance of early detection and management.
In addressing the nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2, nurses can implement various interventions, including personalized education plans, dietary counseling, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Case studies showcase the effectiveness of these methods, demonstrating that thorough education and lifestyle changes lead to better wellness outcomes.
Expert insights emphasize the importance of a collaborative approach in managing these nursing diagnoses. By working closely with patients, healthcare providers can foster a supportive environment that encourages self-management and promotes better health outcomes. As Banting, Best, and Collip stated, "In 1922 Banting, Best, and Collip extracted the hormone insulin from the pancreas of cows at the University of Toronto, resulting in the accessibility of an effective remedy for blood sugar regulation in 1922." This historical context highlights the importance of insulin in regulating blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, promoting self-care and hygiene, especially during surgical procedures, is crucial for maintaining glycemic control and preventing complications. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Identifying Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
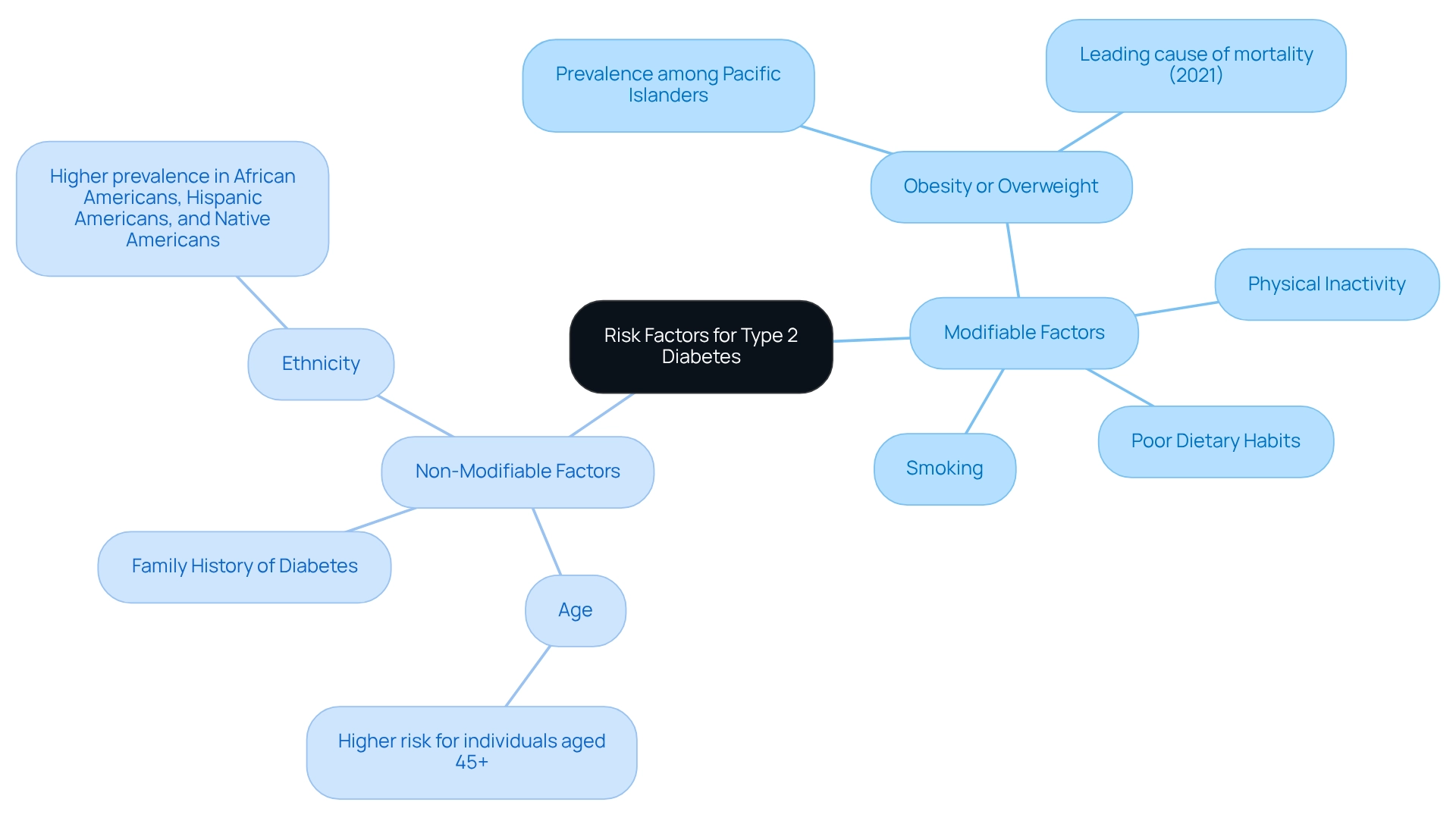
Risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes can be categorized into two main groups: modifiable and non-modifiable factors, each playing a crucial role in the development and management of the condition.
Modifiable Factors:
-
Obesity or Overweight: Excess body weight significantly increases the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes. In 2025, the prevalence of obesity remains a critical concern, particularly among certain populations, such as Pacific Islanders, who are classified as overweight with a BMI of 26 or higher. This highlights the pressing need for effective weight management strategies. It's concerning to note that this condition was the eighth leading cause of mortality in the United States in 2021, with 103,294 death certificates indicating this illness as the underlying reason.
-
Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to insulin resistance and weight gain, both of which are key risk factors for this condition. Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and improving insulin sensitivity.
-
Poor Dietary Habits: Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to obesity and metabolic issues. Emphasizing balanced nutrition is vital for diabetes prevention.
-
Smoking: Tobacco use is linked to an increased risk of diabetes and its complications, making cessation a critical component of risk reduction strategies.
Non-Modifiable Factors:
-
Age: Individuals aged 45 years or older are at a higher risk for developing Type 2 Diabetes, highlighting the importance of regular screenings as one ages.
-
Family History of Diabetes: A genetic predisposition can significantly influence an individual's risk, making awareness of family health history essential.
-
Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Native Americans, exhibit a higher prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes. This necessitates targeted education and prevention efforts within these communities.
