Overview
Understanding the etiology of type 2 diabetes can feel overwhelming, but you're not alone in this journey. This condition is primarily characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency, influenced by various factors including genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices.
Obesity, sedentary behavior, poor diet, and hormonal changes all play significant roles in the development of type 2 diabetes. It’s understandable to feel concerned about these influences, but recognizing them is the first step toward better health.
We emphasize the importance of targeted prevention and management strategies that can improve health outcomes. Remember, reaching out for support and resources can make a significant difference in your journey. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
In a world where chronic diseases are increasingly prevalent, Type 2 Diabetes emerges as a significant concern due to its complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This condition, marked by insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels, can lead to serious health risks, including cardiovascular complications and nerve damage. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by this diagnosis, but understanding the etiology of Type 2 Diabetes is essential for effective management and prevention. This condition encompasses a range of contributors, from obesity to sedentary habits, and recognizing these factors is the first step toward better health.
As T2DSolutions steps forward as a crucial resource for education and community support, it aims to empower individuals with knowledge and strategies to navigate the challenges of this prevalent condition. You're not alone in this journey; there are people and resources ready to support you. By examining the factors influencing Type 2 Diabetes, including lifestyle modifications and the vital role of insulin resistance, the path to improved health becomes clearer. Together, we can foster a supportive community that encourages open dialogue and shared experiences, helping you feel heard and understood.
Define Type 2 Diabetes Etiology
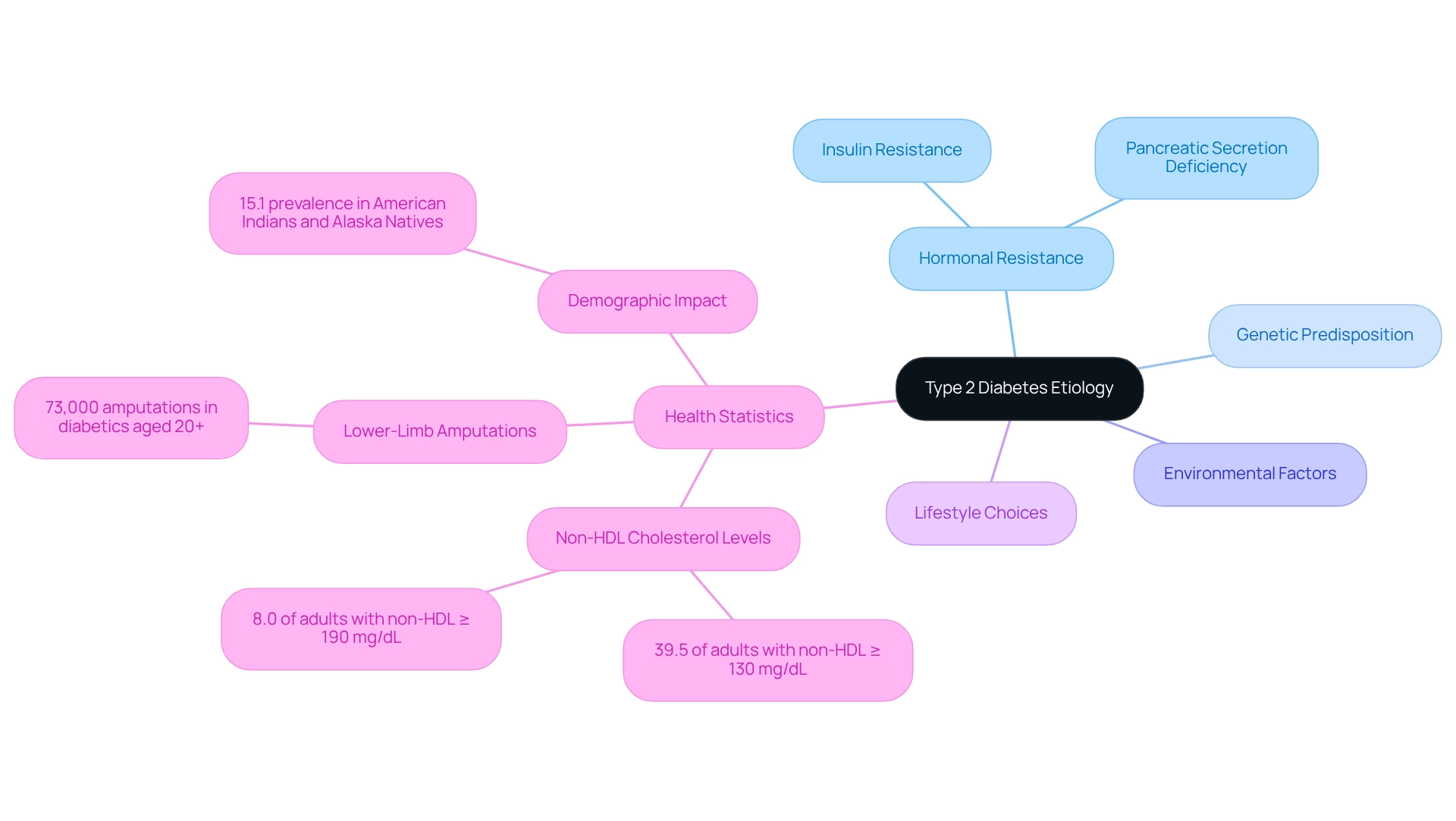
The etiology of type 2 diabetes involves a complex interplay of causes and mechanisms that contribute to its onset. At the heart of its development is resistance to the hormone, where the body's cells struggle to respond adequately, combined with a relative deficiency in secretion from the pancreas. This combination results in elevated blood glucose levels, a hallmark of the disease, which reflects the type 2 diabetes etiology shaped by genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices.
