Overview:
The article focuses on understanding how alcohol consumption affects blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes. It highlights that while moderate alcohol intake can temporarily raise blood sugar levels, excessive consumption may lead to hypoglycemia due to the liver's prioritized metabolism of alcohol over glucose production, emphasizing the need for careful monitoring and moderation in alcohol consumption for effective diabetes management.
Introduction
The interplay between alcohol consumption and blood sugar levels is a critical topic for those managing diabetes. While moderate drinking may offer some benefits, such as a potential reduction in diabetes risk, the complexities of alcohol's effects on glucose regulation cannot be overlooked.
Various factors, including the type of beverage, the presence of food, and individual health conditions, contribute to how alcohol influences blood sugar levels. This article delves into the nuances of alcohol metabolism, the risks of hypoglycemia, and essential guidelines for safe consumption, providing valuable insights for individuals navigating their diabetes management journey.
Understanding these dynamics is vital for making informed choices that support overall health and well-being.
The Relationship Between Alcohol and Blood Sugar Levels
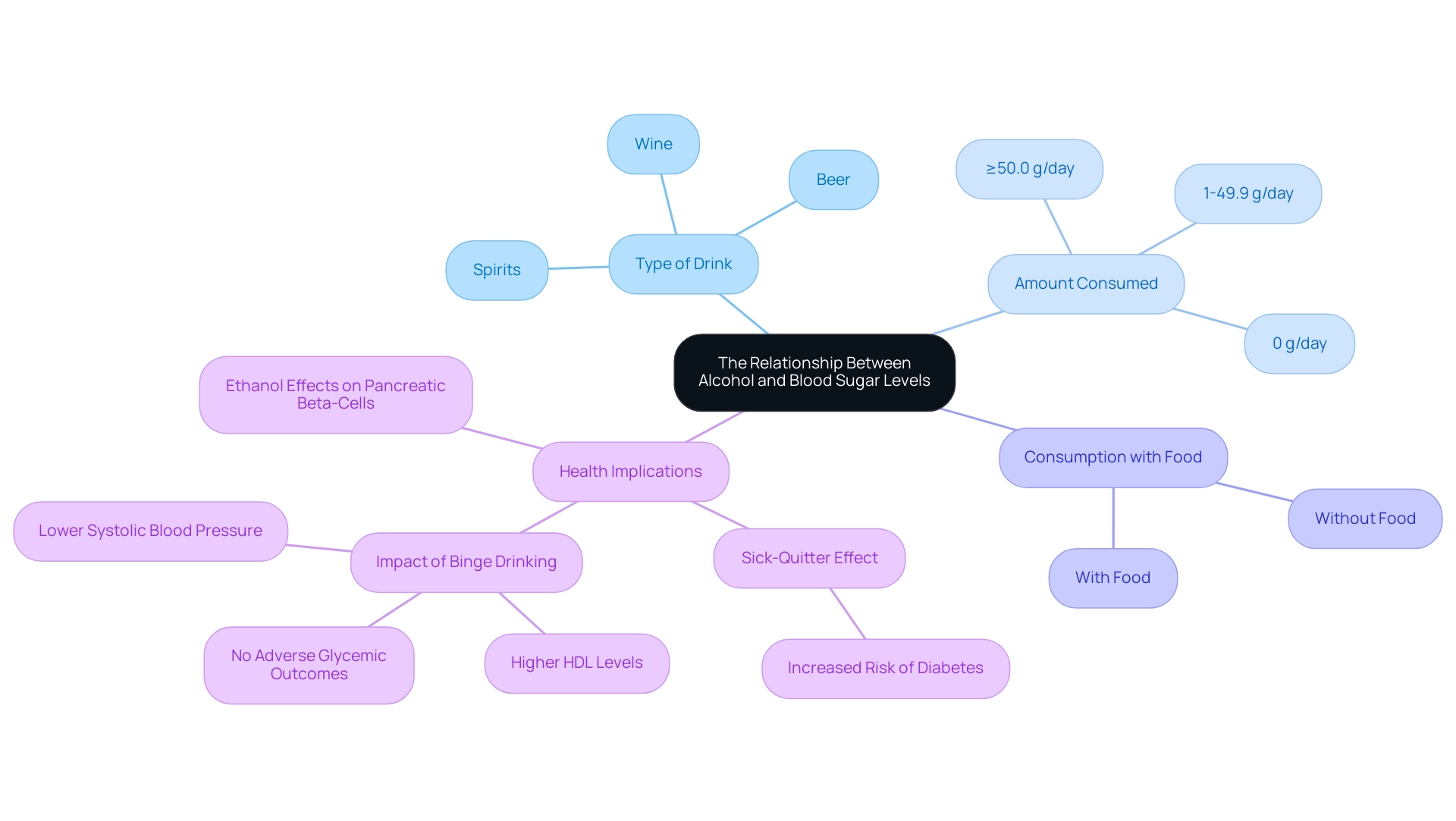
The alcohol effect on blood sugar can be significant and varies depending on the type of drink, the amount consumed, and whether the beverage is ingested with food. Research indicates that moderate beverage intake may result in a temporary increase in blood sugar, demonstrating the alcohol effect on blood sugar, while excessive use can actually reduce these levels. This paradox arises from the substance's influence on liver function, which plays a critical role in glucose production.
