Overview
The ADA 1800 calorie diabetic diet is designed to help individuals manage their blood sugar levels while enjoying a variety of foods, emphasizing balanced nutrition through carbohydrate management and the inclusion of essential food groups. The article supports this by outlining the diet's structure, detailing practical meal planning, and highlighting the importance of understanding food labels, all aimed at promoting sustainable eating habits for better long-term health outcomes.
Introduction
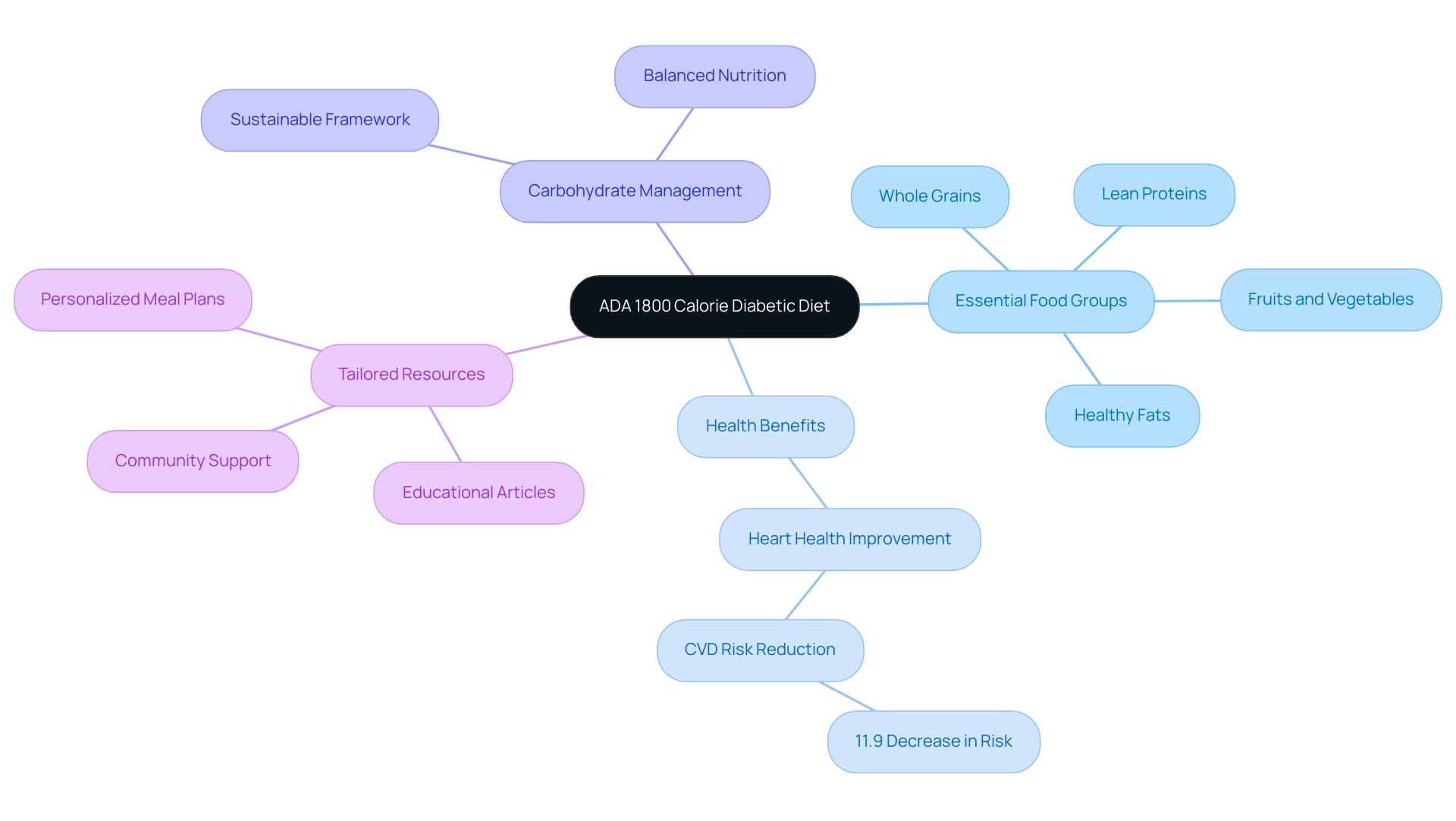
The ADA 1800 Calorie Diabetic Diet offers a structured approach for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes, aiming to balance nutrition while effectively controlling blood sugar levels. As T2DSolutions emerges as a vital resource hub, it emphasizes the importance of carbohydrate management through a diverse range of food options, including:
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats
- An abundance of fruits and vegetables
This comprehensive dietary plan not only supports daily caloric limits but also aligns with research demonstrating its potential to reduce long-term health risks, such as cardiovascular disease. With a focus on personalized meal planning, practical recipes, and educational resources, T2DSolutions empowers individuals to embrace a sustainable dietary framework that enhances overall well-being without sacrificing enjoyment in their meals. As challenges arise in adhering to this diet, effective strategies and community support are essential for navigating the complexities of diabetes management.
