Introduction
The A1C test is a vital tool in the management of diabetes, providing critical insights into blood sugar control over a two to three-month period. By measuring the percentage of hemoglobin with glucose attached, this test not only aids in diagnosis but also plays a key role in guiding treatment strategies and lifestyle adjustments for individuals living with diabetes.
With an increasing number of adults diagnosed with this condition, understanding the implications of A1C results becomes essential for effective diabetes management. This article delves into the importance of the A1C test, interprets the results, and offers practical strategies for lowering A1C levels, all while emphasizing the need for targeted interventions and community support in diabetes care.
Understanding the A1C Test: Importance and Functionality
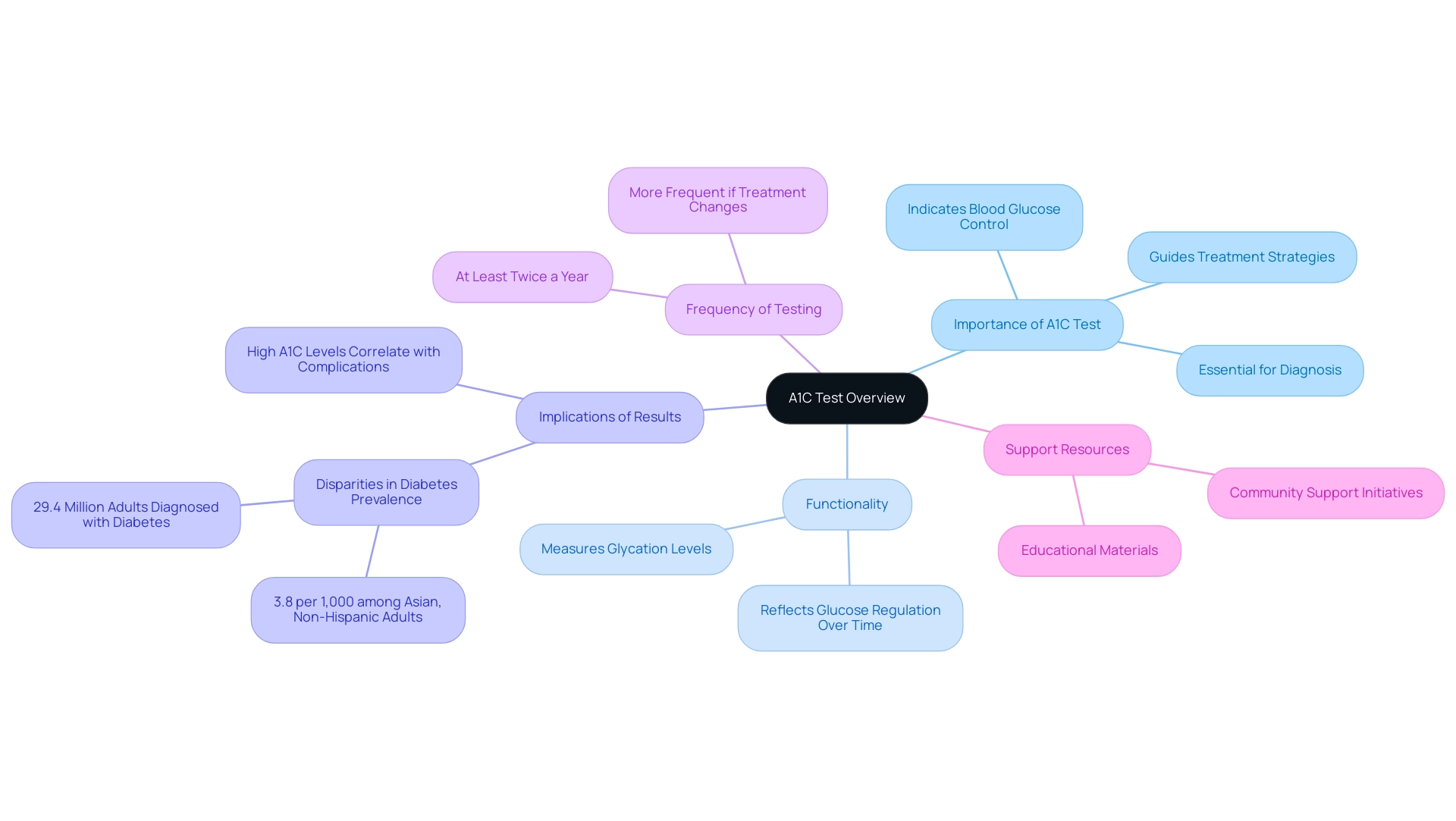
The A1C test quantifies the percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that has glucose attached to it, a process known as glycation. This test is essential in the diagnosis and continuous oversight of blood sugar levels, as it provides a glimpse of glucose regulation over a span of two to three months, which can be evaluated using an a1c to sugar level chart. According to the a1c to sugar level chart, a higher A1C percentage correlates with inadequate blood glucose control, which can lead to serious complications if left unaddressed.