Significantly, beverage consumption categories range from 0 to ≥50.0 g/day, emphasizing the necessity of moderation. In particular, studies have highlighted that ethanol can lead to pancreatic beta-cell death, as noted by recent investigations conducted by Dembele et al. Furthermore, Dolly O Baliunas emphasizes that former drinkers may be at increased risk of developing blood sugar issues due to health concerns, a phenomenon known as the sick-quitter effect.
For persons identified with the condition, it is essential to carefully observe sugar levels when ingesting beverages due to the alcohol effect on blood sugar, as personal reactions can vary significantly. Furthermore, a case study named 'Impact of Binge Drinking on Clinical Markers' discovered that binge drinking was linked to higher HDL levels and lower systolic blood pressure, highlighting the intricate relationship between beverage intake and clinical outcomes. Comprehending these dynamics not only aids in controlling blood sugar levels more efficiently but also highlights the significance of educated decisions concerning beverage intake, particularly regarding the alcohol effect on blood sugar.
Implications of Alcohol Consumption for Diabetic Individuals
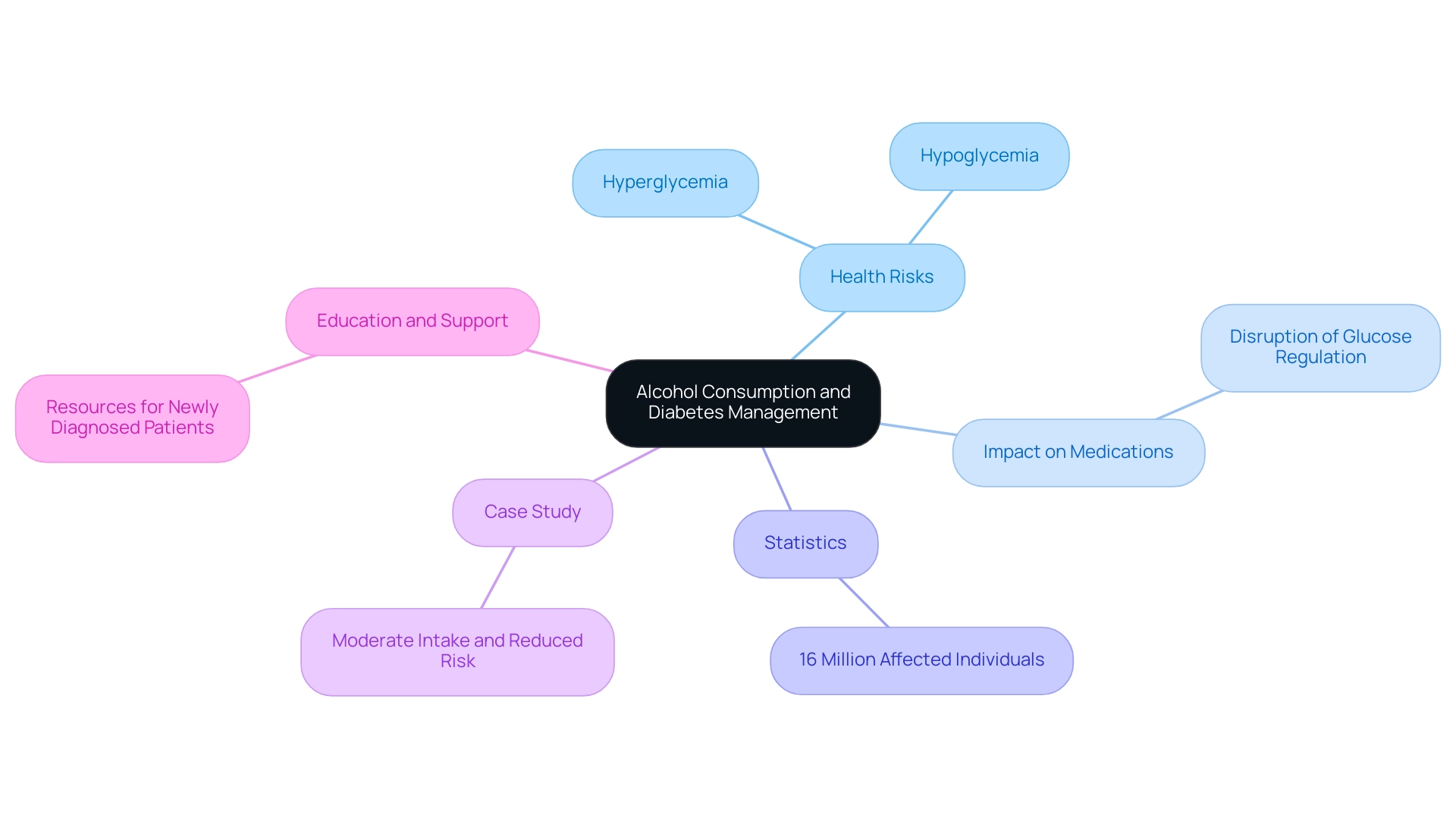
At a2d Solutions, we acknowledge that for individuals diagnosed with this condition, understanding the alcohol effect on blood sugar is crucial, as it can significantly elevate the risks of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. With this condition affecting an estimated 16 million individuals in the United States, our aim is to offer thorough education on such essential subjects. The alcohol effect on blood sugar is recognized to disrupt the effectiveness of glucose regulation medications, leading to unpredictable variations in sugar levels.
This interference poses a serious concern, particularly since beverages can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia, preventing individuals from taking necessary corrective actions. Notably, a case study named 'Alcohol Intake and Type 2 Diabetes Risk' discovered that moderate intake of beverages may be linked to a 30% decreased risk of developing the condition, which emphasizes the alcohol effect on blood sugar management. However, excessive intake of beverages should be discouraged due to potential adverse health effects.
At T 2 Solutions, we are committed to equipping newly diagnosed patients with educational materials, community support options, and access to expert consultations tailored to individual needs. We encourage those managing blood sugar issues to thoroughly understand their unique health circumstances and seek guidance from healthcare professionals regarding the alcohol effect on blood sugar before considering consumption. Such consultations can offer customized guidance that aligns with personal treatment plans and overall health goals, reflecting our commitment at t2d solutions to support your journey towards effective management.
