Overview:
The article provides a comprehensive tutorial on understanding the A1C chart, emphasizing its significance in diabetes management by illustrating average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It supports this by detailing how A1C measurements inform treatment efficacy, highlight personalized target levels for health outcomes, and recommend regular testing frequencies based on individual conditions, thereby underscoring the A1C chart's role in enhancing patient care and management strategies.
Introduction
Hemoglobin A1C, often referred to as A1C, serves as a critical indicator of blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, playing a pivotal role in diabetes management. This essential blood test measures the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transport in red blood cells.
With diabetes care continuously evolving, understanding A1C levels is not just a clinical necessity but a vital component for patients aiming to make informed decisions about their health. As healthcare providers focus on the significance of A1C in assessing treatment effectiveness and predicting potential complications, the implications of these measurements extend across various demographics, emphasizing the need for tailored strategies in diabetes management.
This article explores the intricacies of A1C testing, its importance in setting health targets, and effective strategies for achieving optimal levels, ensuring that individuals with diabetes are equipped with the knowledge and resources necessary for improved health outcomes.
Understanding Hemoglobin A1C: The Key Biomarker for Diabetes Management
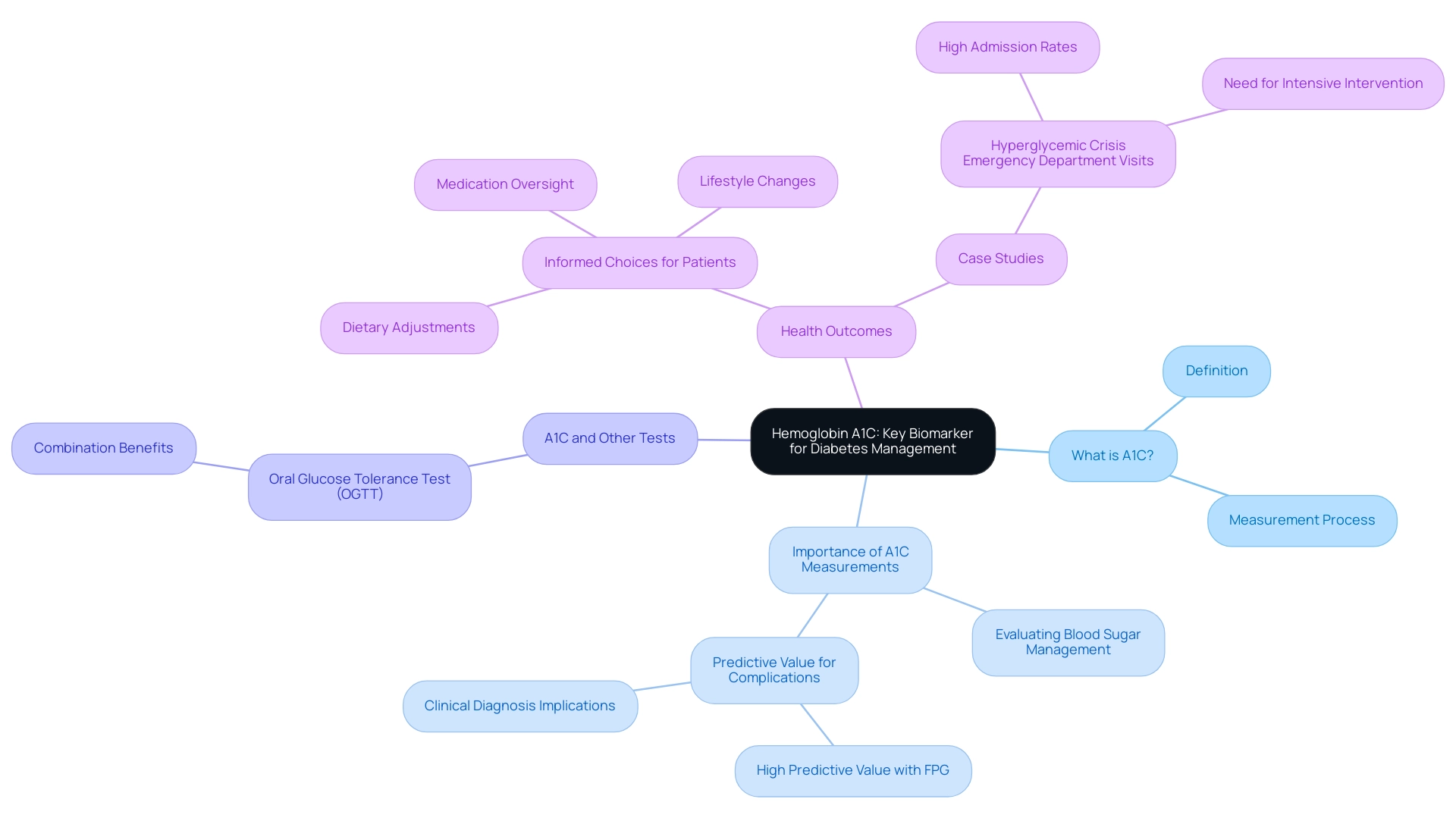
Hemoglobin A1C (commonly referred to as A1C) is an essential blood test that reflects average blood glucose amounts over the previous two to three months, which is represented in the A1C chart ADA. This test measures the percentage of glucose bound to hemoglobin, the protein within red blood cells that facilitates oxygen transport. A1C measurements, which are reflected in the A1C chart ADA, are crucial for evaluating blood sugar management, as they offer important perspectives on the efficiency of treatment approaches.
