Overview
The article focuses on understanding the conversion between milligrams (mg) and milliliters (ml), emphasizing the importance of accurate dosage calculations in medication administration. It explains that the conversion is based on the density of the substance, providing a formula to facilitate this process, and highlights the critical need for precision to prevent medication errors, which can lead to severe health consequences.
Introduction
In the field of medicine, understanding the distinction between milligrams (mg) and milliliters (ml) is crucial for ensuring the safe and effective administration of medications. These units represent mass and volume, respectively, and their accurate conversion is vital for preventing dosing errors that can lead to serious health consequences.
With the increasing complexity of prescriptions and the prevalence of medication-related errors, a clear grasp of how to convert between these units is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
This article delves into the fundamentals of mg and ml conversions, practical applications in medication dosage, common pitfalls to avoid, and the tools available to facilitate accurate calculations, ultimately emphasizing the importance of precision in medication safety.
Understanding the Basics of Milligrams and Milliliters
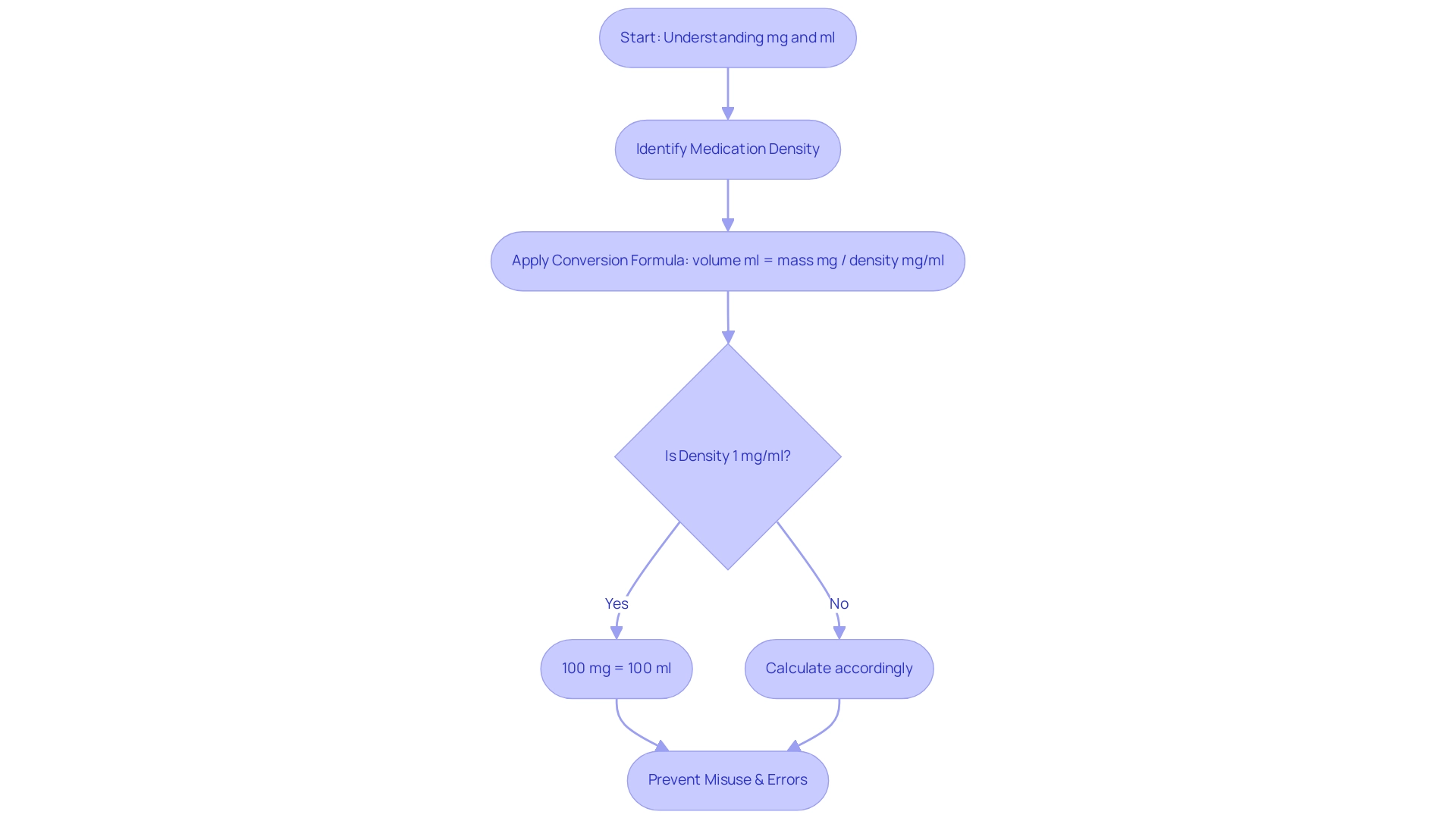
In the realm of medicine, a key consideration is how many mg in ml, as milligrams (mg) represent mass and milliliters (ml) indicate volume. Milligrams quantify weight, which is crucial for treatments requiring precise dosages, while milliliters denote the volume of liquid substances. To accurately translate between these units, one must consider how many mg in ml of the substance involved, as this property directly influences the factor for changing units.