Overview of the ADA 1800 Calorie Diabetic Diet
As the new resource hub launches for people managing Type 2 and Type 3 conditions, we present the ADA 1800 calorie diabetic diet, meticulously structured to assist those in effectively managing their blood sugar levels while still allowing for a diverse range of food options. This dietary plan emphasizes balanced nutrition and incorporates all essential food groups within a caloric limit of 1800 calories per day. Central to the diet’s philosophy is carbohydrate management, promoting the consumption of whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables.
Research indicates that adherence to this diet can lead to significant health benefits, including a notable decrease in the average 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, which was reduced by 11.9% in a year-long study of a very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD). Experts emphasize that 'A well-structured diet can significantly impact long-term health outcomes for people with diabetes.' T2D Solutions is dedicated to supporting newly diagnosed patients by providing comprehensive resources, including personalized meal plans, educational articles, and access to community support forums that adhere to the ADA 1800 calorie diabetic diet.
The primary objective of this diet is to establish a sustainable dietary framework that supports overall health and well-being while ensuring that people do not have to sacrifice taste or enjoyment in their meals. Moreover, a case study on dietary prescriptions and monitoring in geriatric patients revealed that only 30% of patients received an energy-enriched diet despite 60% needing it, underscoring the importance of tailoring diets to meet specific nutritional requirements, which aligns perfectly with the goals of the ADA 1800 calorie diabetic diet. T2D Solutions is committed to empowering individuals in their journey towards better health through these tailored resources.
Practical Meal Planning: Sample Menus and Recipes
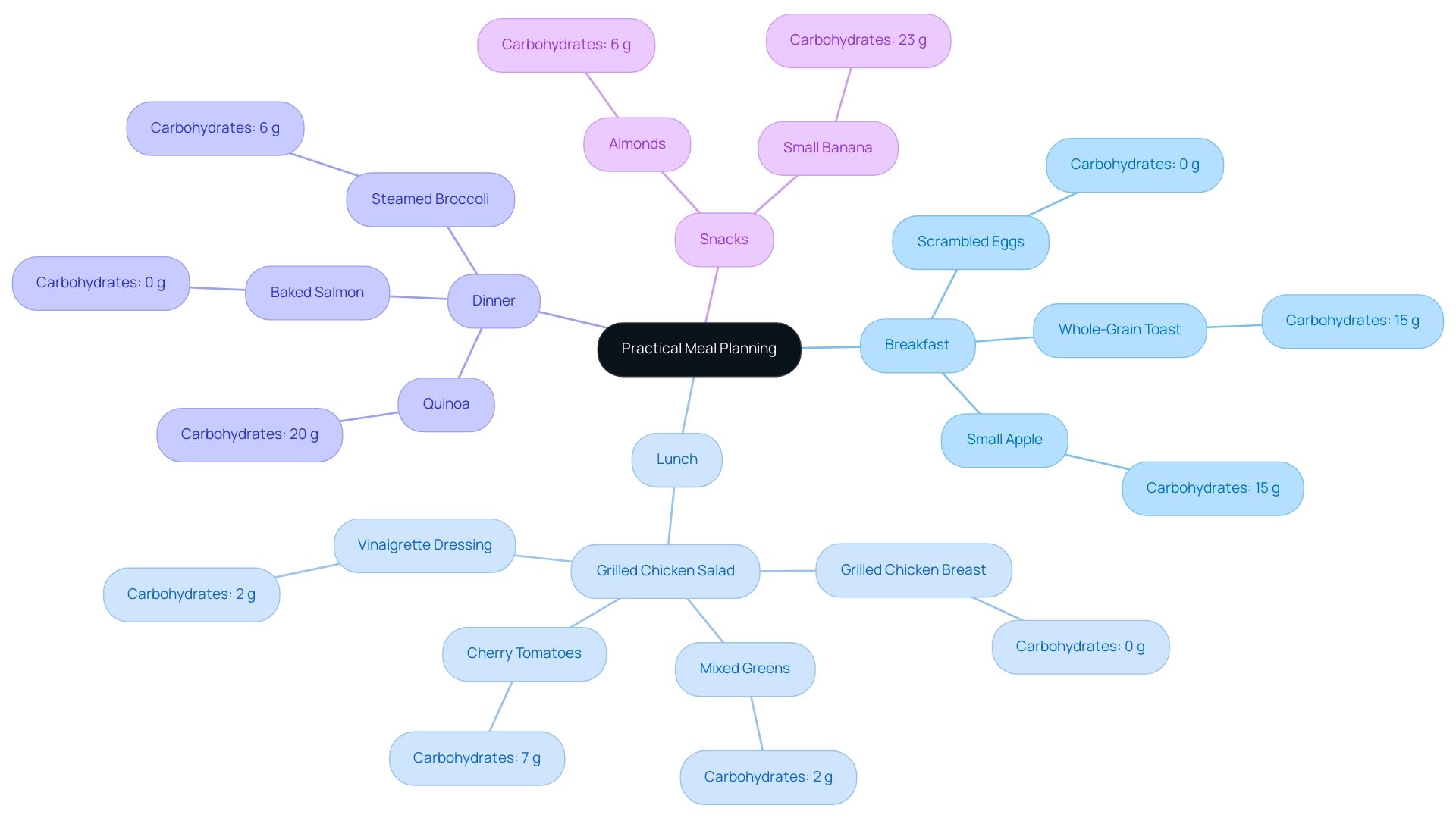
Sample Menu:
- Breakfast: 2 scrambled eggs (0 g carbs), 1 slice of whole-grain toast (15 g carbs), and 1 small apple (15 g carbs) - Total: 30 g carbs.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad featuring 4 ounces of grilled chicken breast (0 g), mixed greens (2 g), ½ cup of cherry tomatoes (7 g), and vinaigrette dressing (2 g) - Total: 11 g.
-
Dinner: Baked salmon (0 g carbohydrates) served with 1 cup of steamed broccoli (6 g carbohydrates) and ½ cup of quinoa (20 g carbohydrates) - Total: 26 g carbohydrates.
-
Snacks: 1 ounce of almonds (6 g carbohydrates) or a small banana (23 g carbohydrates) - Total: 6 g carbohydrates (almonds) or 23 g carbohydrates (banana).
Recipes:
-
Grilled Chicken Salad: This nutritious option combines 4 ounces of grilled chicken breast with 2 cups of mixed greens (2 g carbs), ½ cup of cherry tomatoes (7 g carbs), and ¼ cup of low-fat dressing (2 g carbs). It ensures a balanced intake of protein and carbohydrates while adhering to caloric limits.
The total for this salad is 11 g carbohydrates. -
Baked Salmon: To prepare, season a 4-ounce salmon fillet with lemon, herbs, and spices. Bake at 375°F for 15-20 minutes.
Serve alongside 1 cup of steamed broccoli (6 g carbs) and ½ cup of quinoa (20 g carbs) to create a nutrient-rich dinner with a total of 26 g carbs.