It’s concerning that approximately 39.5% of adults with this condition have a non-HDL cholesterol level of 130 mg/dL or higher, indicating a significant risk for cardiovascular disease, often linked to insulin resistance. Furthermore, recent research highlights that 8.0% of adults diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes have a non-HDL level of 190 mg/dL or higher, underscoring the importance of monitoring lipid profiles in managing this illness. Additionally, around 73,000 lower-limb amputations were performed in diabetics aged 20 and above, illustrating the serious complications that can arise from poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
At T2DSolutions, we understand how vital education and assistance are in managing this condition. Case studies on blood sugar management strategies reveal that effective lifestyle changes and medical care can significantly enhance outcomes for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. One noteworthy case study emphasizes that with proper management, individuals can lead full and active lives. Practical examples illustrate how insulin resistance manifests in daily life, affecting energy levels and overall well-being, as ongoing studies continue to explore the type 2 diabetes etiology, shedding light on the interaction between genetic elements and environmental factors.
This investigation is crucial for developing targeted prevention and management strategies, ultimately empowering individuals to take control of their health. Importantly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that American Indians and Alaska Natives experience a prevalence of 15.1 percent for this condition, highlighting its demographic impact. At T2DSolutions, we are committed to providing resources and community support to help individuals navigate these challenges effectively. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Explore Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Explore Causes of T2
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for diabetes education and community support, it's essential to understand the causes of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) for those who have recently received a diagnosis. The type 2 diabetes etiology is complex, shaped by a blend of genetic predispositions and environmental influences. Let’s take a closer look at some key contributors:
-
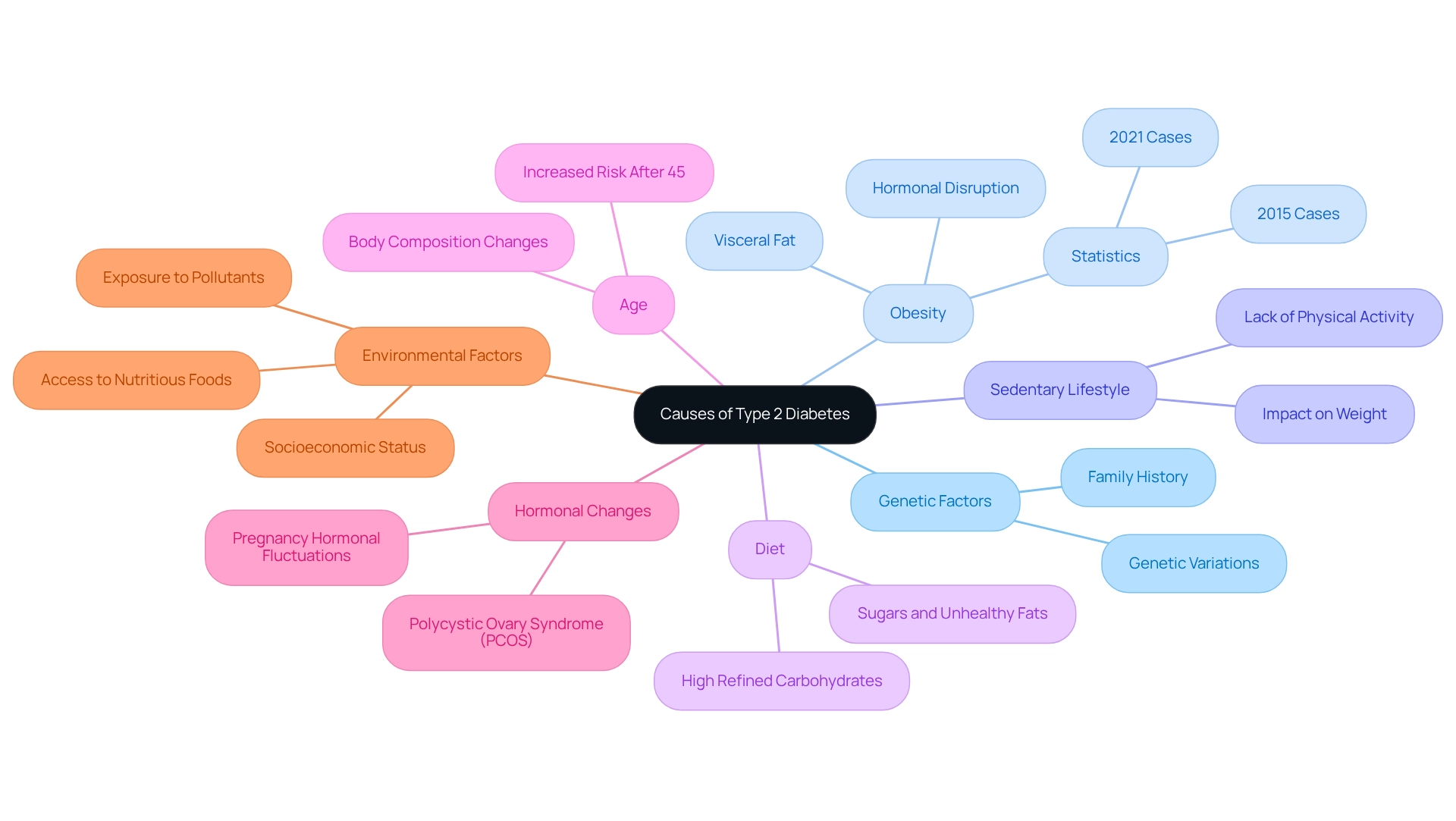
Genetic Factors: If you have a family history of Type 2 Diabetes, your risk may be significantly higher. Certain genetic variations can affect your body's sensitivity to glucose and its ability to secrete it, underscoring the hereditary nature of this condition.
