Overview
The article titled "Understanding the DKA Protocol: A Comprehensive Tutorial for Effective Management" focuses on the effective management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), detailing the protocol's steps and the importance of early intervention. It emphasizes that adherence to the DKA protocol, which includes careful monitoring, fluid resuscitation, and insulin therapy, is crucial for preventing severe complications and improving patient outcomes, supported by case studies and statistics highlighting the economic burden of DKA and the benefits of education and community support in managing the condition.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) stands out as a formidable challenge, marked by its rapid onset and severe health implications. This critical condition, primarily linked to Type 1 diabetes but also affecting some individuals with Type 2 diabetes, demands urgent recognition and intervention to prevent dire consequences. With symptoms ranging from excessive thirst to abdominal pain, the stakes are high, and the need for effective management strategies is paramount.
As healthcare professionals and patients alike grapple with the complexities of DKA, understanding its diagnostic criteria, treatment protocols, and preventive measures becomes essential. This article delves into the intricacies of DKA, exploring:
- Clinical guidelines
- The role of healthcare providers
- Innovative solutions aimed at minimizing risks and enhancing patient outcomes
1. Name: What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
The DKA protocol addresses Diabetic Ketoacidosis, a critical complication in managing blood sugar, characterized by the body’s production of elevated ketone levels, which leads to metabolic acidosis. While DKA is predominantly associated with Type 1, the DKA protocol is also relevant for individuals with Type 2, particularly under certain stressors such as infections or poor glycemic control. Symptoms of DKA are often acute and include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- A distinctive fruity odor on the breath
The urgency of early symptom recognition cannot be overstated, as following the DKA protocol is crucial since DKA can escalate swiftly, resulting in severe health repercussions if not promptly addressed. Recent findings emphasize the necessity for careful observation of individuals with blood sugar issues, particularly those with comorbid conditions or weakened health. A notable statistic from 2024 indicates that the prevalence of the DKA protocol continues to be a pressing concern in diabetes care, with phosphate therapy showing no alteration in the duration of DKA in a study involving 44 individuals.
Additionally, the direct costs of DKA encompass medical expenses, while indirect costs include:
- Lost productivity due to absenteeism
- Reduced productivity
- Unemployment from chronic disability
- Premature mortality