Understanding Alcohol Metabolism and Its Impact on Blood Sugar
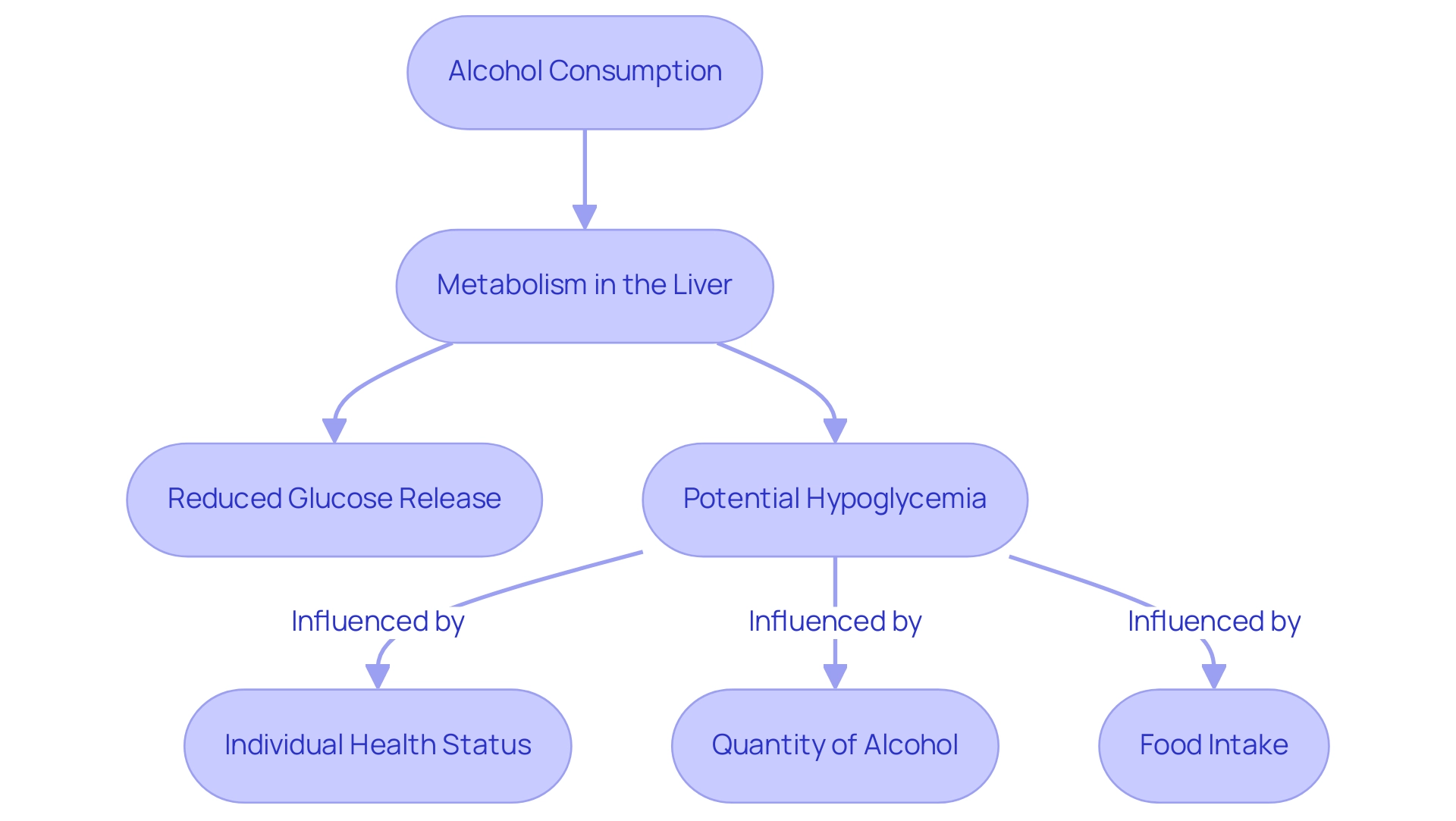
atd Solutions, we understand that managing diabetes effectively requires comprehensive knowledge and resources. Substance metabolism mainly takes place in the liver, which emphasizes the decomposition of the substance over the creation of glucose. As the liver metabolizes ethanol, the alcohol effect on blood sugar may hinder the release of glucose into the circulatory system, potentially leading to reduced sugar levels.
This inhibition can result in severe and prolonged hypoglycemia, especially in individuals who have not eaten for around three to four days before consuming beverages. The alcohol effect on blood sugar can differ among individuals, influenced by factors such as overall health, the quantity of alcohol consumed, and whether food is ingested simultaneously. Comprehending these dynamics is essential for effective sugar management, particularly for individuals recently diagnosed with conditions that influence glucose regulation.
