Introduction
Point-of-care glucose testing (POCT) has emerged as a pivotal component in the management of diabetes, offering immediate results that facilitate timely clinical decisions. With diabetes cases soaring in regions like India, the necessity for efficient monitoring methods has never been more pronounced. This article delves into the various facets of POCT, exploring:
- Its applications across healthcare settings
- The critical importance of accuracy in glucose meters
- Potential interferences that can skew results
- The regulatory standards that govern these testing methods
Furthermore, it highlights:
- The latest advancements in technology
- Future trends that promise to reshape diabetes care
As healthcare providers and patients alike navigate this evolving landscape, understanding these elements will be essential for optimizing diabetes management and improving patient outcomes.
Introduction to Point-of-Care Glucose Testing
Point-of-care glucose testing (POCT glucose) encompasses a range of methods designed to monitor blood glucose levels directly at or near the site of patient care. This method provides immediate results for POCT glucose, which enables swift decision-making essential for effective management of the condition. With approximately 741,947,000 diabetes cases reported in India in 2021, the need for such timely interventions is clear.
POCT glucose is utilized in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, and home care, thereby enhancing a more responsive management strategy. As Andrew St John highlights, 'The potential for PoCT glucose to be part of so-called patient-centric healthcare is obvious and, like acute care where PoCT glucose was first applied, it is based on PoCT glucose providing faster results and facilitating quicker clinical decisions.' Notably, Nova Biomedical's whole blood analyzers are instrumental in providing prompt and cost-effective POCT glucose results for hospitalized and critically ill individuals, showcasing a concrete application of POCT technology.
Furthermore, real-world applications of POCT glucose have demonstrated its effectiveness, as seen in the case study titled 'Point-of-Care Testing in Clinical Medicine,' which reviews its application across various settings and emphasizes the necessity for changes in care processes to maximize benefits. Additionally, major market players, such as Abbott Laboratories and Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., are continuously advancing POCT technology for POCT glucose, which contributes to enhanced management outcomes for blood sugar conditions. As T2D Solutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 health education and community support, it is essential for newly diagnosed patients to understand the transformative role of POCT glucose testing in enhancing their outcomes through improved monitoring and timely interventions.
Ensuring Accuracy: The Reliability of POCT Glucose Meters
T2DSolutions is thrilled to reveal the launch of a new resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education and community support. As we prepare to offer a variety of educational materials, including guides on diabetes management, nutritional resources, and support forums, it's essential to emphasize the reliability of poct glucose devices, which are crucial for informed clinical decision-making. Clinicians are advised to choose devices that have undergone stringent testing and validation processes, ensuring their accuracy in critical scenarios.
Key factors influencing the reliability of these devices include:
- The meter's calibration
- The quality and integrity of the test strips
- The training provided to personnel operating the devices
Regular engagement in quality control measures is essential; clinicians should consistently utilize control solutions and adhere to recommended storage conditions for test strips. Such practices are vital for minimizing errors and enhancing the accuracy of poct glucose testing results.
A study conducted at Massachusetts General Hospital’s Diabetes Research Center from September 2014 through December 2014 revealed that only 17.24% of POC measurements in individuals in shock fell within target limits, highlighting the need for stringent quality oversight. This underscores the importance of structured approaches, as demonstrated by the use of FDA-approved insulin dose calculators, which aid individuals in accurately calculating their insulin doses. Expert Douglas B. Coursin emphasizes, 'Ensuring the reliability of these devices is a fundamental aspect of effective diabetes management.'
As we launch T2DSolutions, we encourage newly diagnosed patients to subscribe to our platform to stay updated on the latest resources and support available, strengthening the argument for the critical role of quality in blood sugar testing.
Understanding Interferences in Glucose Testing
Interferences in blood sugar testing can originate from multiple sources, including medications, hematological factors, and environmental conditions. A notable concern is the impact of substances such as ascorbic acid (vitamin C), which can lead to inaccurately low or high sugar readings. Medications, especially those that affect sugar metabolism or interact with blood sugar monitoring devices, can also distort results.
For example, clinicians have noted that certain antihypertensives and corticosteroids may result in misleading readings, potentially complicating diabetes management. Additionally, hematological factors, such as anemia or dehydration, can significantly affect test outcomes. Recent findings suggest that abnormal hematocrit levels are more common than previously thought, highlighting the necessity for clinicians to consider these variations when choosing measurement devices for their patients.