Improved education on medication adherence and the ability to identify these symptoms is essential for adhering to the DKA protocol and preventing episodes. This is where T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource hub for individuals who have recently received a diagnosis.
T2DSolutions aims to provide comprehensive education and community support, assisting patients in understanding the DKA protocol and how to manage it. Case studies have demonstrated improved compliance and reduced incidence through effective management education for the condition. Furthermore, a study by Vitale et al. highlighted that in persons with type 2 diabetes taking SGLT2 inhibitors, the risk of euglycemic DKA may be further increased, especially in the context of COVID-19. By utilizing the resources available at T2DSolutions, newly diagnosed individuals can better equip themselves to manage their condition and adhere to the DKA protocol to prevent complications.
2. Name: Clinical Guidelines for DKA Management
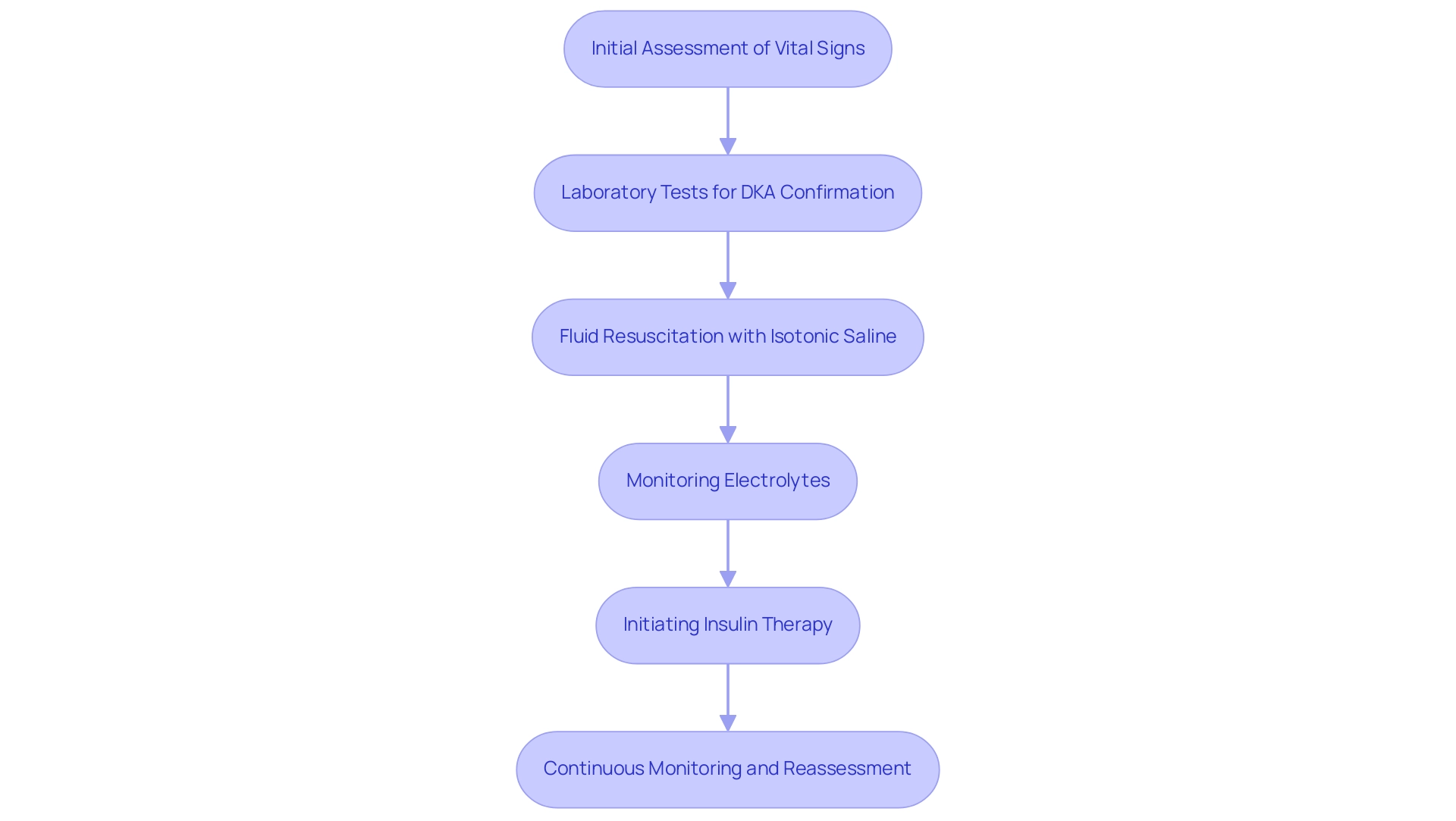
The clinical handling of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) includes several essential steps aimed at stabilizing the individual effectively. The initial phase involves a thorough assessment of the individual's vital signs and mental status, ensuring that any immediate threats to health are identified. Next, laboratory tests are performed to confirm the diagnosis of DKA, which is characterized by hyperglycemia, acidosis, and ketosis.
- Fluid resuscitation with isotonic saline is a foundational component of treatment, helping to restore intravascular volume and improve renal perfusion.
- Monitoring electrolytes, particularly potassium levels, is crucial during this process, as fluctuations can lead to severe complications.
- Following stabilization, insulin therapy is initiated as part of the DKA protocol to efficiently lower blood glucose and ketone levels, which is vital in reversing the metabolic derangements associated with DKA.
Continuous monitoring and reassessment, as outlined in the latest clinical guidelines for the DKA protocol management, are essential to gauge the effectiveness of the treatment and to make necessary adjustments to fluid and insulin infusion rates. Recent advancements in treatment protocols emphasize the importance of the DKA protocol in enhancing clinical outcomes and addressing the substantial economic burden of avoidable hospitalizations due to DKA, which amounts to approximately $2.8 billion annually in the U.S. Notably, the first successful case of DKA treated with insulin was reported by Banting and Best in a 14-year-old boy who presented with a blood glucose of 580 mg/dL and strongly positive urinary ketones at the Toronto General Hospital in 1923.
Moreover, implementing an interprofessional team approach that includes endocrinologists, intensivists, nurses, and social workers can further enhance outcomes by addressing socioeconomic factors that may contribute to non-compliance with treatment protocols.