Furthermore, this test is pivotal in informing treatment strategies and necessary lifestyle modifications for individuals managing this condition. Regular A1C assessments allow healthcare providers to track patient progress effectively using the a1c to sugar level chart and tailor management plans. It is particularly crucial given the estimated 29.4 million adults diagnosed with this condition, with a notable incidence rate of 3.8 per 1,000 among Asian, non-Hispanic adults, highlighting the disparities in prevalence among various racial and ethnic groups.
This necessitates targeted interventions in blood sugar management, especially for adults with type 1 condition, as indicated by the a1c to sugar level chart. Recent data reflects a positive trend in blood sugar management, with hospital discharges for hypoglycemia dropping from 60,000 in 2019 to 51,000 in 2020, indicating improved awareness and management strategies. As Roopa Naik points out, 'The A1C test is essential for understanding how well the condition is being managed over time.'
With ongoing advancements, current guidelines suggest that individuals with high blood sugar should consult the a1c to sugar level chart and have their A1C readings assessed at least twice a year, or more often if their treatment plan changes or if they are not achieving their glycemic goals. At&T Solutions, we strive to assist recently diagnosed individuals by offering resources and educational materials that help them comprehend their A1C values and how to handle them efficiently, cultivating a community of support for improved health oversight.
Interpreting A1C Results: What Do the Numbers Mean for Blood Sugar Levels?
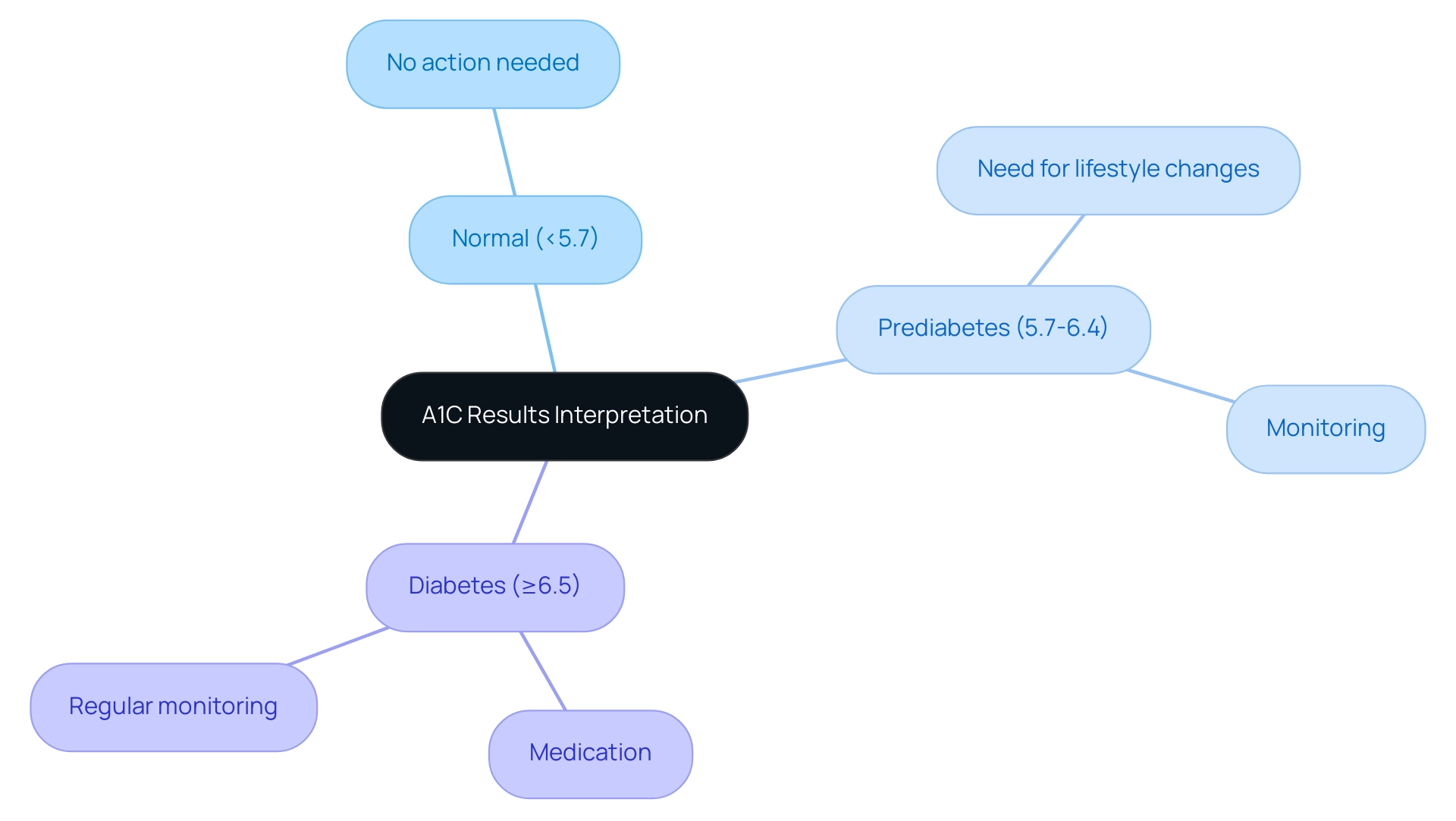
T2DSolutions is thrilled to introduce itself as a comprehensive resource hub for education and community support regarding health conditions. A1C results, presented as a percentage, offer a vital measure for managing blood sugar, and understanding the a1c to sugar level chart is crucial for individuals who have recently been diagnosed. An A1C measurement below 5.7% is classified as normal, while values ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes—a condition affecting approximately 38.0% of adults in the United States, with a notable prevalence of 20.9% among Hispanic adults from 2017 to 2020.