Notably, the absolute median bias for StatStrip and LifeScan models was the lowest among the tested devices, highlighting their reliability. Furthermore, there is a good correlation between blood sugar meters and a plasma hexokinase reference method, although measurements can vary by meter and are influenced by hematocrit levels and other substances. A thorough understanding of these interferences is crucial for accurate patient assessments and poct glucose treatment planning.
As Martha Lyon has indicated, being aware of these factors can greatly enhance the reliability of poct glucose monitoring, ensuring that healthcare providers deliver optimal care based on precise data. Furthermore, case studies, including the assessment of an electrochemical point-of-care device utilized in veterinary medicine, showcase the essential significance of precision in sugar measurements. In this study, the meter's effectiveness in managing sugar levels in livestock was assessed, contributing valuable insights into the implications of interferences across different fields.
By acknowledging and tackling these possible interferences, clinicians can enhance the dependability of testing results and ultimately improve outcomes for individuals.
Navigating Regulatory Standards for POCT Glucose Testing
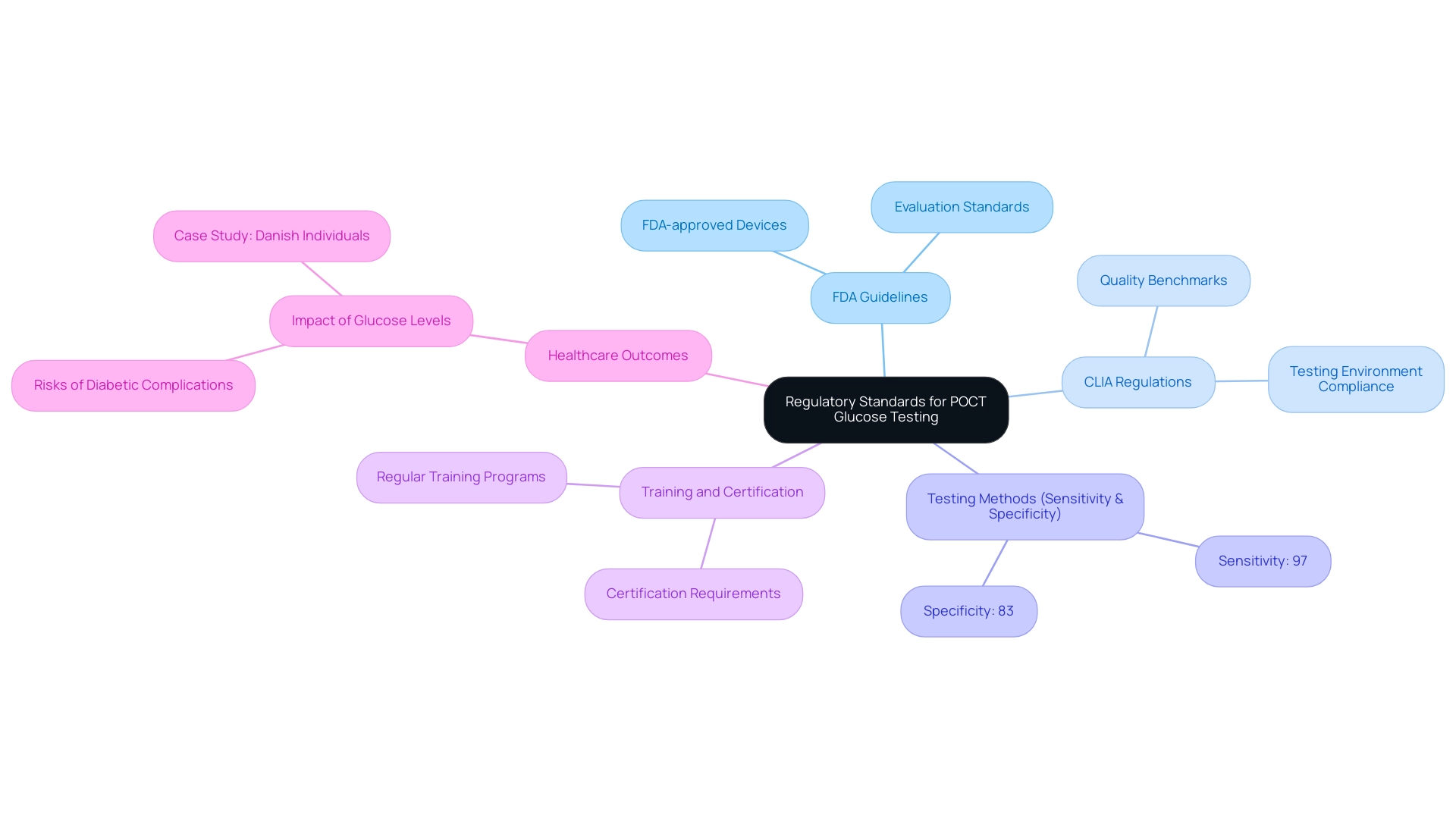
Regulatory standards for poct glucose testing of blood sugar are critical for ensuring patient safety and diagnostic accuracy. These standards are primarily guided by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA). It is crucial for clinicians to use only FDA-approved blood sugar monitors, particularly those that provide poct glucose measurements, as these devices undergo rigorous evaluation to meet safety and accuracy standards.