3. Name: Diagnostic Criteria for Identifying DKA
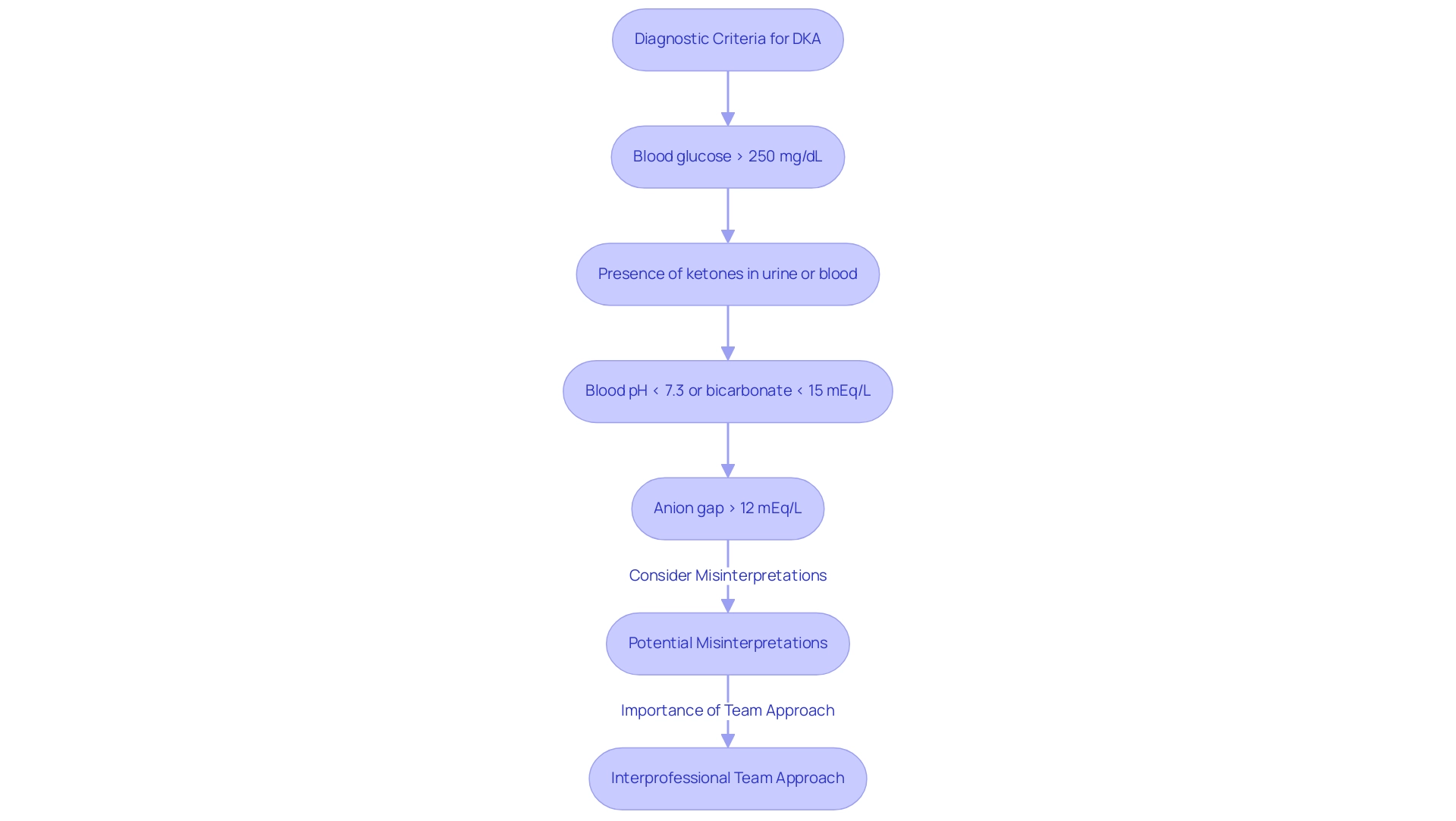
The DKA protocol for diagnosing diabetic ketoacidosis requires careful evaluation based on specific clinical criteria. Healthcare professionals typically assess the following indicators:
- Blood glucose levels exceeding 250 mg/dL
- The presence of ketones in either urine or blood
- Arterial blood pH values falling below 7.3 or bicarbonate levels lower than 15 mEq/L
- An anion gap greater than 12 mEq/L
These diagnostic markers are essential for distinguishing DKA from other diabetic emergencies, facilitating timely and effective intervention.
Misinterpretation can occur, particularly in cases where patients present with leukocytosis or altered serum sodium levels due to hyperglycemia, emphasizing the need for clinicians to differentiate DKA from conditions such as alcoholic ketoacidosis. As Donald W Rucker, MD, emphasizes, recognizing these criteria is critical for suitable oversight. An interprofessional team approach is crucial for effective care under the DKA protocol, as it ensures comprehensive management involving various healthcare professionals.
For those recently diagnosed with the condition, an initial insulin dose of 0.6 unit/kg/day is generally adequate, offering significant context for individuals. Additionally, a case study on common laboratory pitfalls in DKA diagnosis highlights the significance of accurate interpretation of lab results, reinforcing the need for clinicians to differentiate between DKA and other conditions. Recent educational initiatives in diabetes clinics have demonstrated a significant reduction in DKA occurrences, underscoring the importance of self-management education in reinforcing these diagnostic strategies.
Such proactive measures can greatly enhance outcomes by ensuring early recognition and treatment according to the DKA protocol.