The essential formula for converting milligrams to milliliters is given by:
volume ml = mass mg / density mg/ml
For instance, if a particular medication possesses a density of 1 mg/ml, then 100 mg of that medication would correspond to 100 ml. Grasping how many mg in ml is fundamental to ensuring accurate dosing and the safe administration of pharmaceuticals. This awareness is especially important considering recent research emphasizing the frequency of dosage mistakes, which can be reduced through a clear grasp of these transformations.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, two million Americans misused prescription pain relievers in 2017, underscoring the critical need for accurate dosing to prevent such misuse. Furthermore, a study by Shrestha R et al. examined 770 prescriptions and recorded categories of pharmaceutical mistakes, highlighting the significance of comprehending mg and ml transformations in practical situations.
Additionally, pharmacy error prevention strategies advocate for the standardization of internal processes and proper monitoring of drug interactions to enhance dosing accuracy, which is crucial for determining how many mg in ml, reinforcing the vital role of precise conversions in safety.
Practical Applications: Converting for Medication Dosage
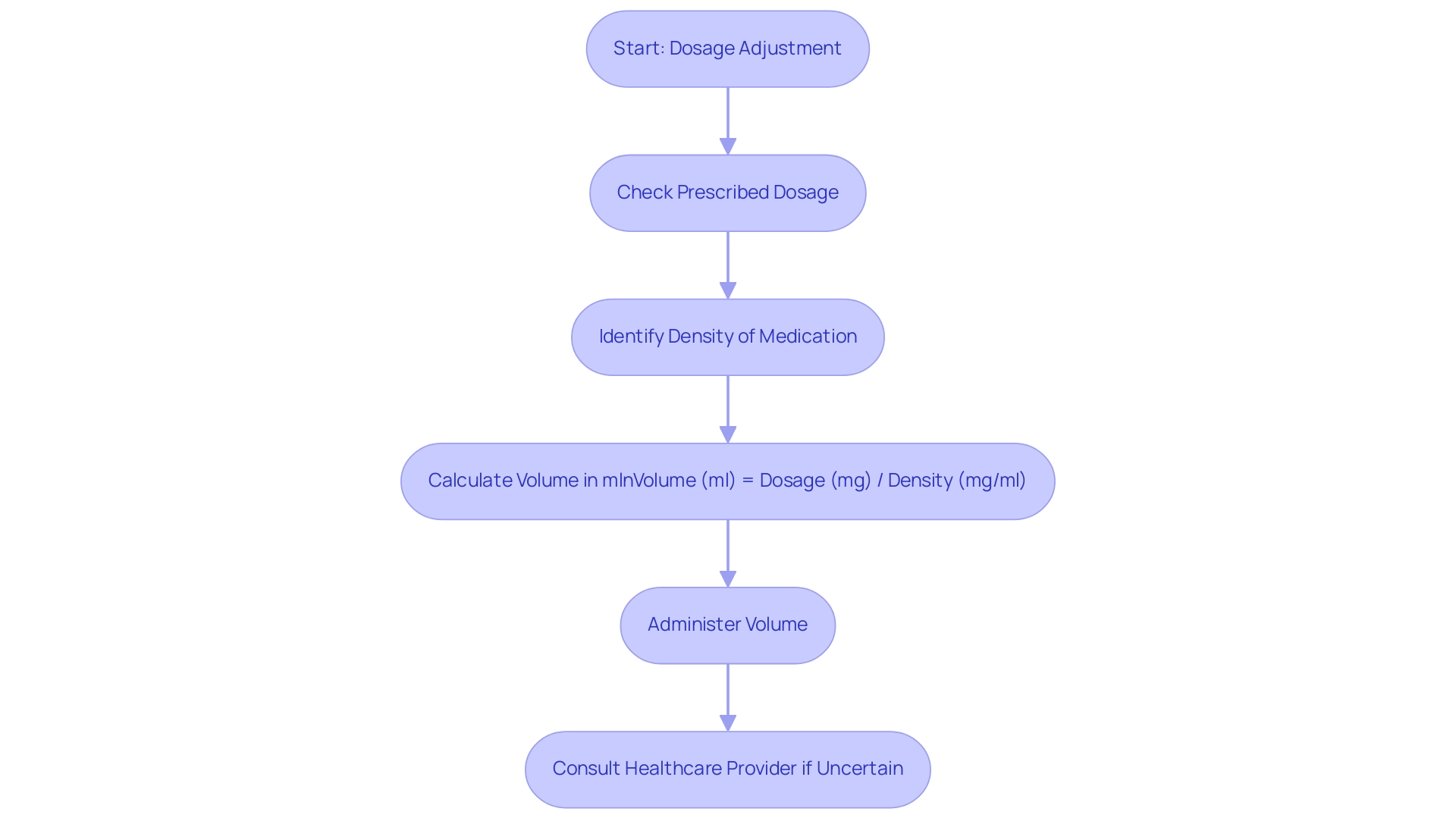
When adjusting dosage amounts, adherence to the prescribed instructions from healthcare professionals is paramount. For instance, consider a prescription that requires an individual to take 50 mg of a liquid remedy, which raises the question of how many mg in ml if the density is 2 mg/ml. The conversion to milliliters can be calculated as follows:
Volume (ml) = 50 mg / 2 mg/ml = 25 ml
In this case, the patient should administer 25 ml of the medication.
Precise conversions are crucial in preventing both underdosing and overdosing, which can have severe health repercussions. As per the FDA, medication mistakes are characterized as avoidable situations that can result in improper medication use or harm to individuals. Medication mistakes, particularly those linked to dosage miscalculations, have been shown to contribute significantly to patient harm; for instance, a study revealed that the number of interventions ranged from 64 in a study that included 60 patients to 843 in a population of 1271 patients.