In 2024, average A1C values among individuals with blood sugar issues will be illustrated in the A1C chart ADA, which remains a focal point for healthcare providers, reflecting ongoing trends in managing these conditions. A systematic review has shown that A1C measurements, as illustrated in the A1C chart ADA, are significant among individuals aged 18 years and older, highlighting its relevance across different age groups. Recent studies have indicated that increased levels of both A1C and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) have a strong positive predictive value for the subsequent clinical diagnosis of this condition and related complications.
Experts agree that utilizing the A1C chart ADA alongside other tests, such as the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), allows for a more precise prediction of the condition's progression, particularly in individuals with glucose intolerance. As Shimazaki observed, 'The combination of A1C and OGTT allows for more accurate forecasting of progression to the condition in individuals with glucose intolerance.' For patients, understanding the A1C chart ADA results is essential for making informed choices regarding dietary adjustments, medication oversight, and lifestyle changes, ultimately enhancing health outcomes.
T2DSolutions is committed to enhancing health oversight through extensive resources, including educational webinars and support groups designed for recently diagnosed individuals. Furthermore, case studies, such as the significant admission rates for hyperglycemic crisis in emergency departments—where 84.4% of cases were admitted—underscore the necessity for effective monitoring and intervention based on the A1C chart ADA. As healthcare experts stress, mastering the A1C chart ADA is essential for achieving optimal control of blood sugar.
Stay tuned for upcoming articles on T2D Solutions that will delve deeper into these resources and provide further insights into managing blood sugar.
The Importance of A1C Levels: Setting Targets for Better Health