4. Name: Treatment Strategies for Effective DKA Management
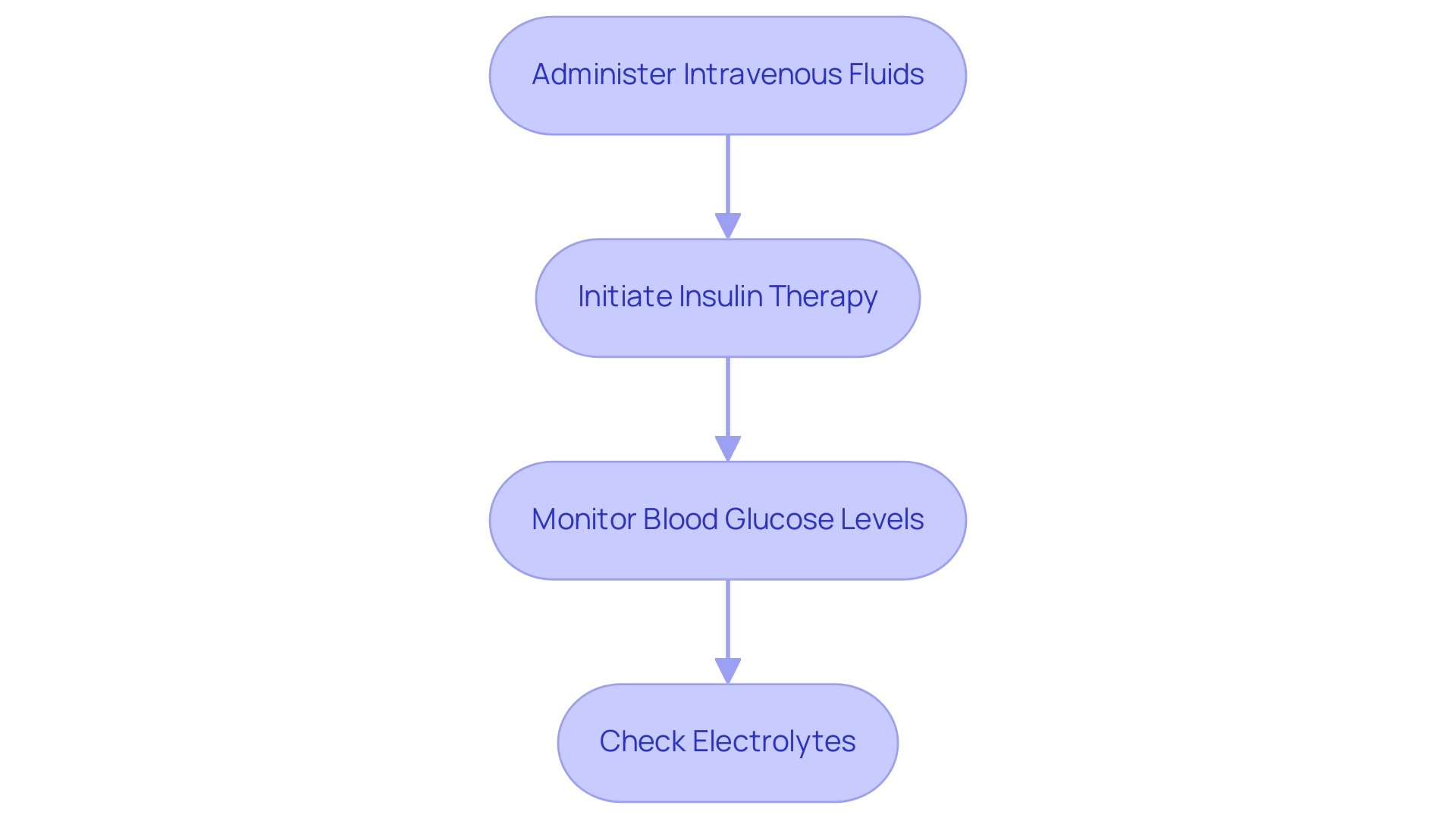
Effective oversight of the DKA protocol for diabetic ketoacidosis requires a systematic approach that encompasses several critical steps:
- Administer intravenous fluids to rehydrate the patient and restore electrolyte balance, starting with isotonic saline; this helps to mitigate dehydration and supports overall metabolic function.
- Initiate insulin therapy promptly to decrease blood glucose levels and halt ketone production. Continuous infusion of insulin is preferred to maintain stable glucose control.
- Closely monitor blood glucose levels and adjust the insulin dosage as necessary to ensure safe and effective control of hyperglycemia.
- Regularly check electrolytes, with particular attention to potassium levels, due to the risk of hypokalemia as insulin drives potassium back into cells.
Azza B. El-Remessy emphasizes,
Detection of ketonemia is the key for DKA risk mitigation along with consumption of oral carbohydrates, fluids, and insulin for successful treatment.