Additionally, analgesics are recognized as the most dangerous category of drugs, with opiate overdoses comprising half of the incidents resulting in permanent harm, life-sustaining interventions, and even fatalities. A case study titled 'Data Analysis Methodology for Medication Errors' utilized a combination of quantitative and qualitative analyses to evaluate the characteristics and causal factors of numeracy errors in pharmaceutical administration, emphasizing the significance of precise dosage transformations. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or pharmacist if there is any uncertainty regarding dosage conversions.
This practice ensures both safety and efficacy in the delivery of drugs.
Common Mistakes in Converting Mg to Ml
A frequent oversight in medication dosing is the failure to check the density of the substance being measured. Given that different substances possess varying densities, assuming a standard density can result in erroneous conversions, potentially leading to adverse outcomes. Statistics indicate that medication-related mistakes contribute to 5% to 41.3% of all hospital admissions and account for 22% of readmissions after discharge.
Misinterpreting prescription dosages is another frequent mistake that can result in individuals consuming incorrect quantities of medicine. This underscores the necessity for meticulous verification in calculations, as even minor arithmetic mistakes can precipitate significant dosing issues. As emphasized in recent discoveries, medical mistakes are involved in 30% of injuries resulting from prescribed drugs within hospital settings.
For instance, the case study titled 'Consequences of Medication Errors' illustrates how a single miscalculation can lead to adverse drug events, new medical conditions, and even fatalities, impacting both individuals receiving care and healthcare providers. Additionally, five studies were at low risk of bias, thirteen at moderate risk, and six at high risk, highlighting the necessity for careful interpretation of treatment mistake statistics. To mitigate these risks, it is imperative to verify information through reliable sources or consult healthcare professionals when uncertainties arise.
As Lindson-Hawley N. noted, interventions aimed at reducing harm from medication errors are crucial in safeguarding patient safety, emphasizing the dire need for accuracy in medication administration.
Tools and Resources for Accurate Conversion
For precise transformations between milligrams and milliliters, it's important to know how many mg in ml, and a variety of online calculators and mobile applications are readily available. These tools can carry out automatic transformations, depending on how many mg in ml of the substance in question. For instance, to understand how many mg in ml, 400 mg of water, with a density of 1 g/mL, equates to 0.4 mL, reinforcing the importance of precision in these calculations.