-
Obesity: Carrying excess body weight, particularly visceral fat, is a critical risk factor. Adipose tissue releases hormones that can disrupt glucose regulation, leading to insulin resistance. This accumulation can trigger increased glucose production, reduced glucose elimination, and compromised hormone secretion, which are hallmarks of diabetes. Recent studies show a concerning link between obesity and the rising prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes, with the International Diabetes Federation noting an increase from 415 million diagnosed cases in 2015 to approximately 573 million in 2021.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: A lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain and exacerbate glucose resistance. Regular exercise is vital for maintaining a healthy weight and improving insulin sensitivity.
-
Diet: Consuming diets high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats can promote obesity and metabolic dysfunction, raising the risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Your nutritional choices are pivotal in preventing this condition.
-
Age: The likelihood of developing Type 2 Diabetes increases with age, especially after 45. This rise can be attributed to factors such as decreased physical activity and changes in body composition.
-
Hormonal Changes: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can heighten the risk of glucose intolerance, emphasizing the importance of hormonal health in metabolic conditions.
-
Environmental Factors: Socioeconomic status, access to nutritious foods, and exposure to environmental pollutants can greatly influence the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes. Systematic reviews provide evidence-based insights into the multifaceted causes of type 2 diabetes etiology and effective prevention strategies, making it vital to understand these various causes for creating tailored interventions that address individual needs. T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering support and resources for managing this condition. We emphasize the urgent need for discovering multi-targeted compounds that can effectively treat both obesity and Type 2 Diabetes, given their close relationship. As highlighted in JAMA Surgery, five-year data indicates that 36% of patients achieved complete remission and 28% achieved partial remission, compared to only 1.2% and 1.6% of individuals treated with medical therapy alone. You're not alone in this journey; stay tuned for upcoming resources from T2DSolutions that will further assist you in diabetes management.