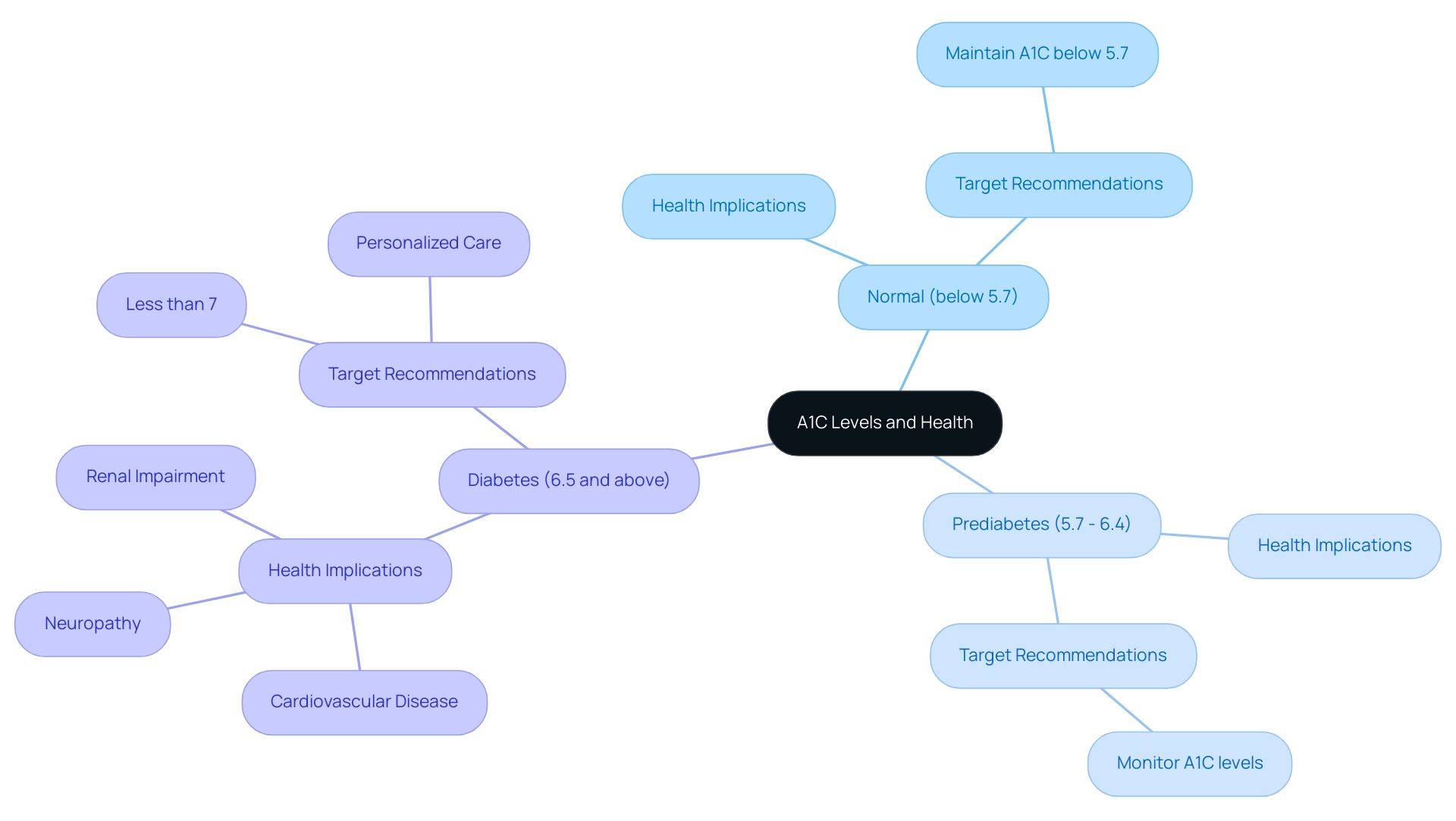
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. We encourage you to subscribe to our updates and remain informed about the latest resources and information available to assist you in managing your condition effectively. According to the A1C chart ADA, A1C levels are classified based on their implications for health:
- An A1C below 5.7% is considered normal.
- Levels from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate a state of prediabetes.
- An A1C of 6.5% or higher can be assessed using the A1C chart ADA, indicating the existence of the condition.
For most adults diagnosed with the condition, the A1C chart ADA recommends a target of less than 7% to minimize the risk of serious complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Neuropathy
- Renal impairment
It is essential to recognize that personalized A1C objectives may vary based on factors such as age, the duration of the condition, and the presence of comorbidities, as outlined in the A1C chart ADA.
The American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee emphasizes the importance of personalized care, noting that tailored targets, like those represented in the A1C chart ADA, can lead to improved health outcomes and enhanced quality of life. Additionally, considering that in 2020, 23.4% of Medicare PPO patients displayed poor HbA1c control (>9.0%), it is evident that establishing attainable A1C targets according to the A1C chart ADA is essential for effective care. This statistic highlights the necessity for continuous research to create a reproducible classification system for older individuals with blood sugar issues, as their care can be especially intricate.
For instance, insulin therapy requires good visual, motor, and cognitive skills for administration, and while long-acting insulin analogs are preferred to reduce hypoglycemia risk, multiple daily injections may be too complex for some older patients. Addressing these factors through a comprehensive approach can significantly enhance patient care and outcomes. We encourage you to explore our resources as you handle your condition.