This menu aligns with the recommendations from the American Diabetes Association and reflects T2DSolutions' commitment to providing comprehensive resources for managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes, such as the ada 1800 calorie diabetic diet. By choosing fresh, canned, or frozen fruits without added sugar, people can better manage their blood sugar levels.
The total carbohydrates for this sample day can be adjusted as necessary to maintain the target intake of 158 grams, as observed in recent meal planning examples within the ada 1800 calorie diabetic diet. By monitoring carbohydrate intake and selecting low-GI foods, people can enhance their overall health. Personalized meal plans should be created to address individual needs, preferences, and health objectives, highlighting the comprehensive support the organization aims to offer.
T2DSolutions will also provide continuous education and community assistance, ensuring that newly diagnosed patients have access to the resources they require for effective management.
Understanding Food Labels and Carbohydrate Counting
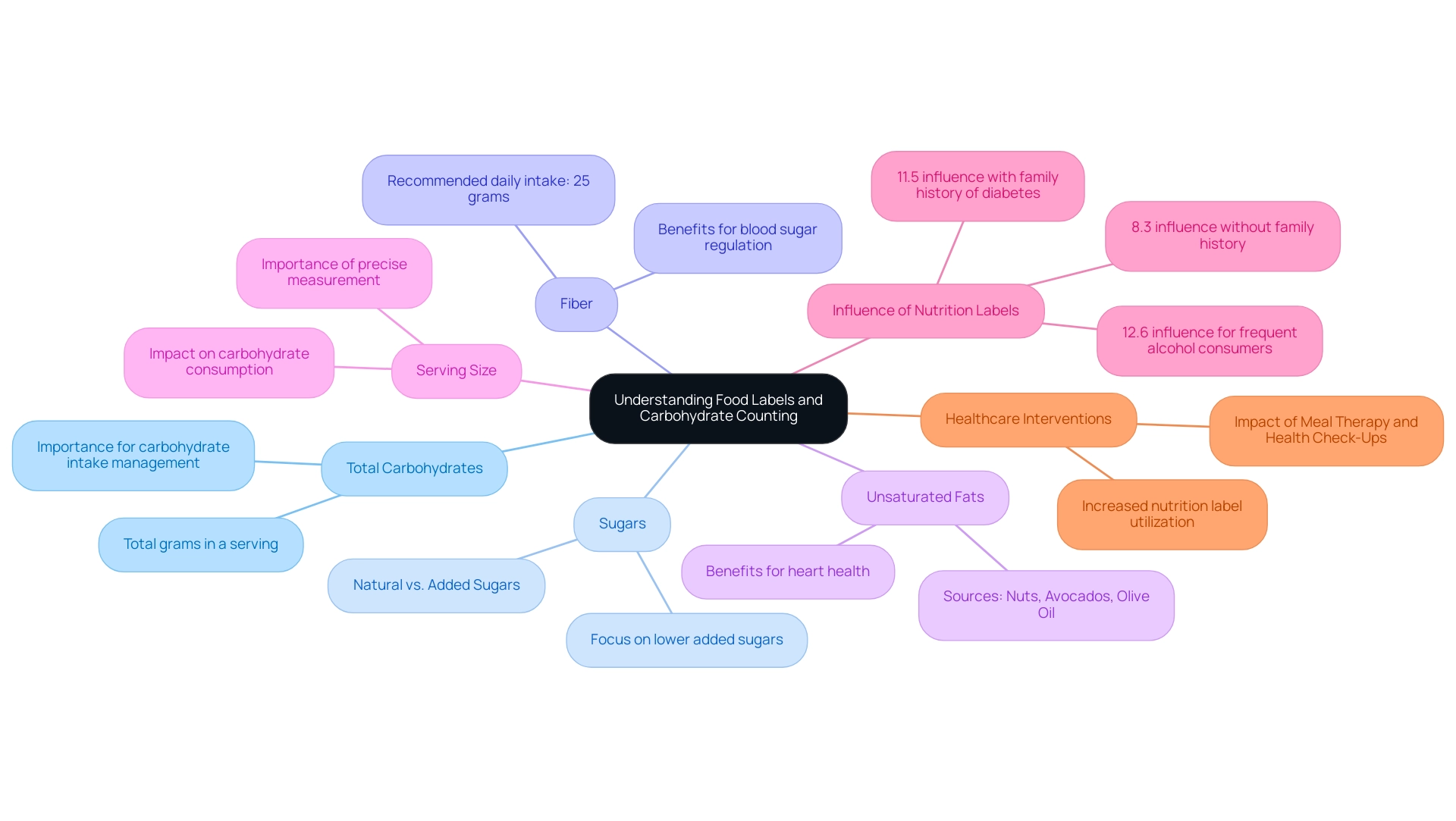
Food labels serve as a vital resource, offering comprehensive details about the nutritional content of packaged foods. These labels include critical information such as total calories, carbohydrates, sugars, and fiber, all of which are essential for effective carbohydrate counting—a fundamental practice in managing blood sugar. Understanding how to read these labels can significantly influence dietary decisions, particularly for those managing diabetes.