Identifying these risk factors enables healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, to tailor education and interventions effectively. By addressing both changeable and unchangeable factors, nurses can utilize a nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2 to empower individuals to take proactive measures in lowering their risk of developing this condition or its complications. This approach not only improves health outcomes but also aids in the larger objective of addressing the increasing financial burden of diabetes-related issues, which amounted to $413 billion in the U.S. in 2022. Additionally, a straightforward blood examination can ascertain if an individual has diabetes, and subsequent testing is advised for precise outcomes. Early identification is crucial in managing risk factors.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to offering newly diagnosed individuals the resources and support they require to comprehend and manage their risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes. Our platform provides educational materials, community support, and guidance to help you navigate your journey towards better health. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
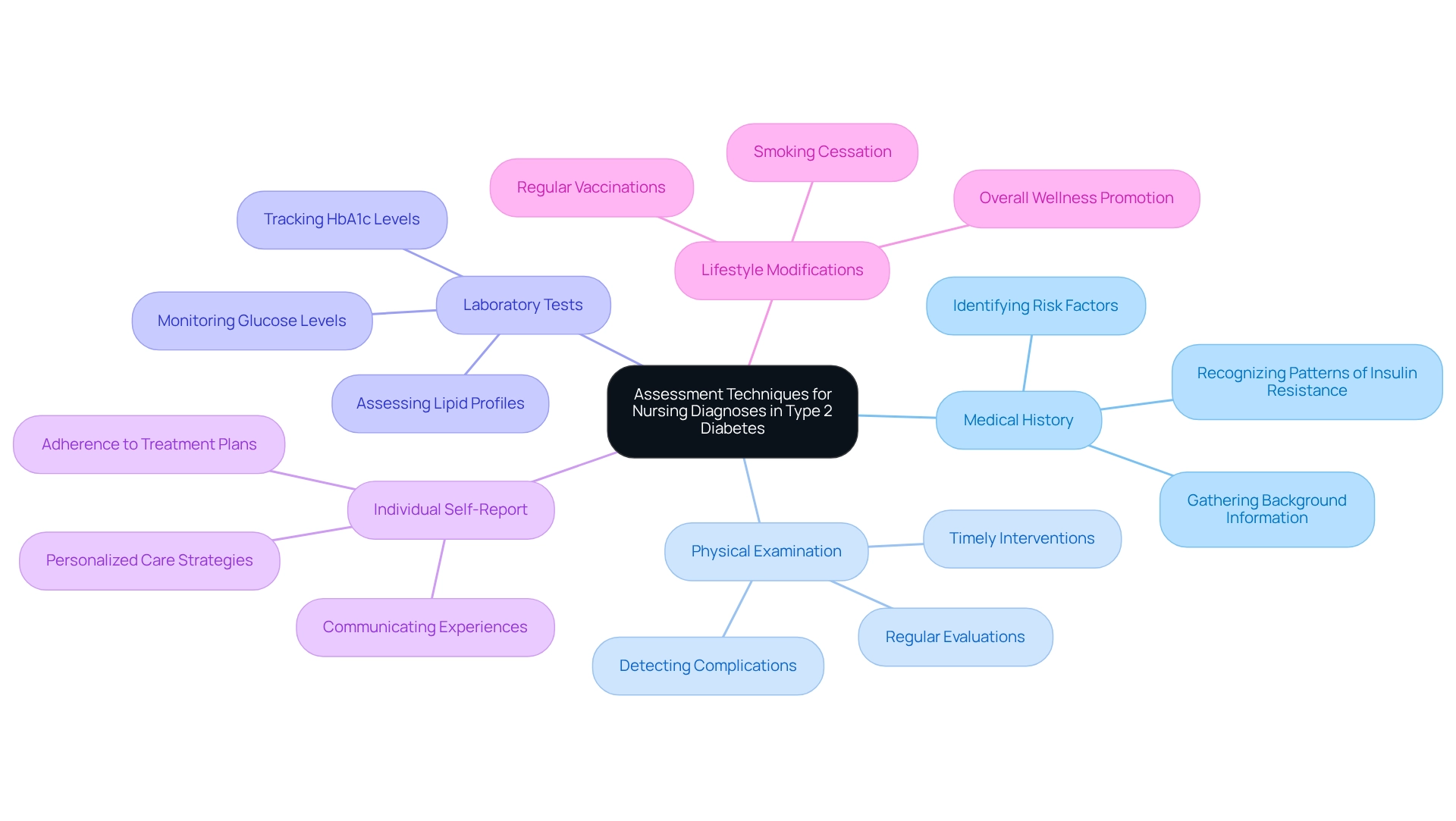
Assessment Techniques for Nursing Diagnoses
Assessment techniques for nursing diagnoses in Type 2 Diabetes are crucial for effective patient care, and they encompass several key components:
-
Medical History: Gathering detailed information about your medical background, family history, and lifestyle factors is essential. Understanding your unique background helps recognize risk factors and tailor treatment strategies just for you. For instance, a comprehensive history can reveal patterns of insulin resistance or complications that may not be immediately apparent.
-
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is vital for detecting signs of diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy, skin infections, or cardiovascular issues. Regular evaluations can help identify these complications early, allowing for timely interventions that can significantly enhance your outcomes.
-
Laboratory Tests: Utilizing laboratory tests is fundamental in managing blood sugar conditions. Blood tests to monitor glucose levels, HbA1c, and lipid profiles provide critical data that inform treatment decisions. For example, maintaining an HbA1c level below 7% is associated with a reduced risk of complications, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring.
-
Individual Self-Report: It's essential to motivate individuals to communicate their experiences, symptoms, and challenges in managing their condition. Self-reported information offers valuable insights into daily life and adherence to treatment plans, which are crucial for creating personalized care strategies.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Emphasizing lifestyle changes, such as smoking cessation and regular vaccinations, is vital for preventing complications. These adjustments not only promote your overall wellness but also improve blood sugar control by lowering the risk of additional health issues.