This structured approach promotes a gradual and effective correction of the metabolic state while minimizing complications. Significantly, a retrospective analysis of individuals treated for DKA or HHS found that those managed according to the DKA protocol had a shorter mean duration of time to resolution, underscoring the effectiveness of this systematic method. Additionally, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the overlap of symptoms between COVID-19 and DKA has raised concerns about care, as emphasized in the case study titled 'Impact of COVID-19 on DKA Care.'
This emphasizes the necessity for vigilant monitoring and tailored care strategies in individuals with diabetes during such challenging times. Future studies are essential to refine the DKA protocol for treatment, especially for those on SGLT2 inhibitors and in special populations.
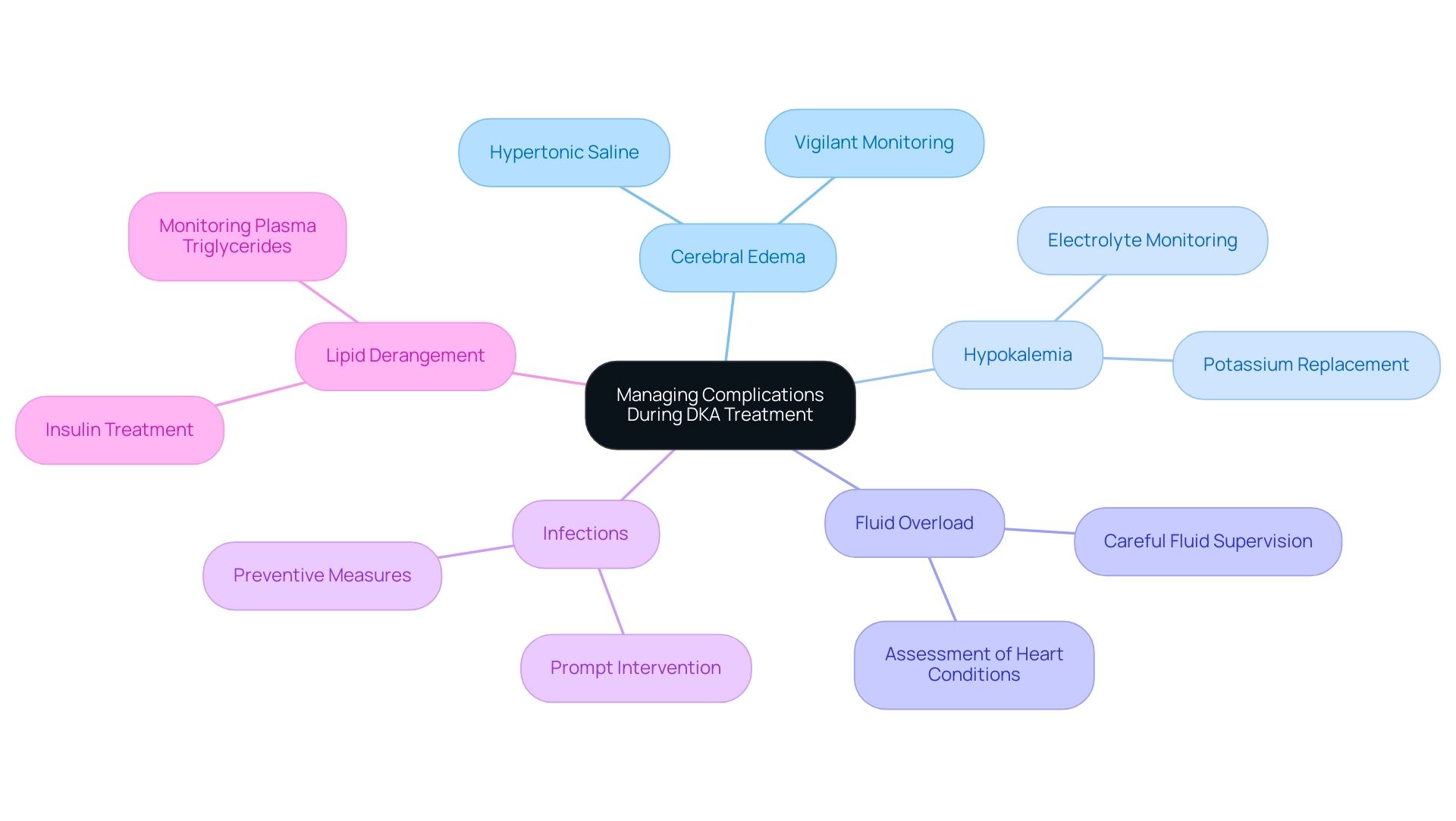
5. Name: Managing Complications During DKA Treatment
During the treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA), several complications can arise that necessitate vigilant monitoring and immediate intervention. Among these, cerebral edema is particularly concerning, especially in young individuals. This condition may require hypertonic saline treatment to mitigate pressure increases in the brain.