Notably, using two or more tests can increase sensitivity to 97% but reduce specificity to 83%, highlighting the importance of selecting the right testing methods. Recent advancements suggest that professional-use blood sugar devices approved by the FDA now offer improved functionalities, including electronic medical record communication, which emphasizes the significance of regulatory adherence in poct glucose management. Moreover, adherence to CLIA regulations ensures that testing environments meet necessary quality benchmarks.
Regular training and certification of personnel involved in poct glucose testing are also imperative to uphold compliance and maintain high standards of care. The Diabetes Technology Society has promoted better FDA approval criteria, stating, 'A new FDA approval standard for BG meters is needed to enhance safety for individuals.' This emphasizes the importance of stringent regulatory frameworks.
Furthermore, a study of 117,193 Danish individuals found that higher random glucose concentrations, even within the normoglycemic range, were associated with increased risks of diabetic complications. This case study illustrates the real-world implications of regulatory compliance and its impact on healthcare outcomes. By effectively navigating these regulations, healthcare providers not only enhance the quality of care but also contribute to improved outcomes for individuals.
Future Trends in Point-of-Care Glucose Testing
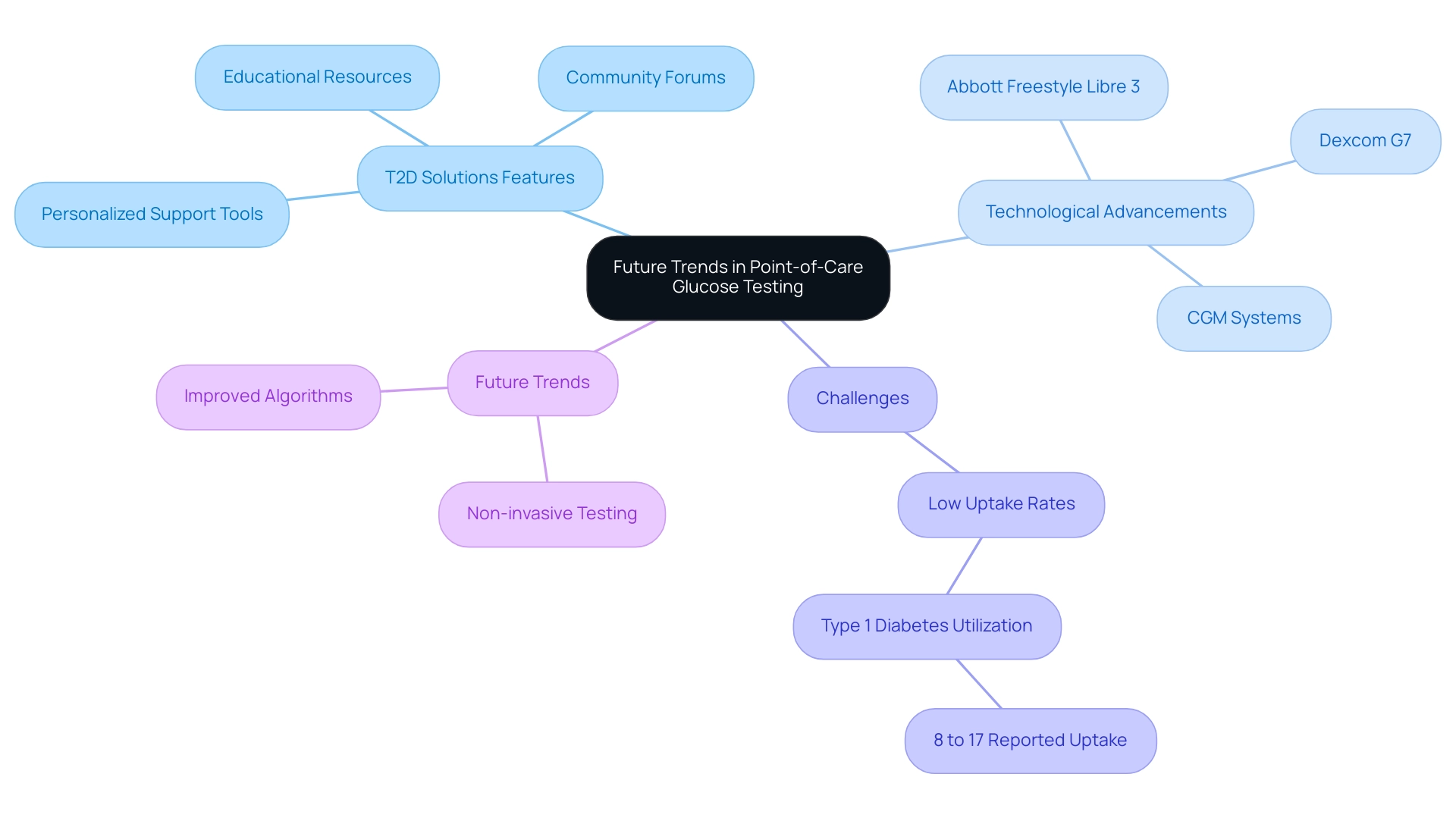
As we launch T2D Solutions, a comprehensive resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support, we are excited to offer a variety of features designed specifically for newly diagnosed individuals. Our platform will provide access to educational resources, community forums, and personalized support tools that empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. We acknowledge the substantial change in poct glucose testing, with the growing use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and smartphone-integrated devices improving user engagement.
Notable advancements, such as the Abbott Freestyle Libre 3 and Dexcom G7, have successfully overcome previous technical barriers, enhancing management capabilities for patients. Furthermore, 33% of healthcare providers have mentioned MyFitnessPal as a frequently recommended tool, illustrating the integration of digital resources in managing blood sugar. Despite the evident advantages of CGMs, low uptake rates among individuals with type 1 conditions, reported at only 8% to 17% in adults, highlight ongoing challenges in accessibility and literacy that T2 Solutions aims to address.