This highlights the urgent need for awareness and intervention within diverse populations. An A1C of 6.5% or greater, verified through two distinct tests, indicates the condition. For individuals diagnosed with this condition, the usual objective is to keep an A1C under 7%, as elevated amounts are associated with a higher risk of serious complications, including neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disease.
Understanding these A1C ranges empowers patients to evaluate their management strategies using the a1c to sugar level chart and pursue timely interventions. Furthermore, findings support the implementation of prevention programs, which may not only help in controlling blood glucose levels but also contribute to reducing the incidence of cancer. As highlighted by S. Tsugane, a lead researcher, 'Our findings indicate that these efforts may also help in lowering the occurrence of cancer, offering further robust backing for policymakers to adopt such prevention programs.'
This connection highlights the essential role that the a1c to sugar level chart plays in the efficient control of blood sugar, which is crucial for improving overall health results. T2DSolutions aims to provide comprehensive resources, including educational materials, community support, and innovative insights, that emphasize the importance of preventive measures and early intervention strategies, as highlighted in the case study titled 'Prediabetes Statistics.
How to Use the A1C to Blood Glucose Chart: A Step-by-Step Guide
Welcome to T2. Please refer to the A1C to sugar level chart for more information. DSolutions, your comprehensive resource hub for Type 2. Please refer to the A1C to sugar level chart for more information and Type 3. Refer to the A1C to sugar level chart for further details on blood sugar management education and community support. As we are currently in development, we invite you to subscribe to stay updated on our progress and receive notifications when new content is published. As you navigate your diabetes management journey, effective utilization of the A1C to sugar level chart is essential.