The Role of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes
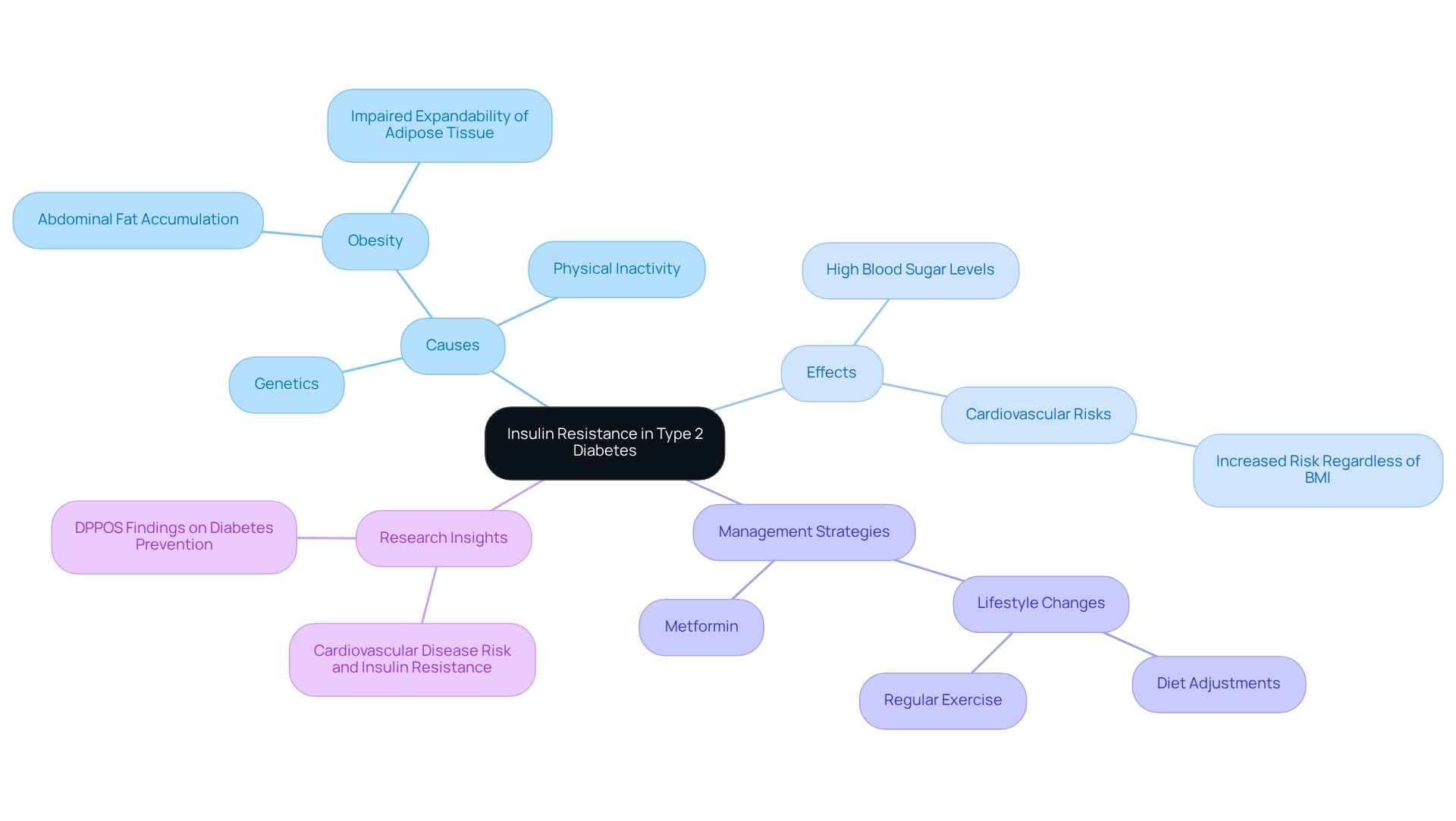
At T2DSolutions, we genuinely care about providing valuable resources for those affected by Type 2 Diabetes. Understanding glucose resistance, a key characteristic of type 2 diabetes etiology, is essential. This resistance occurs when the body's cells become less sensitive to insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. As a result, glucose struggles to enter cells for energy, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. In response, the pancreas attempts to compensate by producing more insulin, but this increased demand can overwhelm it over time, resulting in consistently high blood sugar levels.