These assessment techniques not only assist nurses in formulating accurate nursing diagnoses but also play a pivotal role in developing effective care plans. For instance, a case study on insulin pen use illustrates how informing individuals about proper administration techniques can lead to better glycemic control and improved health outcomes. Specifically, individuals who received instruction on insulin pen use demonstrated a significant improvement in their HbA1c levels, reinforcing the importance of education in managing blood sugar.
Moreover, statistics show that individuals with this condition are six times more likely to need hospitalization during influenza outbreaks, highlighting the necessity for thorough evaluations that encompass preventive strategies such as vaccinations and lifestyle changes.
Incorporating expert insights and feedback from nursing professionals about effective assessment methods can further enhance the quality of care delivered to individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. As William Hoyos mentioned, 'All authors have read and approved the final manuscript,' emphasizing the collaborative effort in ensuring best practices in managing health care. By utilizing these methods, healthcare professionals can guarantee a comprehensive approach to blood sugar regulation, ultimately resulting in enhanced health outcomes and quality of life for individuals. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
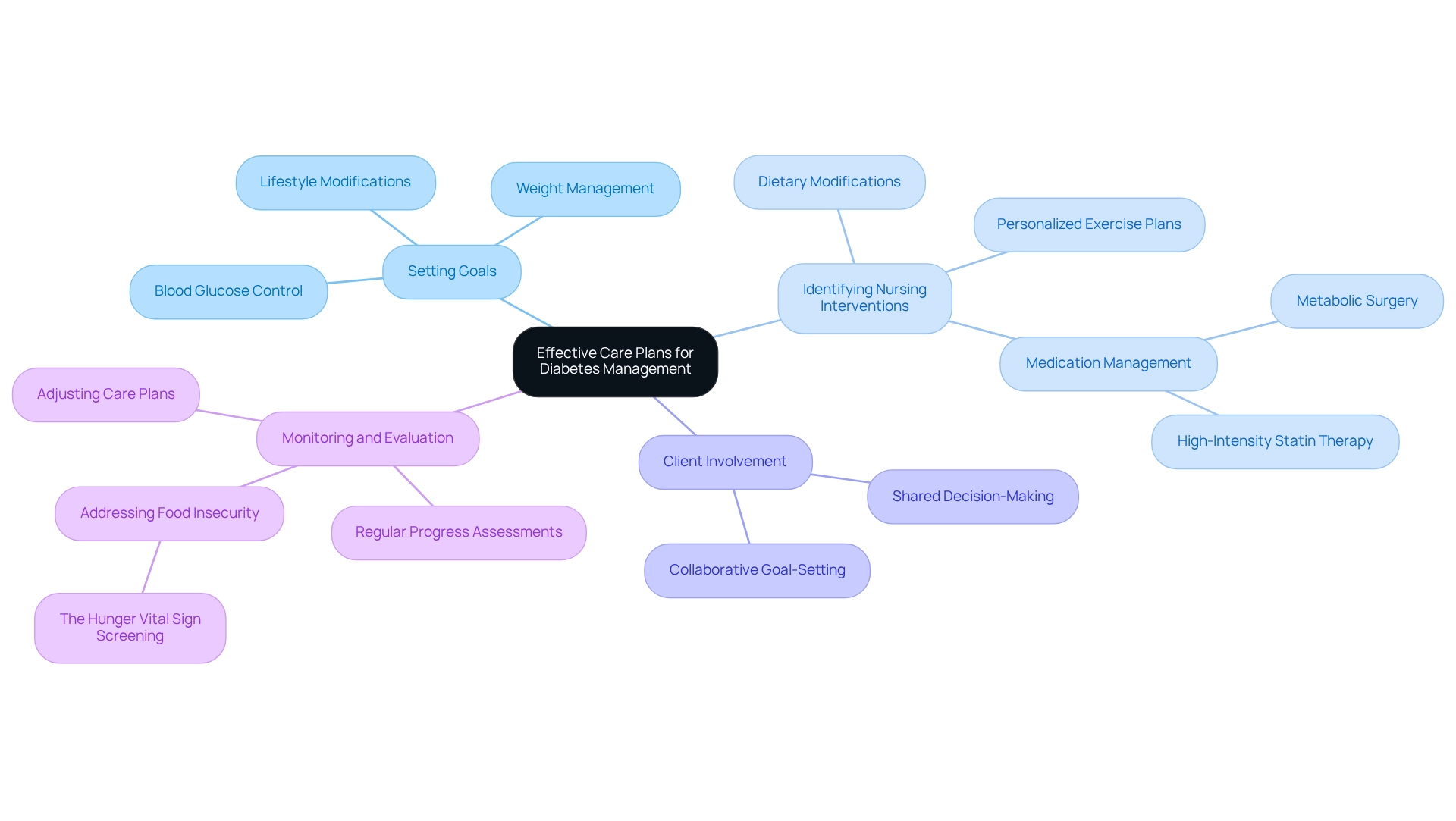
Creating Effective Care Plans for Diabetes Management
Developing effective care strategies for blood sugar control is a multifaceted process that significantly impacts patient outcomes. At&T Solutions is dedicated to offering resources that enhance this important journey. Here are some key components to consider:
-
Setting Goals: Establishing realistic and measurable objectives is crucial for effective diabetes control. These goals should encompass blood glucose control, weight management, and lifestyle modifications tailored to your individual needs. Studies suggest that individuals who set specific, attainable objectives are more likely to experience improved health outcomes. T2DSolutions provides tools and resources to assist you in setting and tracking these goals effectively.
-
Identifying nursing interventions is essential, particularly within the context of a nursing diagnosis for type 2 diabetes. This may involve dietary modifications, personalized exercise plans, and medication management strategies that align with your goals. For instance, high-intensity statin therapy is suggested for individuals aged 40–75 with elevated cardiovascular risk, aiming to lower LDL cholesterol by at least 50% from baseline. Additionally, metabolic surgery may be recommended for certain candidates with type 2 diabetes who do not achieve weight loss and improvement in comorbidities through nonsurgical methods. T2DSolutions offers educational resources to help you understand these interventions better.