Notably, red wine contains roughly 3.84 grams of carbohydrates, while white wine has about 3.82 grams per 5 fluid ounce serving, which can also influence blood sugar levels. Insights from specialists, including Robert M. Swift, M.D., Ph.D., emphasize the complexities of liver function and glucose production during the intake of beverages, particularly focusing on the alcohol effect on blood sugar, which highlights how the liver's prioritization of metabolizing substances can significantly impact glucose regulation. Furthermore, a relevant case study titled 'Substance and Asthma' explores the relationship between beverage consumption and asthma, demonstrating how such substances can exacerbate breathing difficulties, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
This connection reinforces the importance of understanding the substance's effects on health, especially for those managing specific health issues. As T2DSolutions launches, we aim to provide a comprehensive resource for educating and supporting individuals in their diabetes management journey. Our offerings will include educational materials, community forums, and expert consultations to help newly diagnosed patients navigate their health challenges.
Moreover, data extraction from recent studies, evaluated using the 5-point Jadad scale, highlights the reliability of findings concerning the alcohol effect on blood sugar levels.
The Risk of Hypoglycemia from Alcohol Consumption
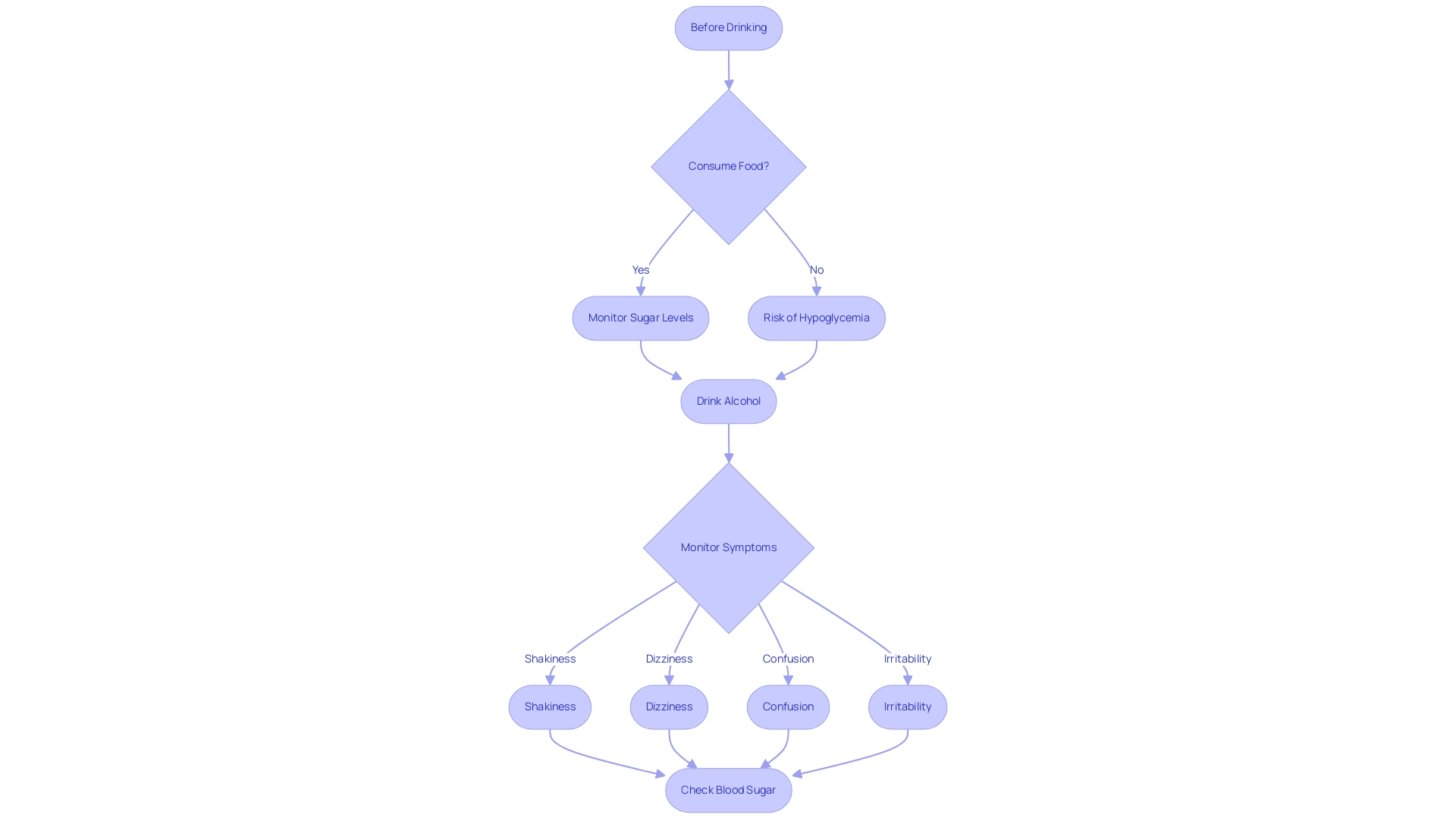
Hypoglycemia can manifest several hours after beverage intake, particularly when it is consumed without accompanying food. The symptoms, which may include shakiness, dizziness, confusion, and irritability, can easily be mistaken for intoxication, complicating self-assessment for those affected. It is crucial for diabetic individuals to have a source of glucose readily available when consuming alcohol, as the alcohol effect on blood sugar can significantly impair the body's ability to regulate sugar levels.