Furthermore, to find out how many mg in ml for an ingredient with a density of 0.7 g/mL, transforming 500 milligrams using the formula results in approximately 0.7143 mL. Pharmacies frequently offer measurement charts that can be useful tools when assessing treatments, ensuring that patients can carry out these calculations with assurance. As Ethan Dederick, PhD, emphasizes, 'Sourcing tools from credible platforms is vital for precise drug transformations.'
For those who favor a more hands-on method, using a scientific calculator can improve accuracy in manual calculations. It is crucial to verify the results with a healthcare provider whenever possible, as this diligence not only fosters accuracy but also reduces potential prescription errors.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
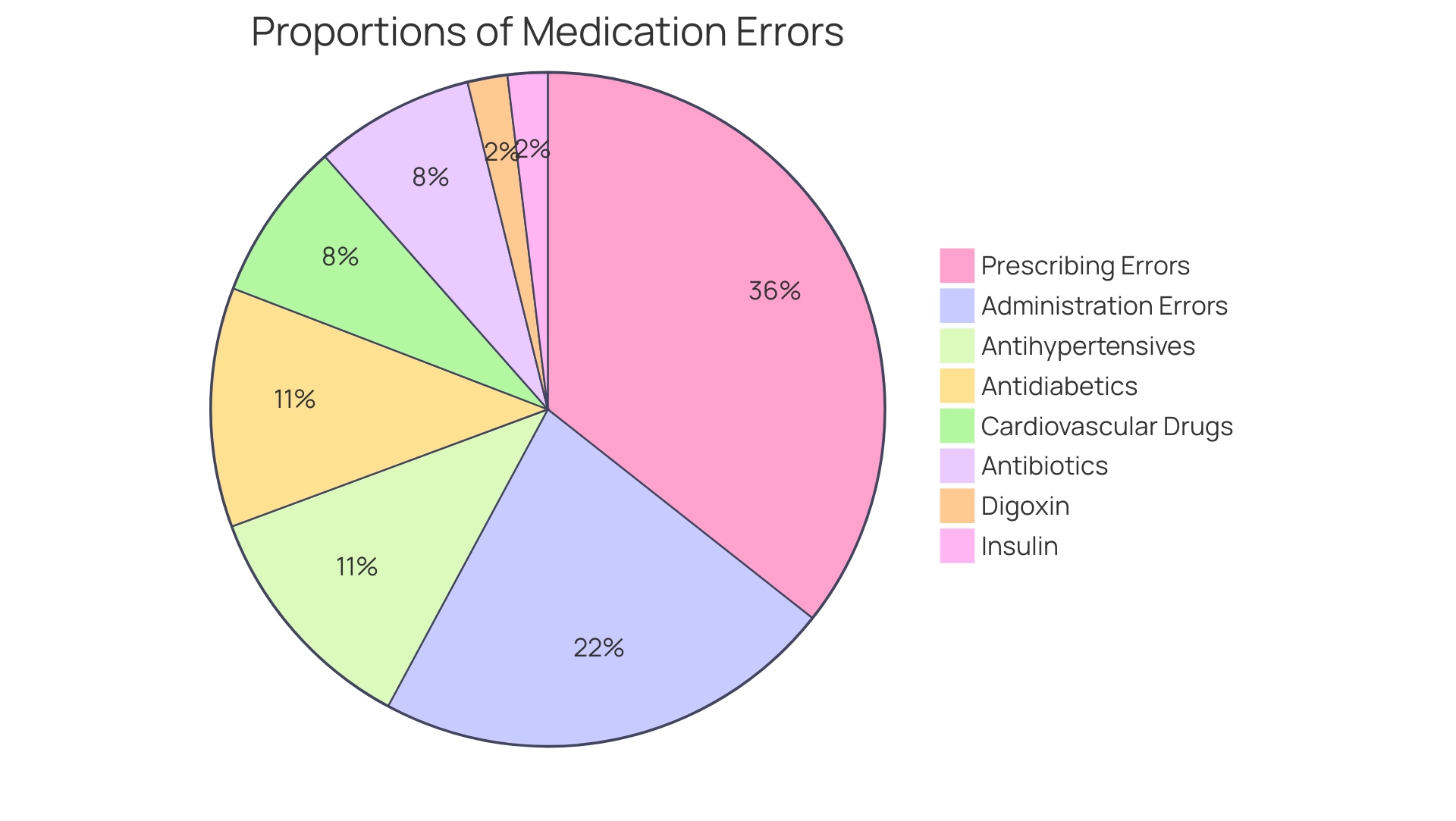
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional whenever there is uncertainty regarding how many mg in ml for dosage amounts or conversions. This is especially crucial in circumstances where the density of a drug is unknown, particularly when it comes to understanding how many mg in ml for interpreting complex prescriptions or if a patient's health status changes, potentially affecting dosage needs. The urgency of this consultation is emphasized by research showing that 29% of pharmaceutical mistakes take place during administration, with a notable share of these issues originating at the prescribing phase, which represents 46.5%.
