Overview
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes among our youth has alarmingly increased since the COVID-19 pandemic. Reports indicate a staggering 77.2% rise in new cases, particularly impacting minority populations. It’s understandable to feel concerned about this trend, as it stems from lifestyle changes that many of us have experienced—such as increased screen time, reduced physical activity, and unhealthy eating habits.
This situation underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions and community support. You're not alone in this journey; many are facing similar challenges. Together, we can address this public health crisis and work towards healthier futures for our children. Let’s explore ways to foster healthier habits and provide the support that’s so desperately needed.
Introduction
The rise of Type 2 diabetes among youth is a deeply concerning public health issue, especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many have experienced significant changes in their lifestyles during lockdowns, leading to an alarming increase in new diabetes cases, particularly among adolescents and minority populations already grappling with health disparities. It's understandable to feel worried about these developments.
This article explores the various factors contributing to this increase. Reduced physical activity, heightened stress, and poor dietary choices all play a role. It's crucial to recognize these challenges as we look at the urgent need for targeted interventions and community support systems. Together, we can combat this trend and promote healthier habits among young individuals.
By examining effective strategies and evaluating their impact, we can highlight the vital importance of education and collaboration. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way. Let’s work together to reverse the rising tide of diabetes among our youth.
Background: Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence Among Youth Pre- and Post-COVID-19
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, type 2 diabetes prevalence was becoming increasingly common among youth, especially in communities facing high obesity rates and inactive lifestyles. The CDC reported approximately 5,293 cases of T2D in children and adolescents aged 10 to 19 years in the U.S. It's concerning to note that between 2017 and 2020, roughly 14.7 million children and teens – nearly 20% – suffered from obesity, a significant risk factor contributing to type 2 diabetes prevalence.
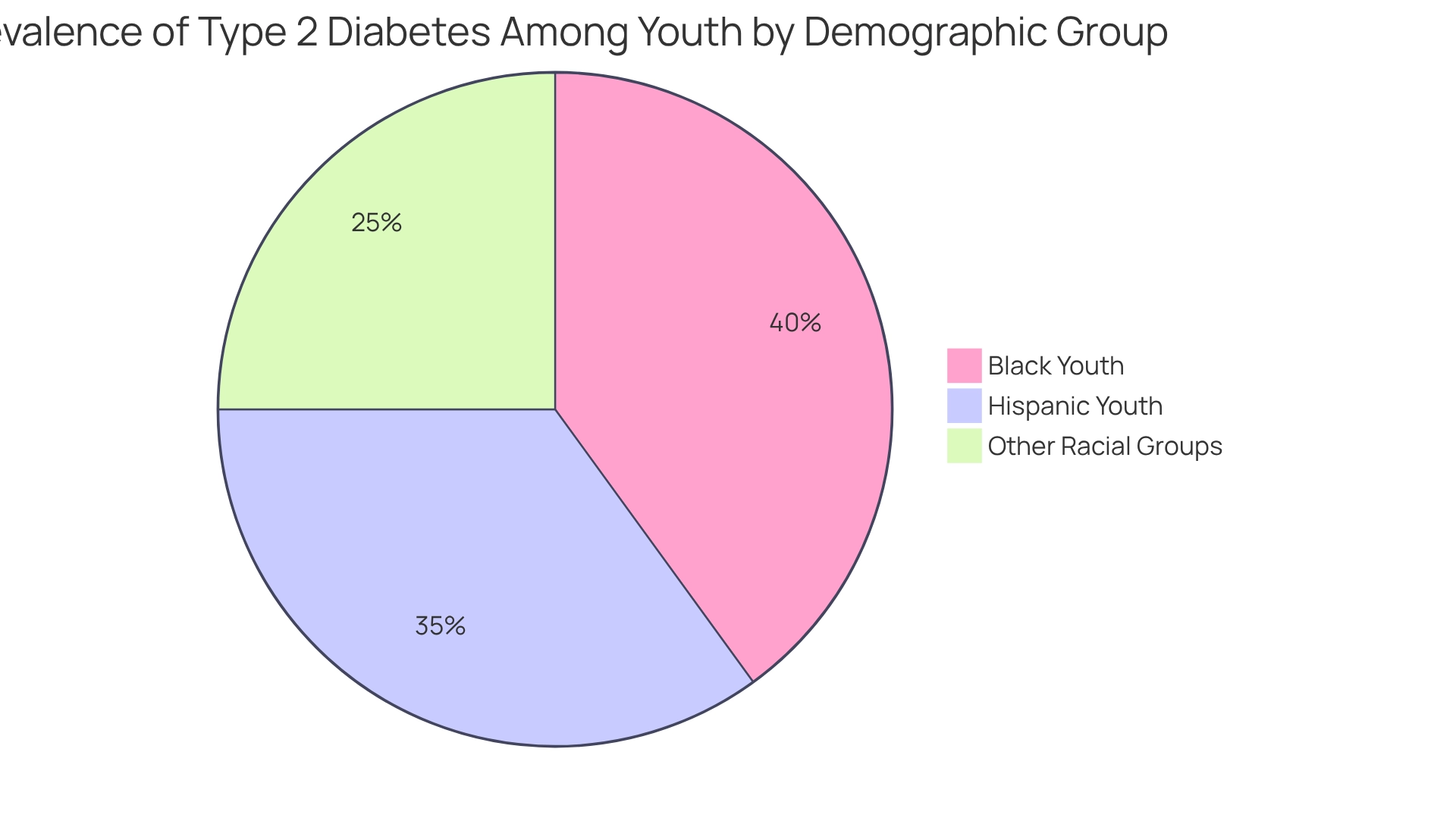
Sadly, the troubling reality is that Hispanic and Black children experienced the highest rates of type 2 diabetes prevalence, which worsened by 2020 as the pandemic led to major lifestyle changes characterized by increased screen time and reduced physical activity. These shifts resulted in a notable rise in type 2 diabetes prevalence, particularly among Black and Hispanic adolescents, who faced compounded risks due to socioeconomic challenges. The financial burden is also alarming; excess medical expenses linked to this condition rose from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022, highlighting the strain this growing public health issue places on families.