-
Client Involvement: Your involvement in the care planning process is vital. When you actively engage, your preferences and concerns are more likely to be addressed, leading to greater adherence to the care plan. Successful examples of involvement include collaborative goal-setting sessions and shared decision-making practices that empower you to take charge of your health. As Ana López-Andrés states, "Effective goal-setting in managing health conditions is crucial for encouraging individual involvement and enhancing results." T2DSolutions encourages this involvement through community support initiatives and educational resources.
-
Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly assessing your progress towards your objectives is necessary for effective health oversight. This includes adjusting the care plan as needed based on ongoing evaluations. A case study titled 'Assessing Food Insecurity in Diabetes Care' highlights the importance of recognizing obstacles that may hinder effective oversight, illustrating how healthcare teams can adapt their approaches to improve outcomes for individuals. T2DSolutions aims to support healthcare providers in this monitoring process by offering tools and resources for evaluation.
This collaborative approach not only enhances adherence among individuals but also fosters a supportive environment that encourages you to take an active role in managing your condition. By applying best practices in care planning and utilizing the resources available at T2DSolutions, healthcare providers can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals managing diabetes-related conditions. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
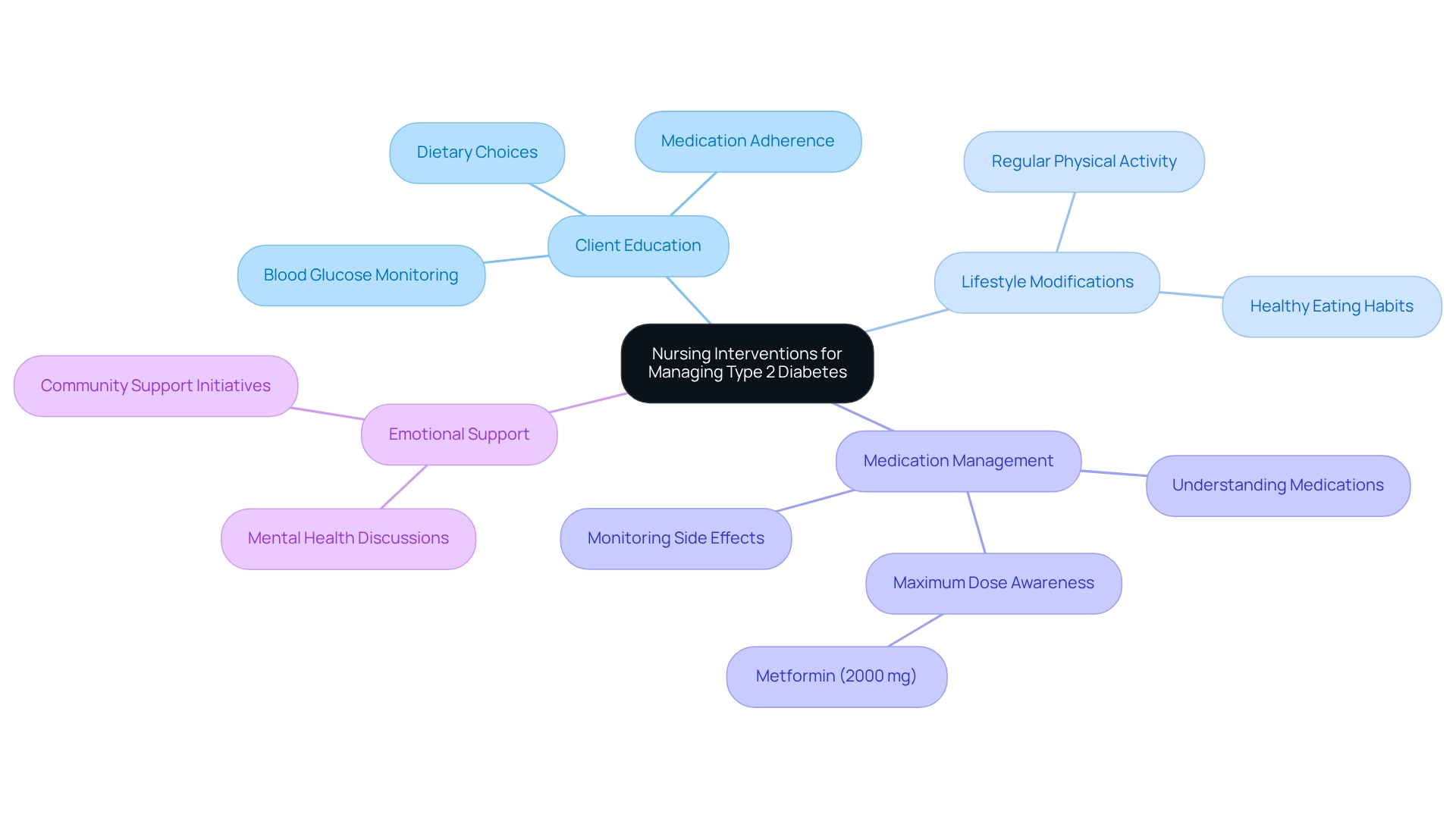
Nursing Interventions for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Nursing interventions related to the nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2 encompass various strategies aimed at empowering individuals and enhancing their self-management abilities. These key interventions include:
-
Client Education: It's essential to instruct individuals about diabetes management. This includes training on blood glucose monitoring techniques, understanding the importance of medication adherence, and making informed dietary choices. Effective client education significantly enhances health outcomes, especially concerning the nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2. When individuals comprehend their condition, they are better prepared to handle it. T2DSolutions offers a variety of educational materials and resources to support those who are newly diagnosed on their learning journey.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Nurses play a vital role in encouraging patients to adopt regular physical activity and healthy eating habits. These lifestyle changes are crucial for improving glycemic control, a key consideration in the nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2 and overall health. Research indicates that consistent exercise and a balanced diet can lead to better management of blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications. T2D Solutions provides guidance and resources to help individuals successfully implement these lifestyle changes.