As we move forward, T2 Solutions will provide insights into future trends, including:
- Non-invasive testing methods
- Improved algorithms for data interpretation
to optimize diabetes management. Our commitment to research and education will ensure that clinicians and newly diagnosed patients alike are equipped with the knowledge to enhance care delivery and patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Point-of-care glucose testing (POCT) stands as a cornerstone in the effective management of diabetes, particularly in regions facing high prevalence rates, such as India. By delivering immediate results, POCT facilitates prompt clinical decisions that are vital for patient care. This article has explored the multifaceted applications of POCT across various healthcare settings, emphasizing its role in promoting timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Accuracy in glucose meters is paramount, as highlighted by the potential for interferences that can lead to misleading results. The reliability of these devices is influenced by several factors, including calibration, quality control measures, and the training of personnel. Understanding these elements is essential for healthcare providers to ensure precise monitoring and effective diabetes management.
Regulatory standards play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of POCT. Adherence to guidelines set by the FDA and CLIA ensures that only validated and approved devices are used, ultimately safeguarding patient safety and diagnostic accuracy. As the landscape of diabetes care evolves, the integration of innovative technologies, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems, presents promising opportunities for enhancing patient engagement and management.
In conclusion, the advancements in POCT, coupled with a thorough understanding of its challenges and regulatory frameworks, underscore the importance of this testing method in the ongoing battle against diabetes. As healthcare providers and patients navigate this dynamic environment, staying informed and engaged with the latest developments will be essential for optimizing diabetes management and improving health outcomes.