-
Total Carbohydrates: This figure indicates the total grams of carbohydrates present in a serving, encompassing sugars, starches, and fiber. Awareness of this value is crucial, as it helps in managing overall carbohydrate intake.
-
Sugars: It is important to differentiate between natural and added sugars. Focus on items with lower added sugars to prevent spikes in blood glucose levels, which are particularly detrimental for diabetics.
-
Fiber: High-fiber foods are beneficial, as they aid in regulating blood sugar levels. The recommended daily intake for fiber is at least 25 grams, and choosing foods rich in this nutrient can support better health outcomes.
-
Unsaturated Fats: Including unsaturated fats in the diet is beneficial for heart health. Beneficial sources consist of nuts, avocados, and olive oil, which can be especially useful for people with blood sugar issues, as they can enhance overall cardiovascular health.
Serving Size: Understanding serving sizes is essential, as they directly affect overall carbohydrate consumption. Precise measurement of servings ensures that people can achieve their carbohydrate targets effectively.
Research indicates that 8.3% of people without a family history of blood sugar issues reported that nutrition labels influenced their food choices, while this influence increased to 12.6% among those who consume alcohol frequently. Moreover, insights from a case study on the impact of meal therapy and health check-ups reveal that patients receiving these interventions demonstrated a significant increase in nutrition label utilization. This suggests that healthcare interventions can enhance patients' ability to make informed dietary choices.
As Rafael Perez-Escamilla observes, 'Our study emphasizes the positive influence of community health workers on the capacity of Latinos with type 2 conditions to enhance their food label use.' By understanding food labels, individuals can take significant strides towards effective management of their condition. For more resources and community support initiatives, visit the website to stay updated on the latest information and tools available for newly diagnosed patients.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Diabetes Management