-
Medication Management: Assisting individuals in understanding their medications, including insulin and oral hypoglycemics, is vital. As part of the nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2, nurses help monitor for side effects and ensure that individuals are aware of the recommended maximum dose for medications like metformin, which is 2000 mg for the extended-release formulation. This knowledge empowers individuals to take an active role in their treatment plans. T2DSolutions also provides resources to help individuals manage their medications safely and effectively.
-
Emotional Support: Providing psychological assistance is crucial for helping individuals navigate the emotional challenges related to the nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2. Nurses can facilitate discussions about mental health, aiding individuals in addressing feelings of anxiety or depression that may arise from managing a chronic condition. T2DSolutions recognizes the importance of emotional well-being and offers community support initiatives to connect individuals with others facing similar challenges.
These interventions are designed not only to empower individuals but also to foster a collaborative approach to blood sugar control. For instance, a case study on teamwork in chronic illness care highlights how synchronized efforts among healthcare providers—including nurses, doctors, and pharmacists—lead to enhanced treatment strategies and improved outcomes for individuals. This comprehensive approach ensures that all aspects of a patient's health are considered, emphasizing the importance of collaboration in managing the condition.
Current statistics reveal that 80.6% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions related to elevated blood sugar levels have a systolic blood pressure of 130 mmHg or higher or are on medication for hypertension. This underscores the necessity for comprehensive management strategies that include regular check-ups and self-monitoring of blood glucose levels. By integrating these nursing interventions and utilizing the resources available through T2D Solutions, healthcare providers can significantly enhance the quality of care for individuals living with Type 2 Diabetes. As Robert Rosseter pointed out, "Employers are showing a strong preference for new nurses with baccalaureate preparation," highlighting the importance of well-trained nursing professionals in delivering effective care for patients with diabetes-related needs.
The Role of Patient Education in Diabetes Care
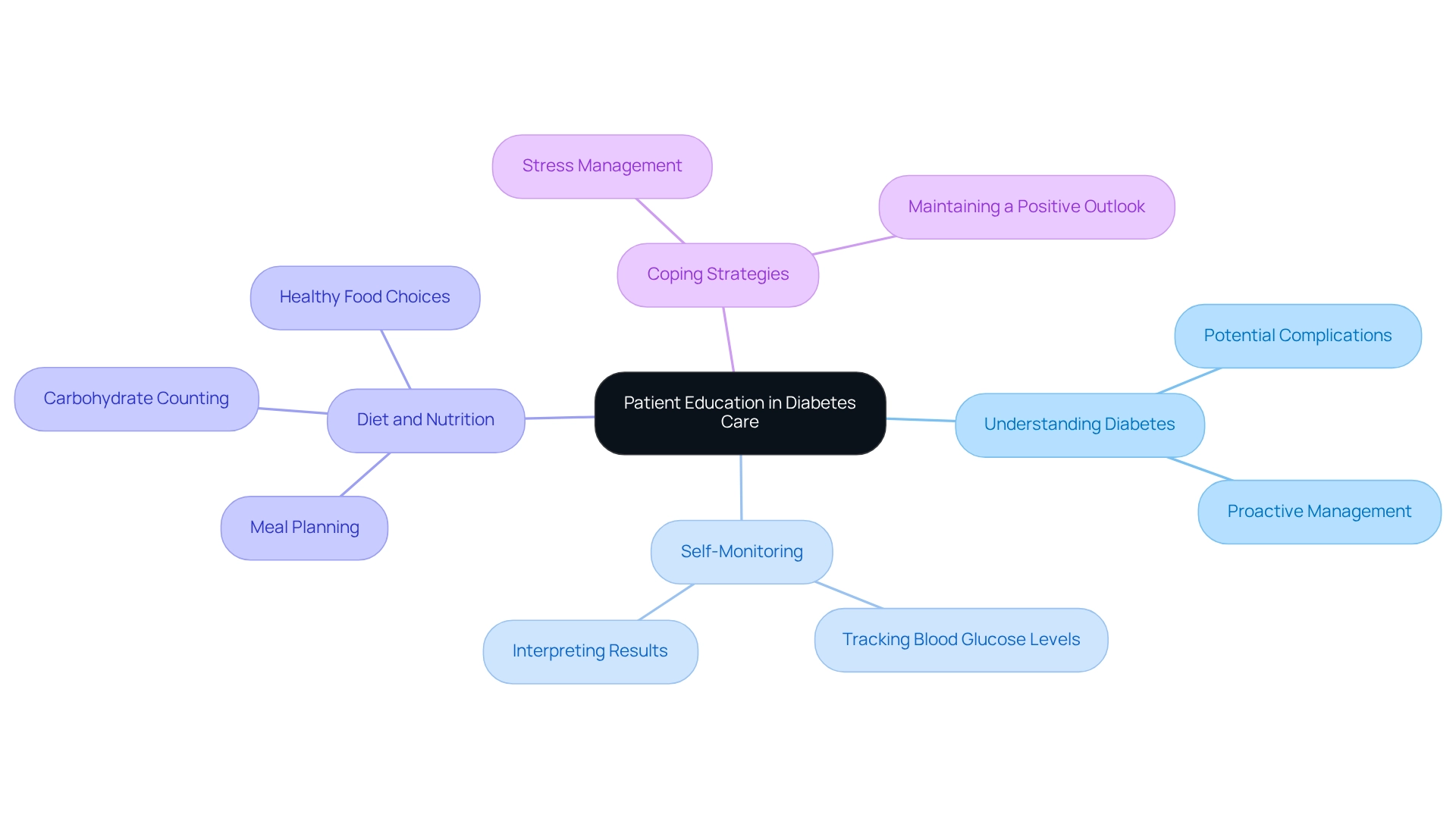
Patient education in diabetes care encompasses several critical components that empower individuals to manage their condition effectively.
Understanding Diabetes: It's essential for you to grasp the nature of diabetes, including its potential complications and the significance of proactive management. This foundational knowledge lays the groundwork for informed decision-making and encourages adherence to treatment plans. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; many have walked this path before you.