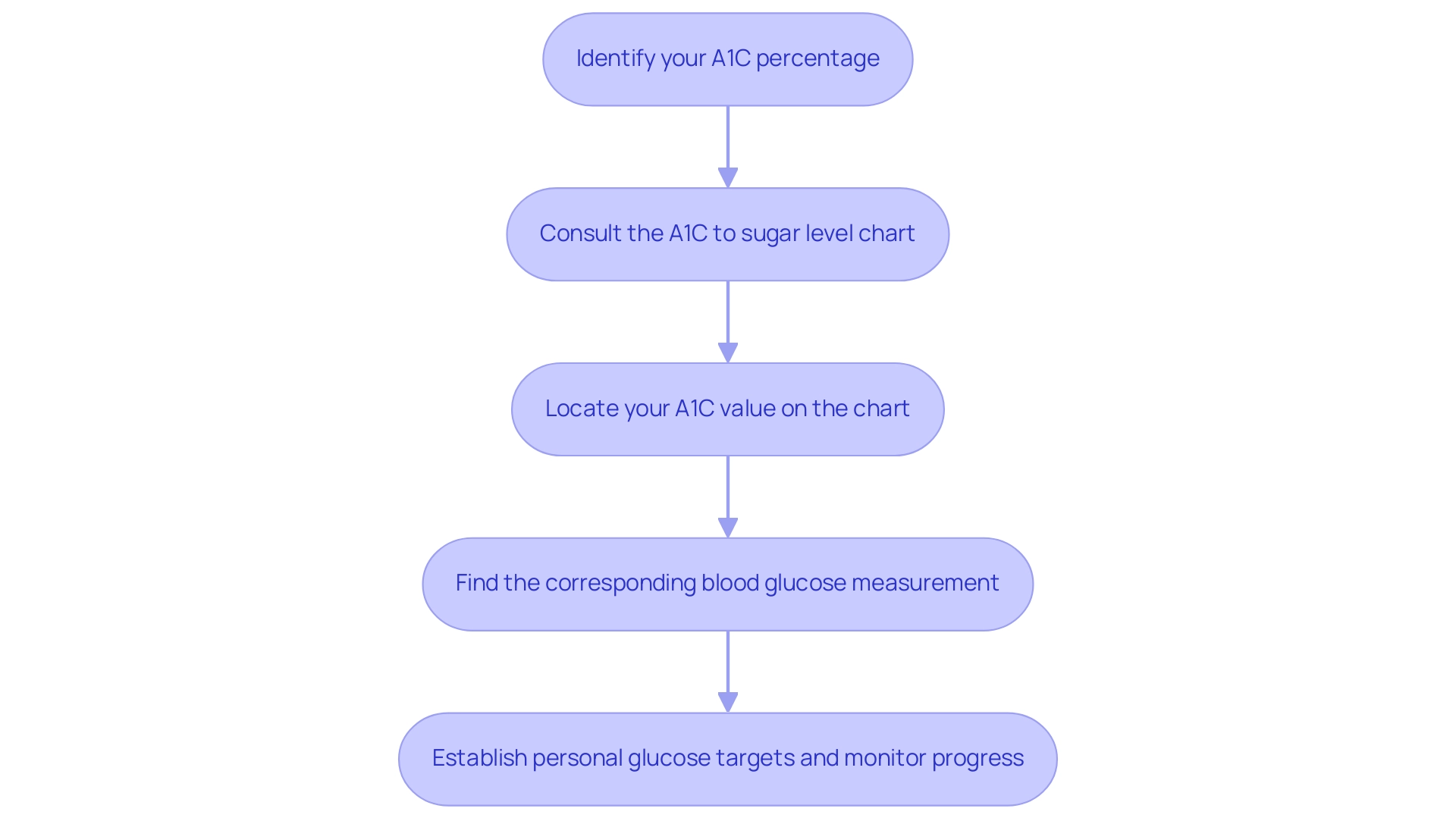
Begin by identifying your A1C percentage, which serves as a pivotal reference point. Patients with minimal comorbidity and a long life expectancy may benefit from more intensive glycemic targets, aiming for an A1C of less than 6.5%, provided that hypoglycemia is not a concern. Next, consult the corresponding blood glucose range on the A1C to sugar level chart, which is typically displayed in mg/dL.
For instance, an A1C reading of 6% correlates to an average blood glucose concentration of approximately 126 mg/dL. Follow these steps for accurate use of the A1C to sugar level chart:
- Locate your A1C value on the left side of the A1C to sugar level chart.
- Move horizontally across the A1C to sugar level chart to find the equivalent blood glucose measurement.
- Use this data to establish personal glucose targets with the A1C to sugar level chart and consistently monitor your progress.
This approach not only improves your understanding of glycemic control but also promotes effective communication with your healthcare team regarding your condition management. Monitoring is especially vital during stressful situations, such as illness, trauma, or surgery, as patients may need more frequent blood glucose checks to maintain control over their A1C values.
Reducing A1C values can greatly decrease the chances of long-term complications linked to high blood sugar, such as nerve damage, eye problems, kidney disease, and cardiovascular issues. As highlighted in the International Multicenter Study on Glycemia Measurement, A1C levels can be consistently represented as estimated average glucose (eAG) for most patients, addressing discrepancies in glycemia reporting and potentially reducing confusion in the care of individuals with elevated blood sugar. Furthermore, as Vivian Fonseca highlighted, comprehending the A1C assay is crucial for effective control of blood sugar levels, underscoring the significance of converting these measurements into practical health strategies.