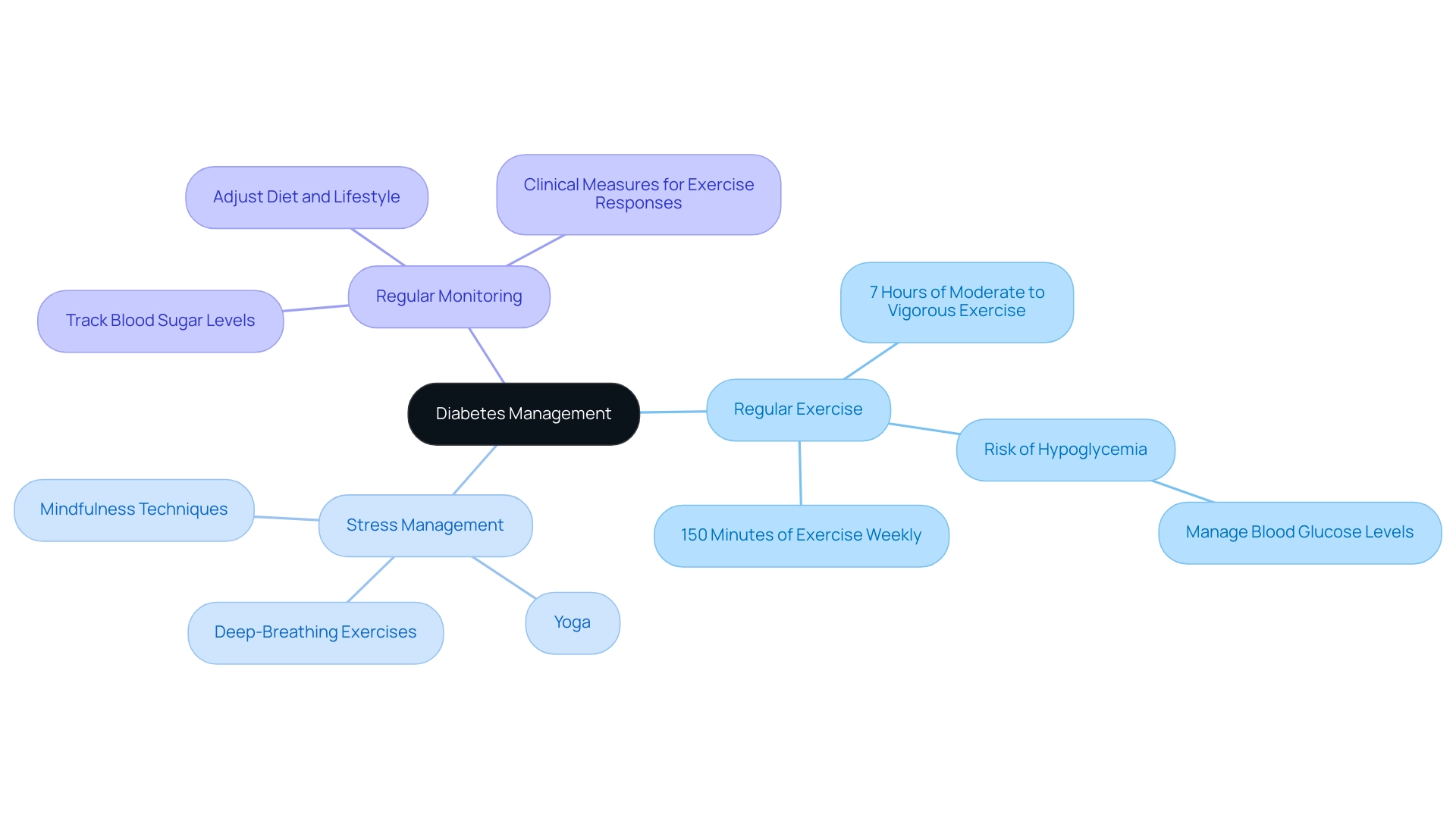
Effective management of the condition necessitates a multifaceted approach that includes dietary modifications such as an ADA 1800 calorie diabetic diet, consistent physical activity, and effective stress management. T2DSolutions is dedicated to serving as your all-encompassing guide for Type 2 and Type 3 health education, providing valuable resources specifically designed for newly diagnosed patients. Key lifestyle changes include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, is crucial as it significantly enhances insulin sensitivity.
Studies show that people who effectively sustain significant weight reduction usually partake in around 7 hours weekly of moderate- to vigorous-intensity exercise, which plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. This engagement not only aids in weight management but also improves overall health outcomes.
-
Stress Management: Implementing techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can effectively lower stress levels. This is particularly significant as heightened stress can result in elevated blood sugar levels, complicating the management of this condition.
-
Regular Monitoring: Consistently tracking blood sugar levels is essential for understanding how food and activity affect the management of this illness. This practice facilitates timely adjustments to diet and lifestyle, allowing for more effective control of blood glucose levels. A study indicated that individuals with blood sugar issues, particularly those on insulin, face heightened risks of hypoglycemia during and after exercise. As noted by Steineck et al., the time patients with T1D spent in hypoglycemia over a 5-day period was similar whether they exercised for 5 consecutive days or not. Therefore, strategies to manage blood glucose levels before, during, and after exercise are crucial to mitigate these risks, ensuring a safe and effective exercise regimen. The case study titled 'Exercise and Hypoglycemia Risk in Diabetes' further emphasizes the necessity of managing blood glucose levels in relation to exercise.