Moreover, medical mistakes account for 30% of injuries caused by prescribed drugs in hospital settings. Common drug classes involved in these mistakes include:
- Antihypertensives
- Antidiabetics
- Cardiovascular drugs
- Antibiotics
- Digoxin
- Insulin
As Mohamed M M Abdel-Latif notes,
The poor knowledge about prescription errors emphasized the urgent necessity to adopt appropriate measures to raise awareness about prescription mistakes in Saudi hospitals.
Furthermore, a study on potentially inappropriate drugs in older adults emphasizes the need for careful evaluation of treatment suitability in this demographic. Therefore, individuals should never hesitate to ask questions. Healthcare providers are dedicated to ensuring that patients receive safe and effective treatments, and seeking their guidance is essential for maintaining medication safety.
Conclusion
Understanding the conversion between milligrams and milliliters is critical in the medical field, as it directly impacts the safe administration of medications. The article outlined the fundamental differences between these units, emphasizing that milligrams measure weight while milliliters measure volume. It highlighted the importance of density in converting these measurements accurately, underscoring that even minor errors can lead to significant health risks.
Practical applications of these conversions were explored, demonstrating how precise calculations prevent underdosing or overdosing. The statistics presented regarding medication errors serve as a stark reminder of the consequences of miscalculations. Healthcare professionals and patients must take care to adhere to prescribed dosages and consult resources or professionals when in doubt.
Common pitfalls such as assuming standard densities and misreading prescriptions were discussed, reinforcing the necessity for meticulous attention to detail. The article also introduced various tools and resources available to assist in accurate conversions, encouraging the use of reliable calculators and charts.
Ultimately, the importance of consulting healthcare professionals cannot be overstated. They play a vital role in ensuring accurate medication administration and addressing any uncertainties regarding dosages. By prioritizing precision in conversions and fostering open communication with healthcare providers, both patients and professionals can work together to enhance medication safety and effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do milligrams (mg) and milliliters (ml) represent in medicine?
Milligrams (mg) represent mass or weight, while milliliters (ml) indicate volume. Understanding the relationship between these units is crucial for accurate medication dosing.
How can one convert milligrams to milliliters?
The conversion formula is: volume (ml) = mass (mg) / density (mg/ml). This means you need to know the density of the substance to perform the conversion accurately.
Why is it important to know how many mg are in ml?
Knowing the mg to ml conversion is fundamental for ensuring accurate dosing and safe administration of medications, which helps prevent dosage mistakes.
What are the consequences of dosage mistakes?
Dosage mistakes can lead to underdosing or overdosing, which can have severe health repercussions. They are associated with improper medication use and can cause significant patient harm.
How prevalent was prescription pain reliever misuse in 2017?
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, two million Americans misused prescription pain relievers in 2017, highlighting the critical need for accurate dosing.
What did the study by Shrestha R et al. reveal about pharmaceutical mistakes?
The study examined 770 prescriptions and recorded categories of pharmaceutical mistakes, emphasizing the importance of understanding mg and ml transformations in practical situations.
What strategies are recommended to prevent pharmacy errors?
Pharmacy error prevention strategies include standardizing internal processes and properly monitoring drug interactions to enhance dosing accuracy.
How do you calculate the volume in milliliters for a specific dosage?
For example, if a prescription requires 50 mg of a liquid remedy with a density of 2 mg/ml, the calculation would be: Volume (ml) = 50 mg / 2 mg/ml = 25 ml. Therefore, the patient should administer 25 ml of the medication.
What should you do if you're uncertain about dosage conversions?
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or pharmacist if there is any uncertainty regarding dosage conversions to ensure safety and efficacy in drug delivery.