Self-Monitoring: Learning how to track your blood glucose levels is a vital skill. This includes not only the mechanics of using glucose meters but also interpreting the results to make informed adjustments to your lifestyle and treatment. Current trends suggest that effective self-monitoring practices can greatly improve outcomes, fostering a sense of control over your well-being. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but with practice, it becomes easier.
Diet and Nutrition: Guidance on meal planning, carbohydrate counting, and making healthy food choices is crucial. Educational resources focusing on nutrition can enhance communication with your healthcare provider, especially if you're navigating health literacy challenges. Tailored educational strategies are essential to meet diverse patient needs. Consider this: the financial consequences of diabetes care are significant, with annual screening for chronic kidney disease costing $21,000. This highlights the importance of education in preventing complications.
Coping Strategies: Managing diabetes often involves navigating emotional and psychological challenges. Learning about coping strategies can help you handle stress and maintain a positive outlook. This holistic approach is vital for fostering resilience and improving your overall quality of life.
Effective education centered around the nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2 not only promotes independence and confidence in managing your condition but also plays a crucial role in improving health outcomes. Statistics indicate that comprehensive educational programs can enhance self-management practices, vital for establishing a nursing diagnosis for diabetes type 2, ultimately lowering the risk of complications related to the condition. As we progress through 2025, the focus on client education remains crucial, with experts promoting innovative strategies that address the distinct needs of each individual.
A case study titled "Portal Utilization and Wellness Literacy" illustrates the challenges faced by individuals with low wellness literacy in accessing management resources for chronic conditions, reinforcing the need for customized educational strategies. Furthermore, the Institute of Medicine emphasizes that the ability to obtain, process, understand, and communicate about health-related information is crucial for making informed health decisions. By emphasizing education, healthcare professionals can significantly impact the lives of individuals living with Type 2 conditions, particularly given the limited knowledge on the effectiveness of information technology for those with restricted literacy in managing their health.
Recent news suggests that personal educational resources have been evaluated to enhance patient-provider communication, underscoring the importance of effective educational strategies in managing healthcare. Remember, you are not alone, and there are resources available to support you every step of the way.
Addressing Mental Health in Diabetes Management
Tackling mental wellness in managing blood sugar levels is essential for enhancing patient results and overall welfare. It's important to understand that mental health plays a crucial role in this journey. Here are some key components to consider:
-
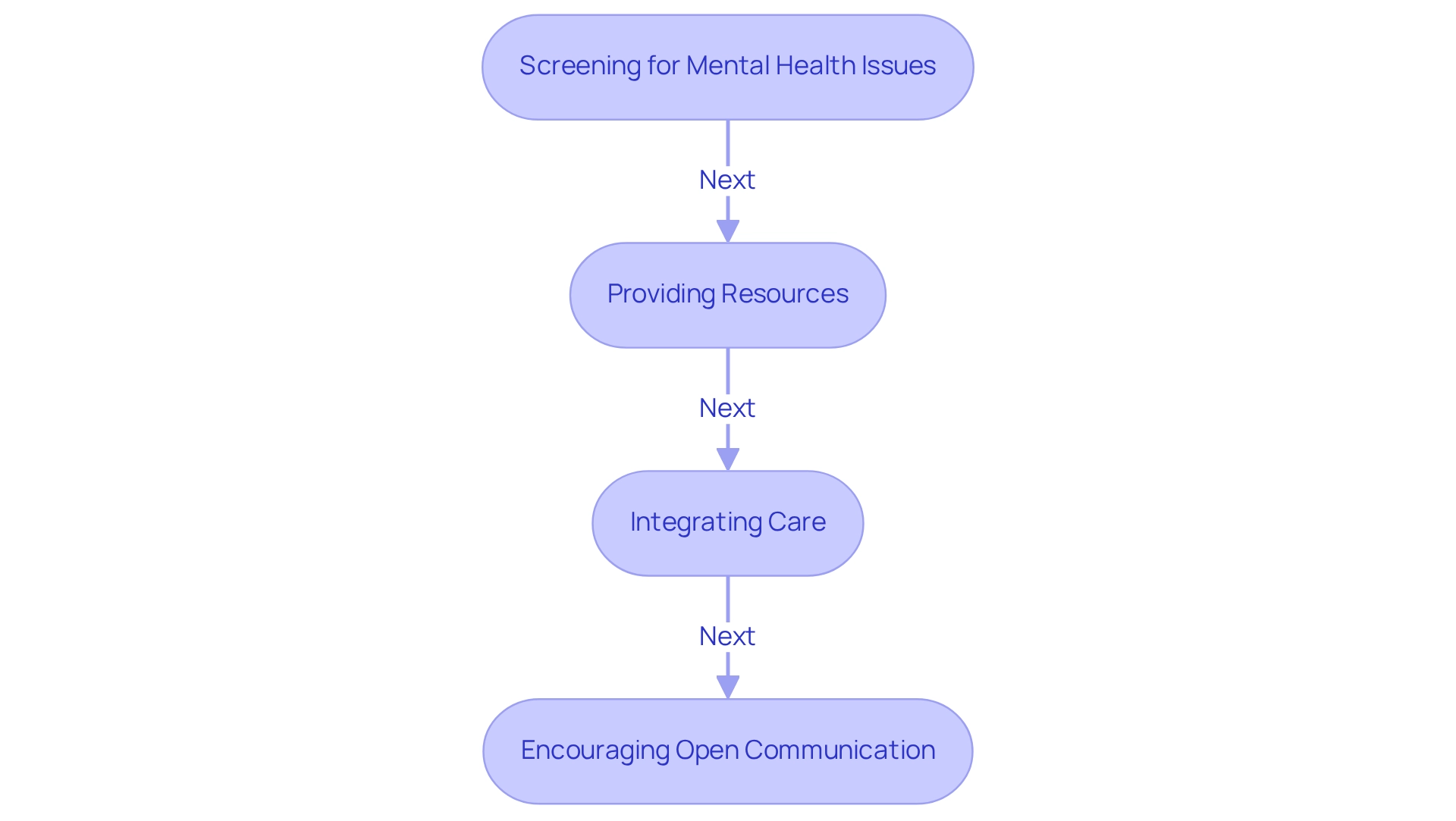
Screening for Mental Health Issues: Regular evaluations for indications of depression, anxiety, and metabolic distress are vital. Research suggests that individuals with elevated blood sugar levels face increased rates of mental well-being disorders. For instance, depression occurrence significantly influences medical service use and expenses. Barbara J. Anderson from Baylor College of Medicine notes, "Depression among individuals with blood sugar issues is also linked to greater medical care use and costs, regardless of age, gender, race/ethnicity, and insurance status." Furthermore, an extensive examination of nearly 490,000 individuals highlights that factors like obesity, neuropathy, and social support are critical in influencing mental well-being for those with blood sugar issues.