Regular monitoring of sugar levels both before and after drinking is strongly advised to avert the adverse effects of the alcohol effect on blood sugar. Notably, studies indicate that ethanol levels in the body can reach as high as 97 mmol/l following sustained administration, further emphasizing the need for careful management. Current guidelines recommend consuming food prior to drinking to mitigate the risk of hypoglycemia, due to the alcohol effect on blood sugar, as the liver prioritizes the metabolism of beverages over the maintenance of blood sugar levels.
Real-world case studies, including one titled 'Risks of Drinking for Diabetics,' have highlighted instances where diabetic individuals experienced severe hypoglycemia after drinking, which underscores the critical importance of recognizing the alcohol effect on blood sugar and maintaining vigilant monitoring. As Mark Cleasby, PhD, points out, understanding the alcohol effect on blood sugar is vital for diabetic individuals to manage their beverage intake safely. T2DSolutions strives to be your complete resource for Type 2 and Type 3 health management, providing educational material on the alcohol effect on blood sugar and practical strategies for safe use.
Our platform will showcase expert articles, community support forums, and personalized guidance to assist newly diagnosed patients in effectively managing their condition and making informed decisions regarding beverage intake.
Guidelines for Safe Alcohol Consumption in Diabetes Management
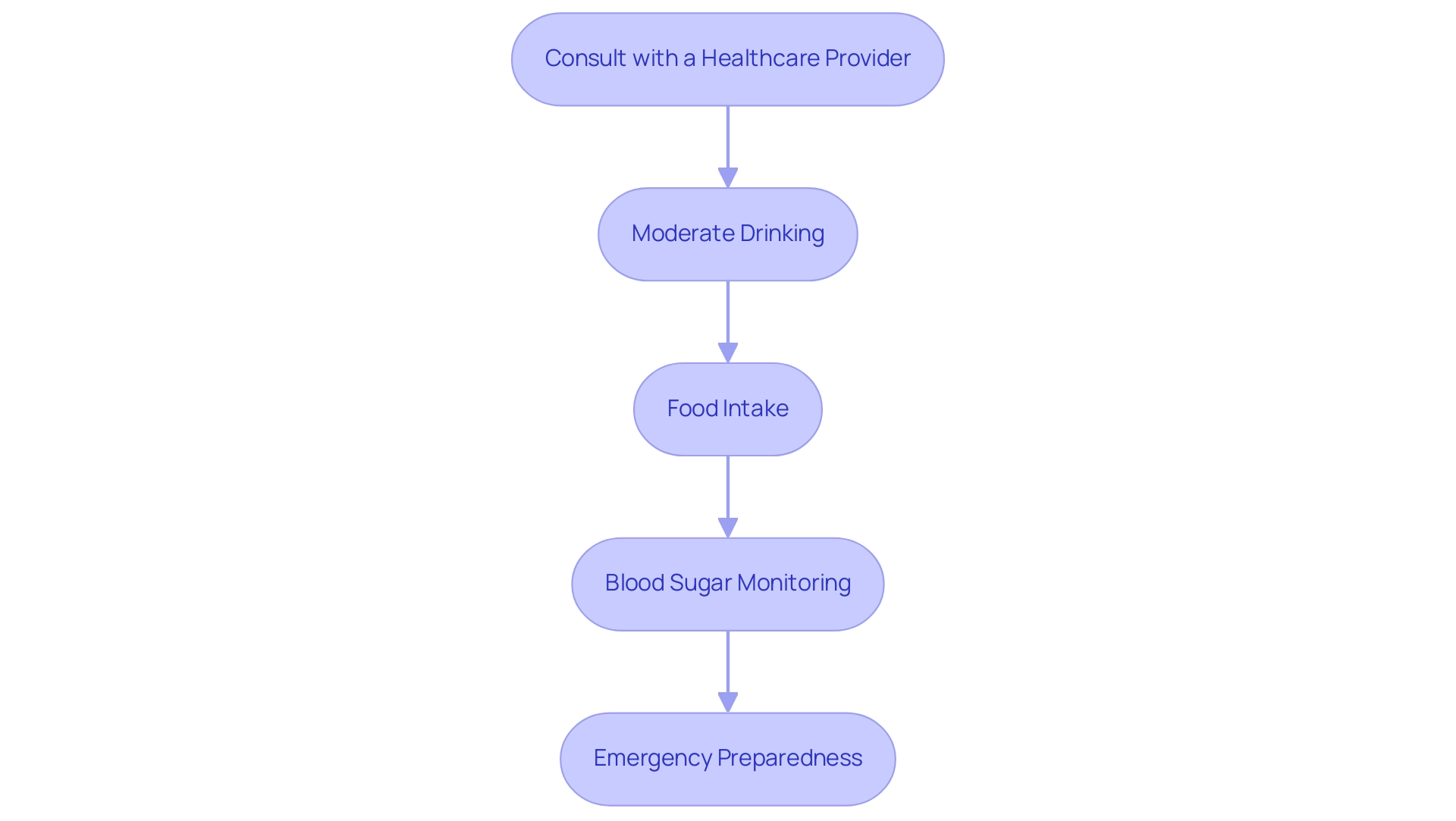
To ensure safe intake of beverages, individuals diagnosed with a metabolic disorder should follow the subsequent guidelines:
- Consult with a Healthcare Provider: It is essential to discuss personal risks associated with beverage intake with a healthcare professional.
- Moderate Drinking: Follow the recommendations from the American Diabetes Association, which advises that 'women should not consume more than one drink per day. Men should not consume more than two drinks per day.' This moderation is backed by findings from a study on beverage intake and type 2 diabetes risk, which indicates that moderate beverage intake, considering the alcohol effect on blood sugar, is linked to a 30% lower risk of diabetes among men and women.