Additionally, shifts in electrolytes during treatment can lead to hypokalemia, which poses significant risks if not promptly addressed. Fluid overload is another issue that can impact individuals with pre-existing heart conditions, highlighting the importance of careful fluid supervision. Furthermore, infections can exacerbate the DKA state, complicating recovery.
The typical yearly rise in DKA hospitalization rates from 2009 to 2014 was 6.3%, emphasizing the increasing necessity for strict handling protocols. Establishing a uniform DKA protocol for DKA is crucial for healthcare workers to ensure consistent and effective care. Furthermore, lipid derangement is common in DKA, and mean plasma triglyceride levels significantly decrease after insulin treatment, which is vital information for managing metabolic changes during treatment.
As Jyotsnav Joynauth noted, timely and improved protocols related to the care of DKA individuals as well as admitting less severe DKA cases due to a lower threshold in admission criteria could be one of the causes of shorter stays observed in 2017. Furthermore, educating individuals on managing diabetes-related issues, including identifying symptoms and grasping treatment alternatives, is crucial for avoiding complications such as DKA. Therefore, continuous monitoring and prompt adjustments to the DKA protocol are essential for effectively managing these complications and enhancing outcomes.
6. Name: Preventive Measures to Avoid DKA
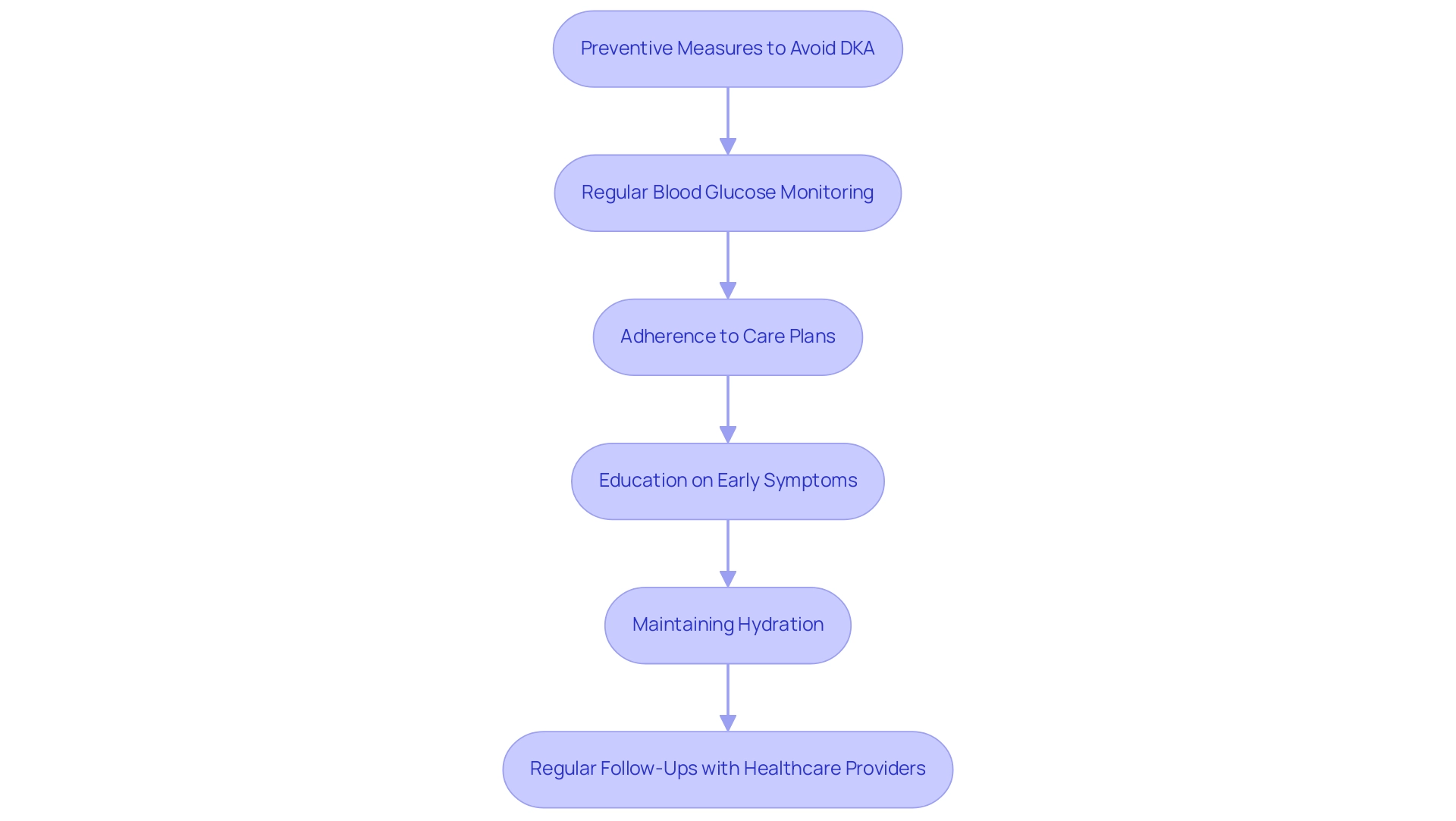
Effective prevention of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is essential for individuals managing their condition, and T2D Solutions is dedicated to empowering people through education and community support regarding the DKA protocol. Key strategies include:
- Regular blood glucose monitoring, essential for early detection and intervention in hyperglycemia, significantly reducing the risk of DKA protocol.