Several factors contribute to the progression of metabolic resistance, with obesity—especially the accumulation of abdominal fat—being a significant contributor to the type 2 diabetes etiology. Physical inactivity and genetic predisposition also play vital roles. Recent studies underline the concerning connection between obesity and blood sugar resistance, revealing that individuals with obesity face a heightened risk of developing conditions related to type 2 diabetes etiology, which can further complicate Type 2 Diabetes. As Silvia Corvera insightfully notes, "Failure to expand subcutaneous adipose tissue in parallel with chronic excess calorie consumption may result from impaired expandability of its extracellular matrix and capillary network, and result in ectopic lipid accumulation."
At T2DSolutions, we emphasize the importance of addressing insulin resistance as it relates to type 2 diabetes etiology for effective management and potential reversal of Type 2 Diabetes. Making lifestyle changes—like adjusting your diet and incorporating regular exercise—can lead to encouraging outcomes in improving glucose sensitivity. Studies have shown that individuals can prevent or delay the onset of Type 2 Diabetes for at least 15 years through these lifestyle modifications or the use of metformin. Additionally, a comprehensive approach to managing metabolic health is crucial, as glucose resistance significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, regardless of body mass index (BMI). A study titled 'Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Insulin Resistance' highlights how insulin resistance, regardless of BMI, substantially raises the risk of cardiovascular disease, underscoring the need for a thorough strategy in managing metabolic health.
In summary, understanding glucose resistance and its impact on blood sugar regulation is vital for those affected by the type 2 diabetes etiology. By making specific lifestyle adjustments, you can enhance your sensitivity to glucose and improve your overall health outcomes. It's also important to monitor triglyceride levels, as elevated levels of 150 mg/dL or more indicate hypertriglyceridemia, a significant factor in metabolic health. We encourage you to explore the resources available at T2DSolutions for further support in managing insulin resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Type 2 Diabetes Development