Stay tuned for more resources and insights as we continue to grow at T2. Please refer to the A1C to sugar level chart for more information.
Common Questions About A1C and Blood Glucose Levels
Patients frequently inquire,
How often should I get my A1C tested?
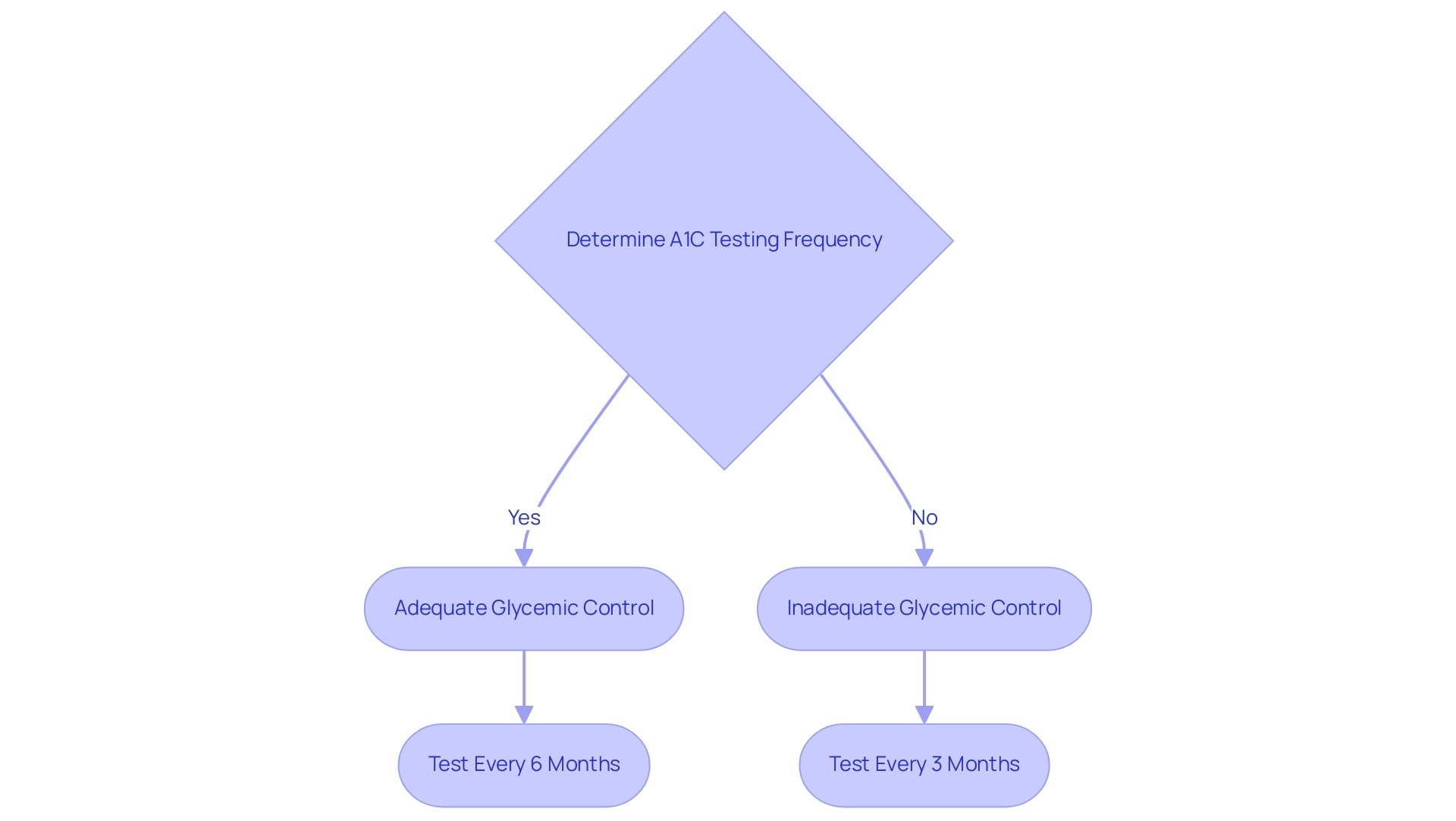
The general recommendation for individuals with this condition is to undergo A1C testing every three to six months, contingent upon their specific treatment plan. The Australian guidelines suggest that patients who demonstrate adequate glycemic control should be tested every six months, while those with inadequate control should have their tests every three months.