The impact of COVID-19 on young people's health is a pressing concern that requires our attention. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these statistics, but please remember, you're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way. Focused measures and education are essential to tackle this problem, and together, we can work towards a healthier future for our youth.
Problem: Surge in Type 2 Diabetes Rates Among Youth During the Pandemic
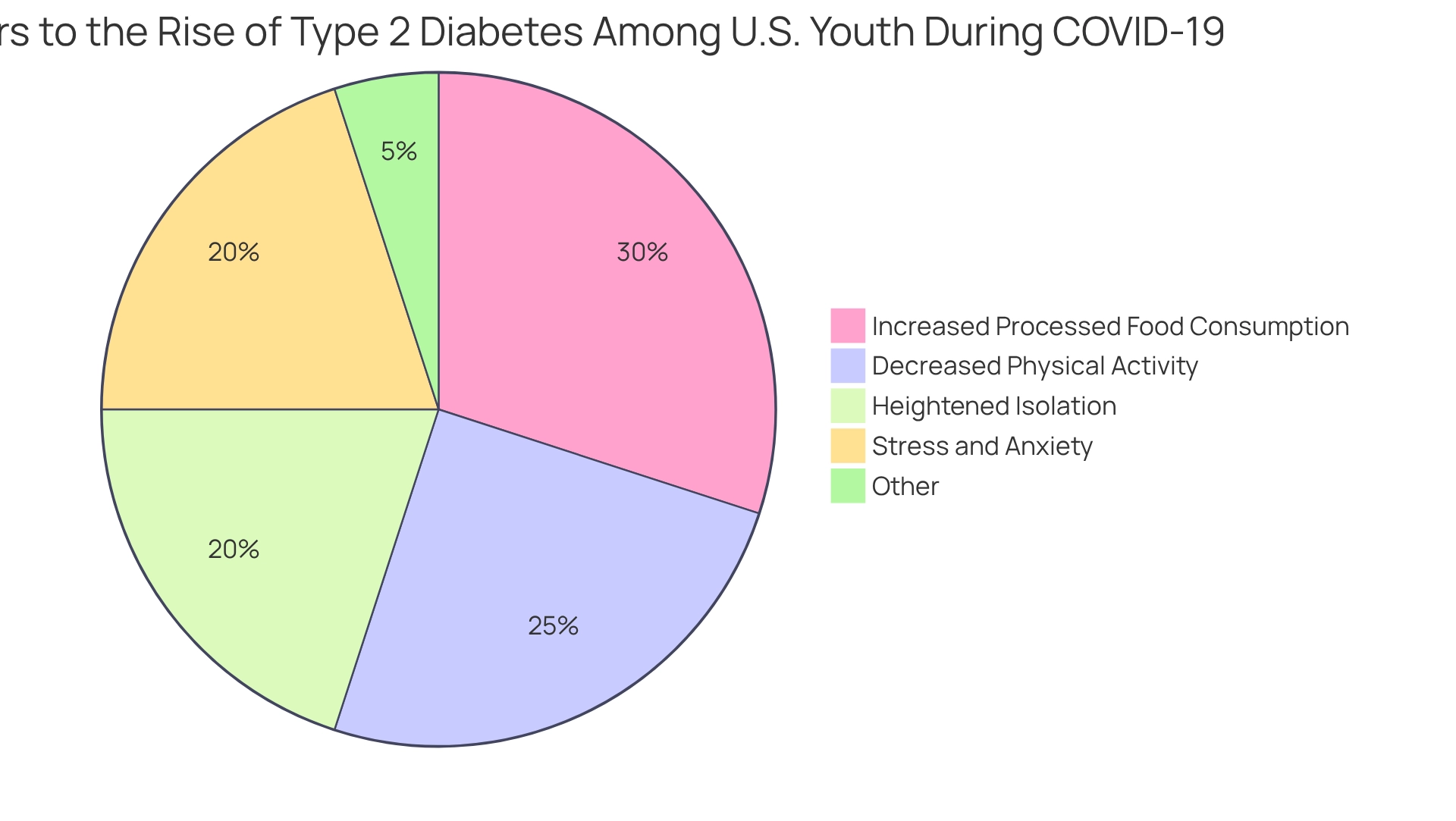
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a startling 77.2% rise in new-onset cases of the second type of blood sugar disorder among U.S. youth during the initial year of the outbreak, compared to the average of the preceding two years. This increase is particularly pronounced in adolescents aged 10 to 19 years, raising significant concerns, especially within minority populations where existing health disparities are highlighted.
It’s understandable to feel worried about these statistics. Contributing factors to this surge include heightened isolation, decreased physical activity due to lockdown measures, and shifts in dietary habits, particularly an increase in processed food consumption. Additionally, the stress and anxiety stemming from the pandemic have likely exacerbated unhealthy habits, increasing the risk of developing this second form of sugar-related illness.
As Lisa Schnirring points out, "Indiana now has 6 connected cases in Allen County involving 4 children and 2 adults," which illustrates the real-world implications of this alarming trend. This situation underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions and support systems to address the rising type 2 diabetes prevalence among young individuals.