A1C Testing: Frequency and Best Practices for Monitoring
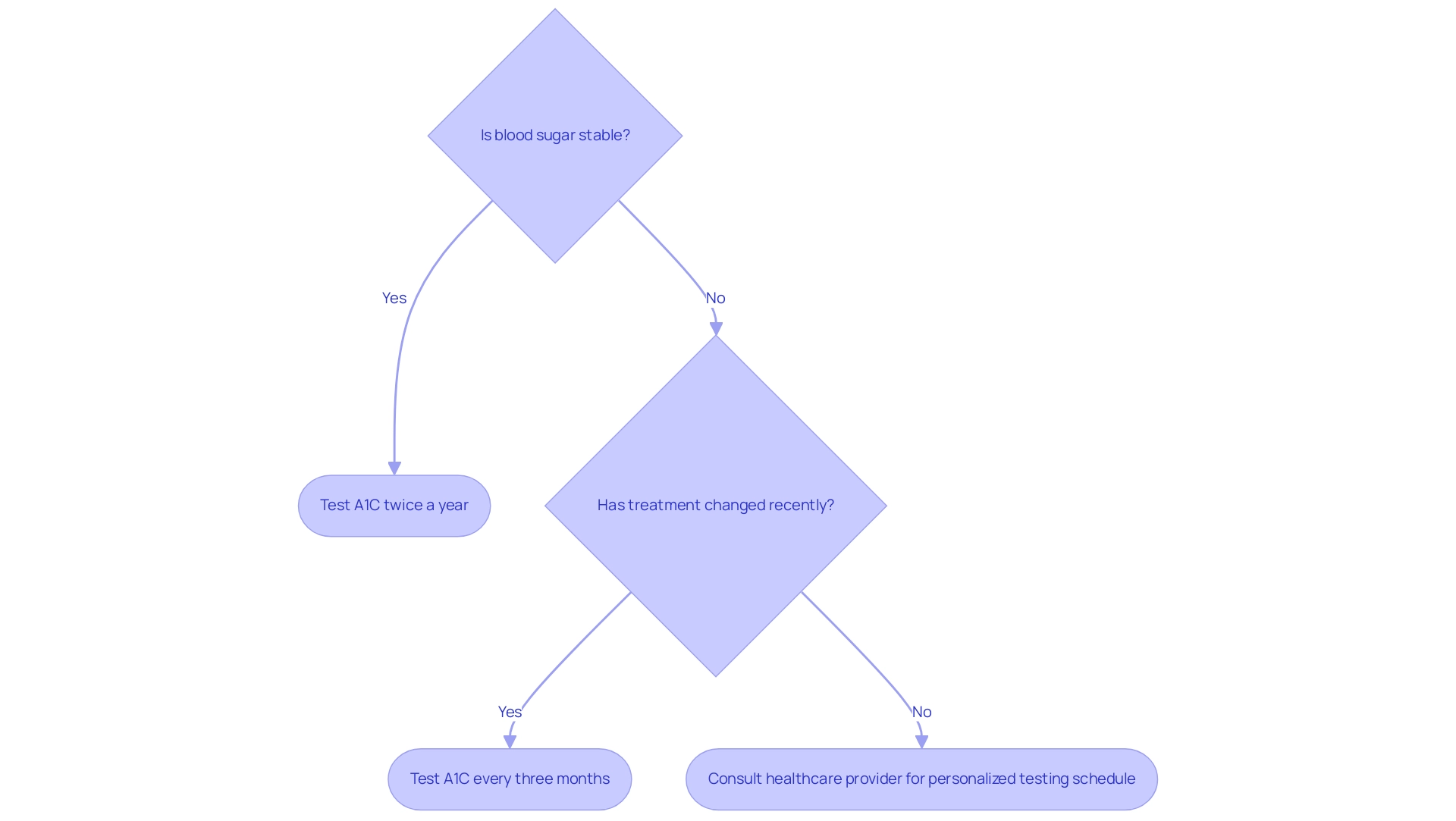
The frequency of A1C testing is crucial for effective management of the condition, as shown in the A1C chart ADA, because it directly correlates with the stability of blood glucose levels. T2DSolutions aims to serve as your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support, offering a variety of educational materials and tools to help you manage your condition. The American Diabetes Association suggests that individuals with well-managed blood sugar undergo testing at least twice a year.