Lifestyle factors play a vital role in both the type 2 diabetes etiology and the management of the condition. Here are some key modifications that can make a significant difference:
-
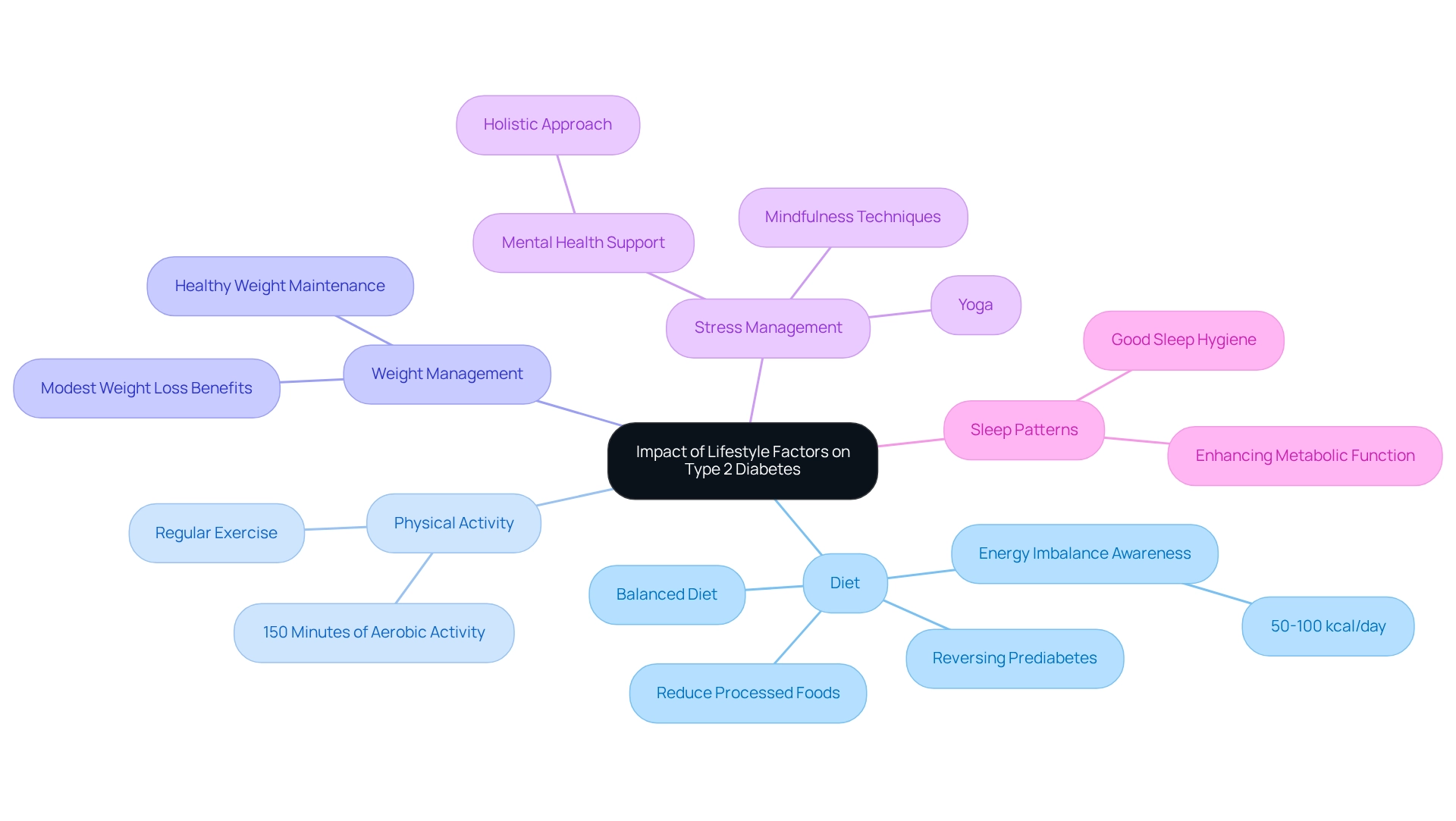
Diet: Embracing a balanced diet that focuses on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and improving insulin sensitivity. Reducing processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats can further support these goals. It's important to recognize that dietary choices significantly impact the etiology of type 2 diabetes and its management. Even a habitual energy imbalance of just 50-100 kcal per day can lead to gradual weight gain, a known risk factor for diabetes. Remarkably, individuals can reverse prediabetes through dietary changes, which may provide insights into type 2 diabetes etiology and potentially prevent or delay its onset. At T2DSolutions, we offer resources and guidance to help you make informed dietary choices.
-
Physical Activity: Regular exercise is crucial for improving insulin sensitivity and supporting weight management. The American Health Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week. Following these guidelines can lead to better blood sugar control and overall health outcomes. T2DSolutions provides guidance on appropriate exercise programs tailored for those managing blood sugar levels.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is critical. Even modest weight loss can significantly reduce the risk related to type 2 diabetes etiology. Many individuals find that effective weight management through lifestyle changes leads to substantial improvements in their blood sugar control. T2DSolutions is here to assist you with weight management strategies and support.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and regular physical activity are effective ways to manage stress, contributing to improved overall health and better blood sugar management. It's essential to acknowledge the mental health challenges linked to managing blood sugar conditions, and incorporating mental health support can create a more holistic approach to care. T2DSolutions emphasizes the importance of mental well-being in managing blood sugar conditions.
-
Poor sleep patterns are associated with insulin resistance and contribute to the type 2 diabetes etiology. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene can enhance metabolic function and overall health, making it a vital part of diabetes management. T2DSolutions offers tips and resources to help improve your sleep quality.