- Adherence to prescribed care plans, including timely medication and insulin regimens, which ensures that blood glucose levels remain stable.
- Education on recognizing early symptoms of DKA protocol, empowering individuals and caregivers to seek prompt medical assistance when necessary.
- Maintaining hydration, particularly during episodes of illness or stress, to prevent fluid deficits that can accompany DKA protocol, potentially reaching up to 10-15% of body weight.
- Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment plans based on individual needs.
As noted by Guillermo E. Umpierrez, strategies such as early screening, close follow-up of high-risk children, and education of parents and communities have been successful in the prevention of diabetes by implementing the DKA protocol at the onset.
Furthermore, innovative approaches like T2D Solutions' Novel Interventions in Children’s Healthcare program have utilized telemedicine to enhance communication, which has contributed to a decrease in readmissions related to the DKA protocol among adolescents. T2D Solutions also provides educational workshops and online materials to assist individuals in comprehending DKA care more effectively. Additionally, community support initiatives, such as peer support groups, provide newly diagnosed individuals with the opportunity to connect and share experiences.
Effective handling of DKA includes fluid resuscitation and careful monitoring of potassium levels to mitigate the risk of hypokalemia. Through these comprehensive preventive measures, including educational resources and community support, T2D Solutions aims to ensure better health outcomes and minimize the risk of DKA protocol for individuals who are newly diagnosed.
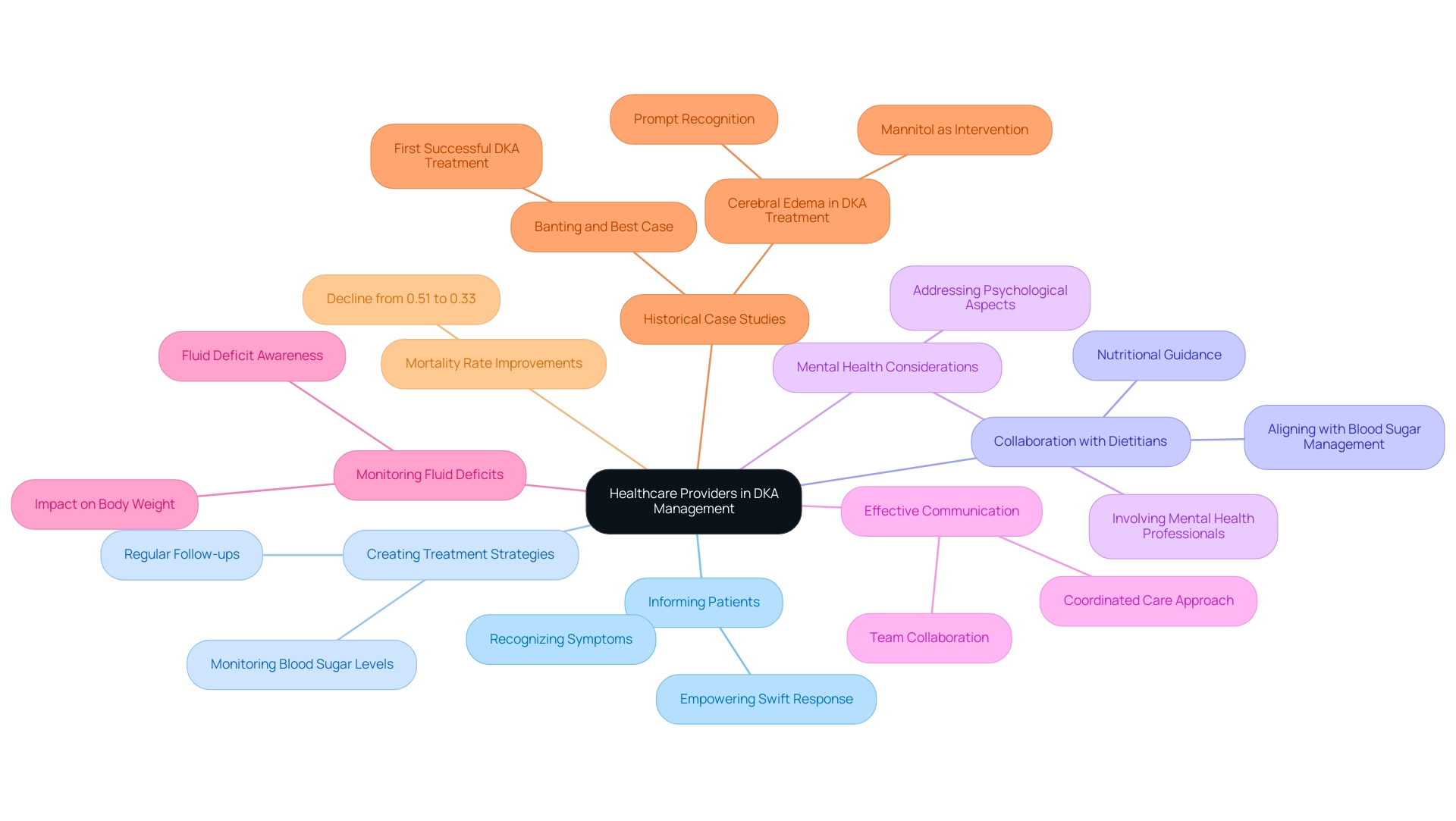
7. Name: The Role of Healthcare Providers in DKA Management
Healthcare providers are indispensable in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis through the DKA protocol and several key actions. Firstly, they inform individuals about the early signs and symptoms of DKA, empowering them to recognize and respond swiftly to potential crises. Secondly, creating a thorough treatment strategy is essential, which involves regular monitoring and follow-ups to ensure optimal control of blood sugar levels.
Notably, about 10% of individuals with type 1 T1D on SGLT2 inhibitors develop ketosis, with 5% requiring hospitalization under the DKA protocol, underscoring the importance of vigilant care. Working together with dietitians is also crucial, as they offer nutritional guidance that aligns with managing blood sugar levels, thereby promoting better health outcomes. Furthermore, addressing the psychological aspects of living with diabetes is vital; thus, involving mental health professionals in care plans can significantly enhance individual well-being.