Conversely, patients whose treatment has recently changed or who experience unstable blood sugar readings should schedule A1C tests every three months. This tailored approach allows for timely adjustments in treatment plans, ensuring optimal management of blood sugar levels. According to Andrew Georgiou, 'Regular monitoring of the A1C chart ADA is essential for understanding how well the condition is managed and for making necessary adjustments to treatment.'
Moreover, a study titled 'Longitudinal Change in HbA1c Values by Adherence Group' found that patients with high adherence to their treatment plans maintained their HbA1c levels within the target range, while those with lower adherence experienced increases in their levels over time. Additionally, incorporating physical activity into daily routines, such as engaging in 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days, can significantly improve management of blood sugar levels when combined with regular monitoring using an A1C chart ADA. It is advisable to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate testing schedule based on your unique health situation.
Furthermore, it is imperative to conduct A1C tests in certified laboratories as outlined in the A1C chart ADA to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. By following these guidelines, patients can more effectively manage their condition and maintain their health. Don't forget to subscribe to T D Solutions for ongoing support and resources, and to stay updated on new content as we build this valuable community.
Strategies for Achieving Optimal A1C Levels: Tips and Tools
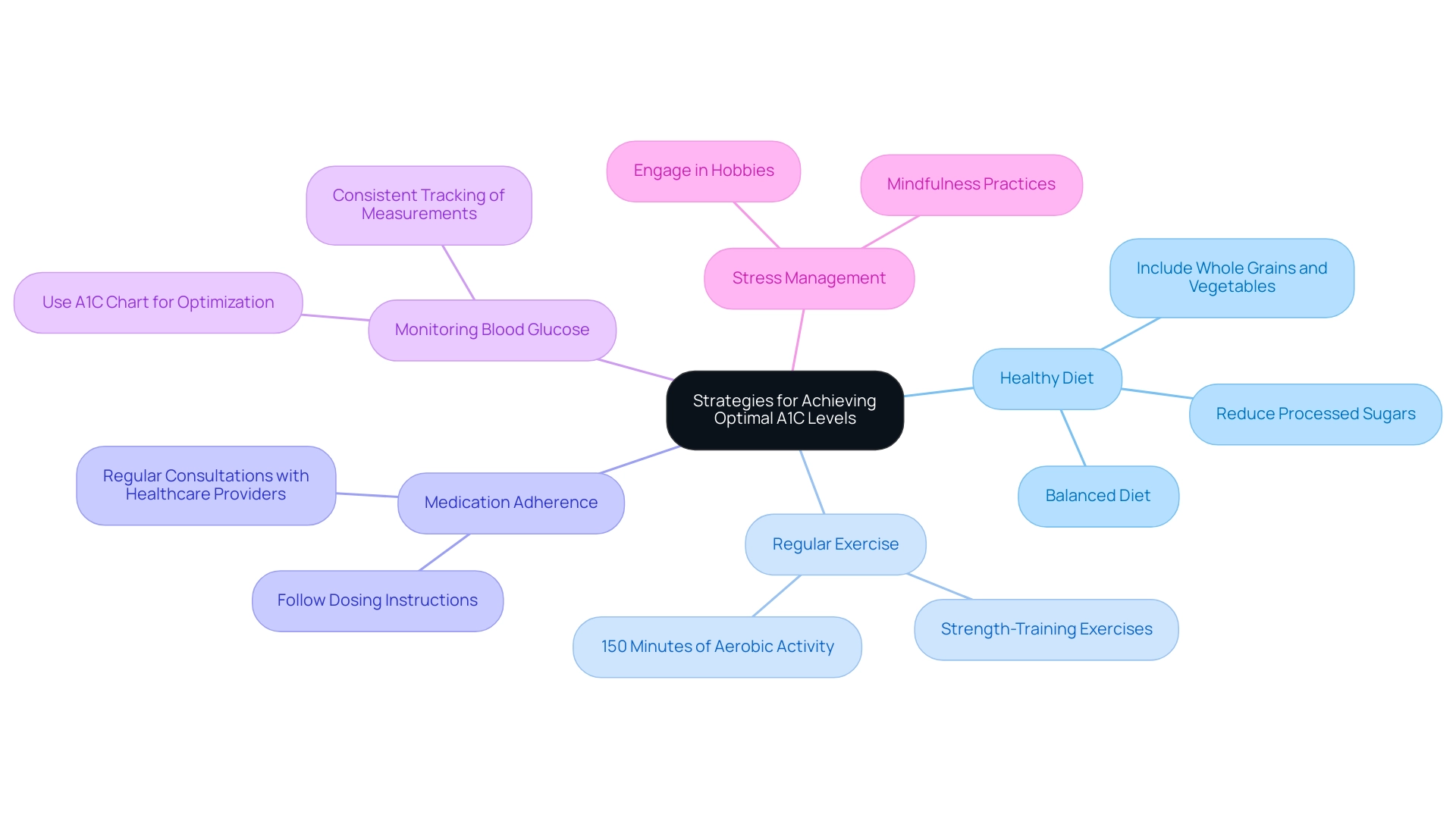
As T2DSolutions debuts as a new resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar education and community assistance, achieving optimal A1C values continues to require a multifaceted strategy that incorporates the a1c chart ada along with lifestyle changes and suitable medical interventions when needed. T2DSolutions will provide a range of resources, including educational materials, community support forums, and personalized coaching to assist individuals in their health management journey. The following strategies are essential:
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. Reducing the intake of processed sugars and carbohydrates is crucial for managing blood glucose effectively.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly, complemented by strength-training exercises. Regular physical activity significantly enhances insulin sensitivity, which is vital for blood glucose regulation.
- Medication Adherence: For those prescribed medications for blood sugar control, it is imperative to follow dosing instructions meticulously. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are critical for monitoring and adjusting medication as needed, using the a1c chart ada to optimize treatment outcomes.