- Food Intake: Eating before or while drinking is essential, as it aids in stabilizing sugar levels during beverage intake.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after consuming beverages to understand the alcohol effect on blood sugar and how it uniquely affects individual responses.
- Emergency Preparedness: Always keep a source of fast-acting glucose on hand to promptly address any potential hypoglycemia.
As T2DSolutions aims to be a comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education, following these guidelines can significantly reduce risks associated with the alcohol effect on blood sugar and foster a balanced lifestyle while managing health. By staying informed and connected to community support, individuals can enhance their diabetes management strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between alcohol consumption and blood sugar levels is essential for individuals managing diabetes. The article highlights how factors such as the type of beverage, quantity consumed, and food intake can significantly influence blood sugar responses. While moderate drinking may offer some benefits, such as a potential reduction in diabetes risk, the risks associated with excessive consumption and the potential for hypoglycemia cannot be overlooked.
The complexities of alcohol metabolism further complicate blood sugar management. Alcohol inhibits glucose production in the liver, potentially leading to dangerous drops in blood sugar levels, especially when consumed without food. This underscores the importance of regular monitoring and having a source of glucose readily available to address any hypoglycemic episodes.
Following established guidelines for safe alcohol consumption is crucial for those with diabetes. Consulting healthcare providers, practicing moderation, and ensuring food intake while drinking can help mitigate risks. By staying informed and proactive about their health, individuals can make educated choices that support their diabetes management and overall well-being.