-
Providing Resources: Offering patients information about mental health services and support groups is vital. Access to these resources empowers individuals to seek assistance and fosters a sense of community, especially considering the emotional challenges related to managing blood sugar conditions. T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource center, providing information and expert insights to enhance the management of the condition and improve users' quality of life.
-
Integrating Care: Collaborating with mental wellness experts ensures a comprehensive care model that addresses both physical and emotional needs. Integrated care strategies have shown promise in improving the quality of life for individuals with diabetes, as they allow for personalized interventions that consider the psychological aspects of managing a chronic condition.
-
Encouraging Open Communication: It's essential to create an environment where patients feel comfortable discussing their mental well-being concerns. Open dialogue can lead to better identification of issues and more effective management strategies. Experts emphasize that addressing mental well-being is not only beneficial but essential for the effective management of blood sugar conditions. Effective methods for handling blood sugar-related stress include consulting with an endocrinologist, seeking mental wellness support, and focusing on small, achievable objectives.
This comprehensive approach not only enhances overall well-being but also aids in better control of blood sugar levels, ultimately resulting in improved health outcomes for individuals facing the challenges of managing their condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Importance of Monitoring and Follow-Up in Diabetes Care
The importance of monitoring and follow-up in managing blood sugar conditions cannot be overstated. A structured approach to these practices is essential for effective control of Type 2 Diabetes. At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to offering resources and assistance for recently diagnosed individuals to aid them in managing their health journey.
Key components include:
-
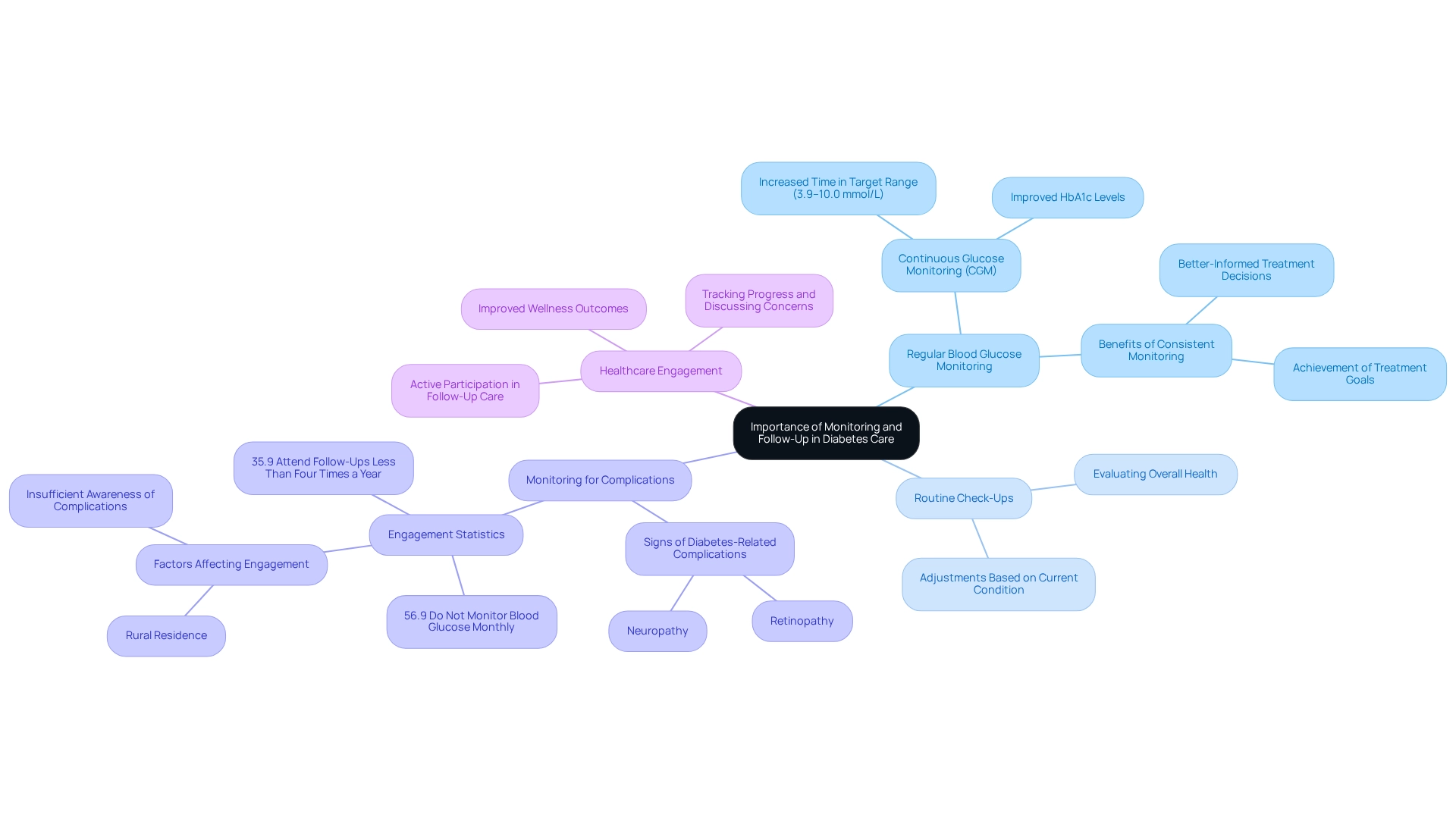
Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring: It's crucial for patients to consistently check their blood glucose levels as recommended. Studies indicate that continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can lead to improved overall glucose control, as evidenced by better HbA1c levels and increased time spent within the target glucose range (3.9–10.0 mmol/L or 70–180 mg/dL). Improved monitoring may lead to better-informed treatment decisions and help achieve treatment goals.