As Mary Tyler Moore poignantly stated, "This condition is an all-too-personal time bomb which can go off today, tomorrow, next year, or 10 years from now – a time bomb affecting millions like me and the children here today." By making these lifestyle adjustments, you can not only help prevent Type 2 Diabetes but also assist those already diagnosed in managing their condition more effectively. Remember, T2DSolutions is here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding the Long-Term Consequences of Type 2 Diabetes
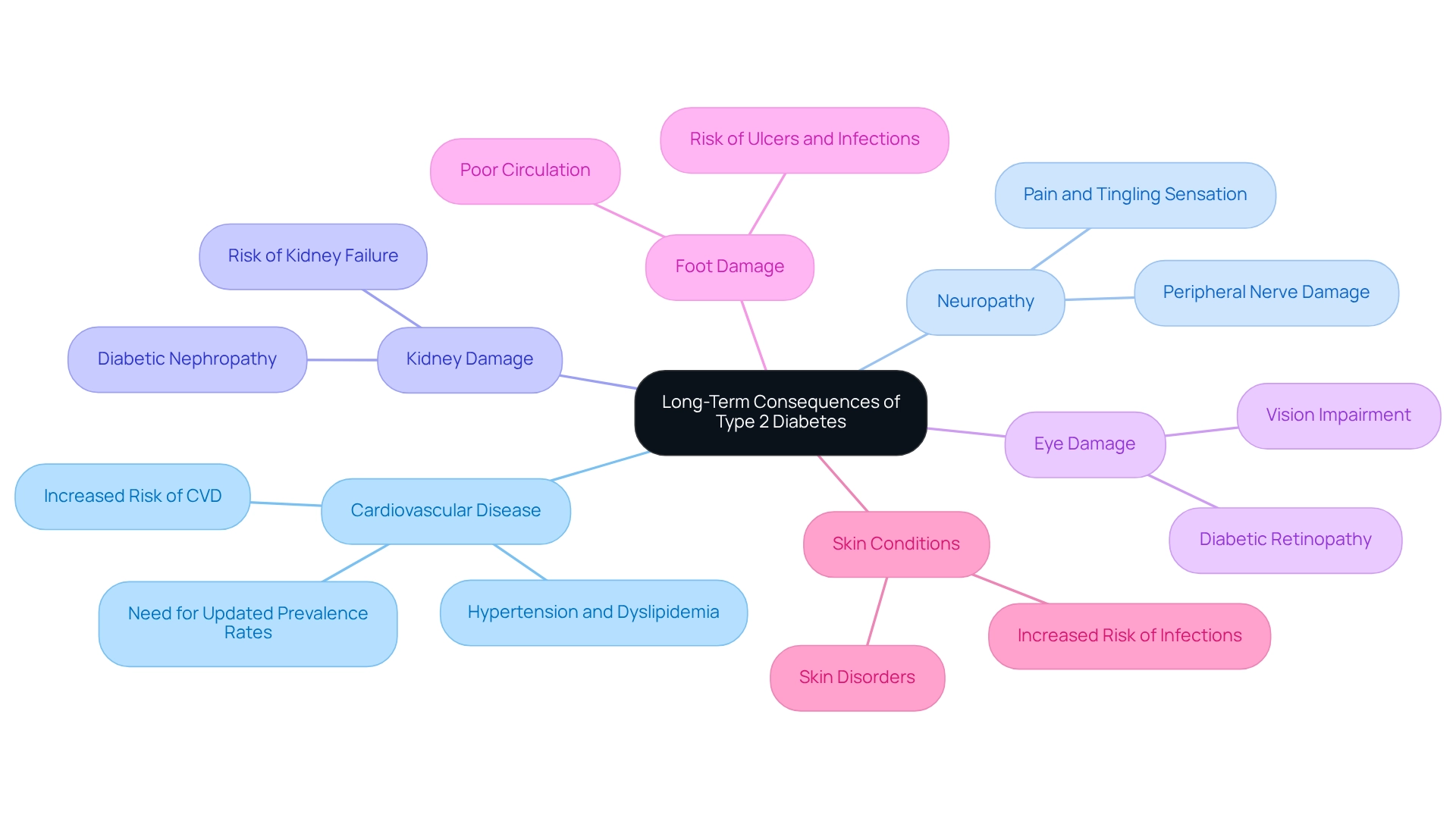
Uncontrolled form 2 of the condition, related to type 2 diabetes etiology, can lead to numerous severe health issues, significantly impacting your quality of life. Understanding these consequences is essential, and we’re here to support you through this journey. Here are some key consequences to consider:
-
Cardiovascular Disease: If you have insulin resistance, you may face a heightened risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Studies show that CVD occurs more frequently in diabetic patients compared to those without diabetes. Recent evaluations stress the need for updated prevalence rates of CVD among individuals with insulin resistance, which can help guide clinical and policy-level decisions. Factors like hypertension and dyslipidemia add to this risk, highlighting the importance of careful management.
-
Neuropathy: Chronic high blood sugar levels can damage peripheral nerves, leading to peripheral neuropathy. This condition can cause pain, tingling, or loss of sensation in your extremities, which may affect your daily activities and overall well-being.