Effective communication within the healthcare team ensures a coordinated approach to care, which is critical for successful treatment outcomes. Fluid deficits in individuals following the DKA protocol can reach up to 10-15% of body weight, highlighting the need for diligent monitoring. As evidenced by a historical case reported by Banting and Best:
- "The first successful case of DKA treated with insulin was reported by Banting and Best in a 14 year old boy who presented with a blood glucose of 580 mg/dL and strongly positive urinary ketones at the Toronto General Hospital in 1923," advancements in the DKA protocol have proven effective.
Recent statistics indicate a decline in mortality rates for individuals with diabetes, as shown by the DKA protocol, from 0.51% in 2003 to 0.33% in 2014, showcasing the positive impact of these collaborative efforts. Additionally, case studies reveal that prompt recognition and treatment of complications such as cerebral edema—an uncommon but serious concern—are essential for safety, with mannitol being a recommended intervention. By fostering a collaborative and well-informed approach, healthcare providers can significantly enhance patient outcomes and encourage better self-management practices.
Conclusion
The complexities surrounding diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) highlight the urgent need for comprehensive management strategies in diabetes care. Understanding DKA's critical nature, characterized by elevated ketone levels and metabolic acidosis, is essential for both healthcare providers and patients. Through a thorough examination of clinical guidelines, diagnostic criteria, and treatment protocols, it becomes clear that timely recognition and intervention are vital in mitigating the severe health risks associated with DKA.
Effective management requires a systematic approach that includes:
- Fluid resuscitation
- Insulin therapy
- Continuous monitoring of electrolytes
Such measures not only stabilize patients but also address the significant economic burden of DKA-related hospitalizations. With an emphasis on prevention through education and community support, resources like T2DSolutions play a crucial role in empowering patients to recognize early symptoms and adhere to treatment plans.
Furthermore, the collaborative efforts of healthcare providers—encompassing education, psychological support, and dietary management—are instrumental in improving patient outcomes. By fostering a coordinated approach and emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring and follow-ups, healthcare teams can significantly reduce the incidence of DKA and enhance the quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
In conclusion, the battle against DKA is multifaceted, requiring vigilance, education, and a proactive stance from both patients and healthcare professionals. Through informed strategies and community resources, it is possible to minimize the risks associated with DKA and ensure better health outcomes for those affected by diabetes.