The organization aims to assist you on this journey by providing insights, educational resources, and community support tailored for recently diagnosed patients, ensuring you have the tools needed for effective management of an ADA 1800 calorie diabetic diet.
Overcoming Challenges on the ADA 1800 Calorie Diet
Adhering to an 1800 calorie diabetic diet presents several challenges that require thoughtful strategies to overcome. At our organization, we are dedicated to assisting newly diagnosed individuals in managing these complexities as part of our extensive resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 management.
-
Dining Out: It is essential to tackle restaurant menus with a proactive attitude. Review menus in advance to identify healthier options, favoring grilled or baked items over fried selections. Do not hesitate to request modifications, such as asking for dressings on the side, which can significantly reduce calorie and fat intake. Given that 26.3% of participants in a related study reported a family history of diabetes, understanding the influence of dietary patterns on health outcomes is essential, especially in environments with high fast-food density. This organization offers resources and tips for making healthier choices while dining out, ensuring you can enjoy meals without compromising your health.
-
Social Gatherings: These situations can pose temptations that may derail dietary adherence. To mitigate this, consider eating a healthy snack before attending an event to curb hunger. Additionally, bringing a nutritious dish to share not only ensures you have something suitable to enjoy but also encourages healthier eating among peers. As noted by JRP, the higher prevalence of fast-food restaurants in predominantly black neighborhoods can complicate these choices, making it crucial to plan ahead. The organization provides guidance on how to navigate social situations while adhering to an ADA 1800 calorie diabetic diet to maintain your dietary goals.
-
Food Cravings: Understanding the triggers behind cravings is essential for managing them effectively. When cravings for sweets arise, opt for healthier alternatives like fresh fruit or a modest portion of dark chocolate, which can satisfy the urge without compromising dietary goals. The organization offers tips and recipes for healthier snack options to help you stay on track.
-
Time Constraints: Busy schedules can often lead to unhealthy eating habits. To combat this, meal prepping can be an effective strategy. Allocate time each week to prepare meals in advance, making it easier to adhere to your dietary plan throughout the week. T2DSolutions assists patients with meal planning resources to make this process easier.
Research shows that dietary patterns greatly affect health outcomes, especially in groups with a family history of the condition. The Longitudinal Analysis of Dietary Patterns, part of the Black Women's Health Study, illustrates how dietary choices can serve as significant predictors of type 2 diabetes incidence over time. By implementing these strategies and being mindful of dietary choices, individuals can successfully navigate the complexities of dining out and social situations while maintaining their health.
T2DSolutions is here to provide ongoing support and resources, including personalized consultations and educational materials, as you embark on your journey to better health.
Conclusion
The ADA 1800 Calorie Diabetic Diet serves as a structured framework designed to assist individuals in managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes effectively. By emphasizing balanced nutrition through whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables, this dietary plan not only helps maintain blood sugar levels but also contributes to long-term health benefits, such as reducing cardiovascular disease risk. T2DSolutions is dedicated to providing personalized meal planning, practical recipes, and comprehensive educational resources to empower individuals in their dietary choices.
Understanding food labels and carbohydrate counting is essential in this dietary approach, allowing individuals to make informed decisions that directly impact their health. Additionally, integrating lifestyle changes—such as regular exercise and stress management—further enhances diabetes management. While challenges may arise in adhering to the ADA 1800 Calorie Diet, strategies for:
- Dining out
- Managing social situations
- Overcoming cravings
can facilitate a successful dietary journey.
Ultimately, the ADA 1800 Calorie Diabetic Diet, supported by T2DSolutions, offers a sustainable path towards improved health and well-being for those managing diabetes. By embracing this structured dietary plan and utilizing available resources, individuals can navigate their health journey with confidence and enjoy a fulfilling, balanced life.