- Monitoring Blood Glucose: Consistent tracking of blood sugar measurements is essential to understand how dietary choices, physical activity, and medication affect the A1C chart ADA values. This data empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their diabetes management.
- Stress Management: Incorporate practices such as mindfulness, yoga, or engaging in hobbies to mitigate stress, which can adversely affect blood glucose readings.
By adopting these evidence-based strategies, individuals can make significant strides toward achieving and maintaining their target A1C values, as referenced on the A1C chart ADA. Notably, recent studies emphasize the importance of dietary choices in influencing A1C levels, indicating that the net change in body weight associated with lifestyle modifications can be as much as -5.9 kg, which significantly impacts the a1c chart ada. Furthermore, understanding disparities in health education, such as the varying awareness rates of prediabetes among racial and ethnic groups—61.8 million White non-Hispanic adults affected with only a 17.3% awareness rate compared to a 30.1% awareness among Asian non-Hispanic adults—can inform tailored strategies for managing this condition.
As noted by Kirsten S. Dorans, ScD, from Tulane University, 'We thank all study participants and research study staff for contributing to the study,' emphasizing the collective effort needed in managing this condition effectively. Stay tuned as T2DSolutions continues to develop and provide valuable resources for your diabetes journey, including success stories from individuals who have effectively managed their diabetes through these strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing Hemoglobin A1C levels is paramount for individuals with diabetes. This key biomarker provides a comprehensive view of blood glucose control over the past few months, making it an essential tool for both patients and healthcare providers. By regularly monitoring A1C levels, individuals can better assess the effectiveness of their treatment plans and make necessary adjustments to avoid complications associated with poorly managed diabetes.
Setting personalized A1C targets is crucial in achieving optimal health outcomes. With recommendations suggesting a target of less than 7% for most adults, it is important to consider individual circumstances, such as age and comorbidities. Tailored strategies not only enhance the quality of care but also empower patients to take control of their diabetes management.
Incorporating a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Dietary changes
- Regular exercise
- Medication adherence
- Stress management
can significantly improve A1C levels. Engaging in these practices, alongside consistent A1C testing, fosters a proactive attitude toward diabetes care. By equipping themselves with knowledge and support, individuals can navigate their diabetes journey effectively, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.