This frequency is crucial as it plays a significant role in diabetes management, a key focus of T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support. T2DSolutions will offer educational articles and tools that assist patients in effectively monitoring their A1C readings through an a1c to sugar level chart. A study titled
Impact of HbA1c Testing Frequency on Patient Outcomes
revealed that better adherence to these recommended testing intervals is linked to improved glycemic control and a reduced risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD), with only 3% of patients developing CKD when adhering to these guidelines.
Additionally, the study found that 1% of patients developed ischaemic heart disease (IHD), highlighting the importance of regular monitoring. Another common concern revolves around the question,
Can my A1C readings fluctuate?
Indeed, A1C levels can vary due to several factors, including dietary changes, illnesses, or adjustments in medication.
Recognizing these influencing elements allows patients to manage their condition more effectively and fosters informed discussions with healthcare providers. As Andrew Georgiou states,
Understanding these fluctuations is essential for effective management of the condition.
Engaging with the latest advancements in blood glucose monitoring technology, as discussed in current news, can also aid in tracking these fluctuations more accurately, further supported by the resources available at T2DSolutions, which includes community forums for shared experiences and strategies.
Effective Strategies for Lowering Your A1C Levels
As part of the launch of T2D Solutions, a new resource hub dedicated to supporting individuals with Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes, we provide essential strategies to effectively lower A1C levels:
-
Improve Your Diet: Emphasize a balanced diet that includes whole grains, a variety of vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is essential to reduce the consumption of sugars and refined carbohydrates, which can cause spikes in blood glucose. Nutritionists frequently highlight that dietary modifications can significantly impact A1C levels. As Xiuli Sun from the Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine observes, "We would like to provide some remarks and propose topics for additional discussion," highlighting the significance of continuous conversation about dietary modifications in the management of blood sugar.
-
Increase Physical Activity: Aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week. Participating in regular physical activity not only helps with weight management but also improves insulin sensitivity, a crucial element in managing blood sugar levels. Research shows that regular exercise can result in a significant decrease in A1C values. Taking into account the average 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk score of 8.0%, sustaining an active lifestyle is crucial for lowering health risks related to metabolic disorders.
-
Monitor Blood Sugar: Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential to understanding how your body reacts to various foods and physical activities. Monitoring these metrics can assist you in making informed dietary choices and adjustments.
-
Medication Adherence: It is vital to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding diabetes medications and insulin. Following prescribed treatment plans is essential for effectively managing blood sugar and achieving desired A1C targets.
-
Manage Stress: Incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation can be beneficial, as stress has been shown to adversely affect blood sugar levels. Effective stress relief techniques can contribute to overall health enhancements and improved blood sugar regulation.
Moreover, T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering innovative resources and assistance as the biopharma landscape transforms through AI technologies, indicating that progress in technology could offer additional solutions for health issues in the future.
To stay updated on our resources and receive valuable insights, we encourage you to subscribe to our newsletter. Implementing these strategies can lead to significant enhancements in A1C levels and overall well-being, which underscores the importance of using an A1C to sugar level chart for a holistic approach to diabetes management. T2DSolutions will offer various tools, including personalized meal plans, exercise guides, and community support, to assist you in your journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is crucial for anyone managing diabetes. This test not only serves as a diagnostic tool but also provides ongoing insights into blood sugar control, allowing for tailored treatment strategies and lifestyle adjustments. Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential, as it empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and facilitates effective communication with healthcare providers.
Interpreting A1C results is equally important. Recognizing the significance of different A1C ranges—from normal to prediabetes and diabetes—can prompt timely interventions and promote awareness, particularly in diverse populations disproportionately affected by diabetes. By maintaining an A1C below 7%, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications associated with the disease.
Implementing effective strategies to lower A1C levels, such as:
- Improving diet
- Increasing physical activity
- Adhering to medication regimens
plays a vital role in diabetes management. Stress management techniques further enhance overall health, creating a comprehensive approach to controlling blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, the A1C test is a cornerstone of diabetes care, guiding both patients and healthcare providers in crafting effective management plans. By leveraging the knowledge gained from A1C results and adopting proactive strategies, individuals living with diabetes can significantly improve their health outcomes and quality of life. Continuous education and community support, such as that offered by T2DSolutions, are essential in fostering a collaborative environment for better diabetes management.