-
Kidney Damage: Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication that can hinder your kidneys' ability to filter waste effectively. This condition may progress to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or transplantation in advanced stages.
-
Eye Damage: Diabetic retinopathy, which affects the blood vessels in the retina, can result in significant vision impairment or even blindness. Regular eye examinations are crucial for early detection and intervention, so don’t hesitate to schedule them.
-
Foot Damage: Poor circulation and nerve damage can lead to foot ulcers and infections. If left untreated, these issues may result in severe complications, including amputation. It’s important to take care of your feet and seek help if you notice any problems.
-
Skin Conditions: High blood sugar levels increase the risk of various skin infections and disorders, complicating overall health management.
Recent research highlights the intricate relationship between age and cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. While some studies indicate a significant connection between increasing age and a higher prevalence of CVD, others present mixed results. This suggests that age may be a complex factor influencing cardiovascular risk in T2DM. Understanding these long-term consequences underscores the critical importance of effective diabetes management and lifestyle modifications to reduce risks and enhance health outcomes, particularly in the context of type 2 diabetes etiology.
For more information on managing these complications and accessing educational resources, visit T2DSolutions, your comprehensive hub for Type 2 Diabetes education and support. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Type 2 Diabetes is a multifaceted condition influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by this diagnosis, but recognizing its etiology, particularly the role of insulin resistance, is crucial for effective management and prevention. Key contributors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and dietary choices play significant roles in the onset of the disease. This highlights the need for targeted lifestyle modifications that can make a real difference.
The serious long-term health consequences associated with unmanaged Type 2 Diabetes, including cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage, underscore the urgency of proactive management strategies. You're not alone in this journey; T2DSolutions stands as a vital resource, providing education and community support to empower individuals diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes. By fostering a supportive environment and offering practical strategies for lifestyle changes, T2DSolutions aims to help you improve your health outcomes and navigate the challenges posed by this prevalent condition.
Through informed dietary choices, regular physical activity, and stress management, individuals can enhance their insulin sensitivity and overall well-being. Remember, every step you take towards better health counts.
Ultimately, the journey toward better health in the context of Type 2 Diabetes requires a comprehensive approach. By recognizing the interconnectedness of various lifestyle factors and their impact on disease management, you can take meaningful steps towards preventing complications and leading healthier lives. With the right resources and support, it is possible to take control of your health and mitigate the risks associated with Type 2 Diabetes. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D)?
The main causes of Type 2 Diabetes include genetic factors, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, diet, age, hormonal changes, and environmental factors.
How does genetic predisposition affect the risk of developing T2D?
A family history of Type 2 Diabetes can significantly increase an individual's risk due to certain genetic variations that affect glucose sensitivity and secretion.
What role does obesity play in the development of T2D?
Obesity, particularly the accumulation of visceral fat, disrupts glucose regulation and leads to insulin resistance, which are critical risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes.
Why is a sedentary lifestyle considered a risk factor for T2D?
A lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain and worsen glucose resistance, making regular exercise essential for maintaining a healthy weight and improving insulin sensitivity.
How does diet influence the risk of developing T2D?
Diets high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to obesity and metabolic dysfunction, increasing the risk of Type 2 Diabetes.
At what age does the risk for developing T2D typically increase?
The likelihood of developing Type 2 Diabetes increases with age, particularly after the age of 45.
What hormonal changes can increase the risk of T2D?
Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy can heighten the risk of glucose intolerance.
How do environmental factors contribute to the risk of T2D?
Socioeconomic status, access to nutritious foods, and exposure to environmental pollutants can significantly influence the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes.
What percentage of adults with T2D have elevated non-HDL cholesterol levels?
Approximately 39.5% of adults with Type 2 Diabetes have a non-HDL cholesterol level of 130 mg/dL or higher, indicating a significant risk for cardiovascular disease.
How many lower-limb amputations were performed in diabetics aged 20 and above?
Around 73,000 lower-limb amputations were performed in diabetics aged 20 and above, highlighting serious complications from poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
What is the significance of monitoring lipid profiles in managing T2D?
Monitoring lipid profiles is crucial as it helps manage the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is often linked to insulin resistance in individuals with Type 2 Diabetes.
What resources does T2DSolutions provide for individuals with T2D?
T2DSolutions offers education, community support, and resources to help individuals manage Type 2 Diabetes effectively.