-
Routine Check-Ups: Arranging regular appointments is essential for evaluating overall health and examining management strategies. These visits enable healthcare providers to make necessary adjustments based on the individual's current condition and treatment response. You're not alone in this journey, and these check-ups are an important part of your care.
-
Monitoring for Complications: It's essential to remain vigilant for signs of diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy or retinopathy. A cross-sectional study conducted in Guangdong province, China, revealed that a significant portion of individuals with Type 2 condition (35.9%) attended clinical follow-ups less than four times a year, and 56.9% did not monitor their blood glucose at least once a month. This lack of engagement was linked to factors like rural residence and insufficient awareness of diabetes complications, underscoring the need for tailored educational approaches.
-
Healthcare Engagement: Motivating individuals to actively partake in their follow-up care is essential. This includes tracking their progress and discussing any concerns with their healthcare team. Involved individuals are more likely to comply with monitoring practices and treatment strategies, resulting in improved wellness outcomes.
At T2DSolutions, we aim to empower individuals by fostering a culture of regular monitoring and follow-up. This proactive approach not only aids in sustaining peak wellness but also contributes significantly to preventing issues related to blood sugar conditions. By providing educational resources and support, T2DSolutions enables patients to take charge of their health, ultimately leading to improved quality of life.
As mentioned by the Keystone Rural Health Consortia, 'However, with proper management and monitoring, individuals with this condition can live a healthy and fulfilling life.' Additionally, the emphasis on person-centered decision-making and quality improvement efforts in diabetes care highlights the need for equitable access to effective interventions.
Conclusion
The significance of nursing diagnoses in managing Type 2 Diabetes is profound. By organizing these diagnoses into actual, risk, and health promotion categories, healthcare professionals can deliver targeted interventions that cater to the unique needs of each patient. Effective nursing diagnoses lay the groundwork for developing personalized care plans, ensuring that patients receive the essential support they need to manage their condition successfully.
Throughout this article, we have highlighted the vital roles of patient education, lifestyle changes, and emotional support as fundamental components of effective diabetes management. By empowering patients with knowledge and resources, nurses can guide them through the complexities of their condition, leading to improved health outcomes. Moreover, integrating mental health considerations into diabetes care promotes a holistic approach that nurtures both physical and emotional well-being.
As we witness the rising prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes, the urgency for comprehensive nursing interventions becomes increasingly clear. By implementing regular monitoring, follow-up care, and encouraging patient engagement, healthcare providers can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. The collaborative efforts of nurses, patients, and the healthcare community will be crucial in addressing this growing health challenge and improving the overall management of Type 2 Diabetes. Together, we can make a difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main categories of nursing diagnoses for type 2 diabetes?
The main categories of nursing diagnoses for type 2 diabetes are Actual Diagnoses, Risk Diagnoses, and Health Promotion Diagnoses. Actual Diagnoses reflect current health challenges, Risk Diagnoses highlight potential medical issues, and Health Promotion Diagnoses emphasize an individual's readiness to enhance their health.
What constitutes an Actual Diagnosis in the context of type 2 diabetes?
An Actual Diagnosis reflects current health challenges faced by the patient, such as 'Ineffective Health Management' or 'Imbalanced Nutrition: More than Body Requirements.' These diagnoses indicate that the patient requires prompt attention and intervention.
What is a Risk Diagnosis for type 2 diabetes?
A Risk Diagnosis identifies potential medical issues that may arise, such as 'Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose Levels.' Recognizing these risks allows healthcare professionals to implement preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of complications.
How do Health Promotion Diagnoses relate to type 2 diabetes?
Health Promotion Diagnoses emphasize the individual's readiness to enhance their health, such as 'Readiness for Enhanced Self-Management.' This category focuses on empowering individuals to take an active role in managing their health.
Why are nursing diagnoses important for managing type 2 diabetes?
Nursing diagnoses are essential for guiding the nursing process, developing tailored care plans, and implementing interventions. They help in addressing both actual and potential health concerns, leading to improved health outcomes.
What are some common nursing diagnoses for patients with type 2 diabetes?
Common nursing diagnoses include: 1. Ineffective Health Management 2. Imbalanced Nutrition: More than Body Requirements 3. Risk for Unstable Blood Glucose Levels 4. Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion 5. Risk for Infection
How can nurses support patients with the nursing diagnosis of Ineffective Health Management?
Nurses can support patients by providing education on diabetes management, helping them understand their condition, and encouraging adherence to treatment plans, which significantly enhances blood glucose control and overall health outcomes.
What role does lifestyle modification play in managing type 2 diabetes?
Lifestyle modification is crucial for improving outcomes for individuals with type 2 diabetes. It includes dietary changes, increased physical activity, and education on maintaining healthy habits, which can lead to better wellness outcomes.
What are the modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Modifiable risk factors include obesity or overweight, physical inactivity, poor dietary habits, and smoking. Addressing these factors can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
What are the non-modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
Non-modifiable risk factors include age (45 years or older), family history of diabetes, and ethnicity (higher prevalence in certain ethnic groups such as African Americans and Hispanic Americans).
How can early identification of diabetes risk factors benefit individuals?
Early identification allows for timely interventions and education, which can empower individuals to take proactive measures in managing their risk and improving health outcomes.
What resources does T2DSolutions provide for individuals newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes?
T2DSolutions offers educational materials, community support, and guidance to help individuals understand and manage their risk factors for type 2 diabetes effectively.