At T2DSolutions, we aim to be a vital resource in this effort. We offer education and community support to assist in managing and preventing the second type of blood sugar condition, especially for those in at-risk groups. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Solution Approach: Interventions to Mitigate Rising Diabetes Rates
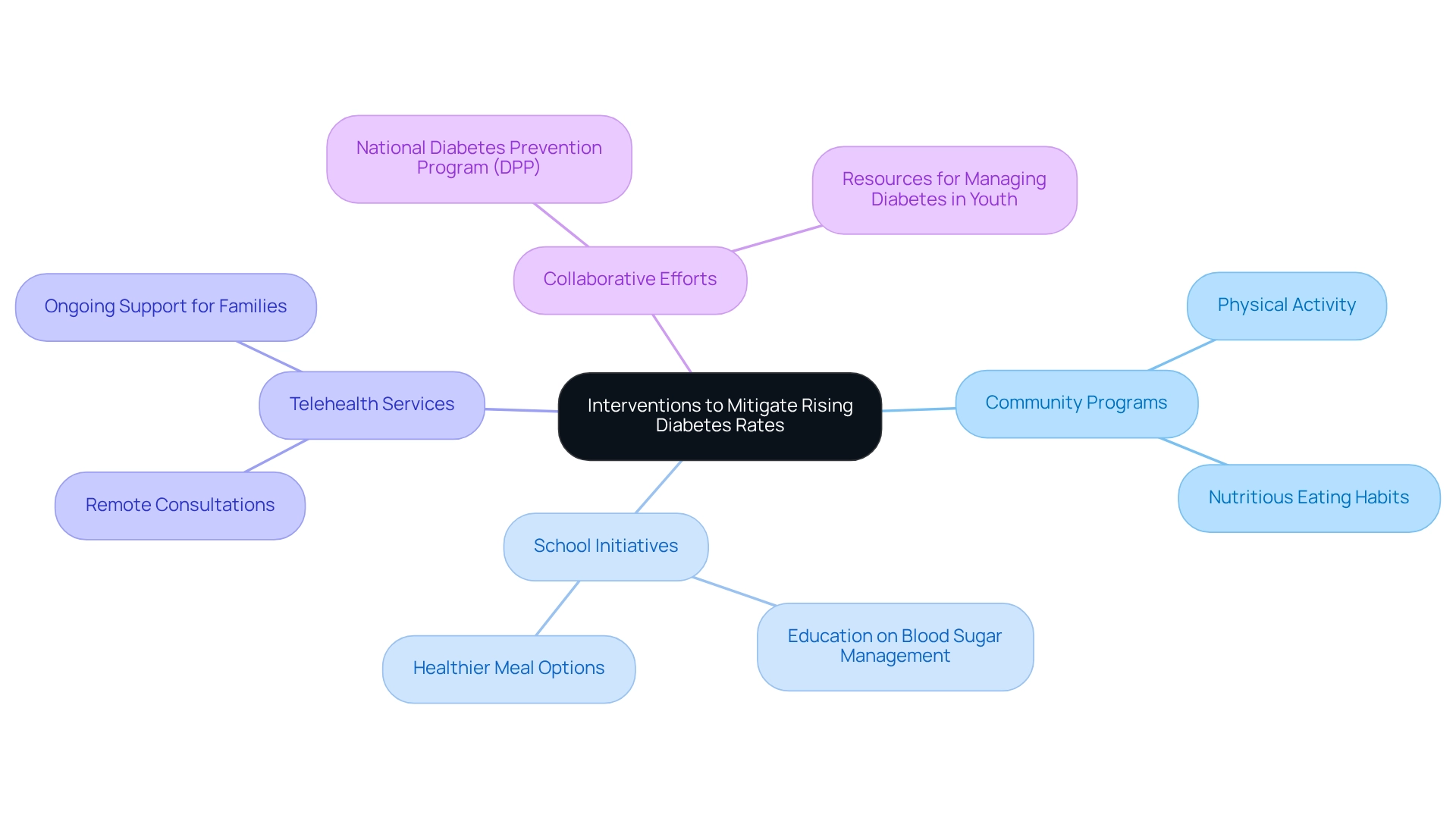
In response to the concerning rise in blood sugar issues among young individuals, a variety of measures have been introduced to promote healthier living. Community-based programs are leading the way, focusing on physical activity and nutritious eating habits. Schools have also made significant strides by integrating education about blood sugar management into their curricula and providing healthier meal options. These steps are vital for fostering awareness and prevention from an early age.
Telehealth services have expanded access to management resources, allowing for remote consultations and ongoing support for families. Notably, initiatives like the National Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) have proven effective in reducing the incidence of type 2 diabetes prevalence through comprehensive lifestyle changes and behavioral assistance. Research indicates that community programs promoting physical activity and nutritious eating can significantly impact type 2 diabetes prevalence rates among young people. For instance, school-based education programs on blood sugar management have been shown to enhance students' understanding of this condition, leading to improved health outcomes. In a related study, self-esteem increased notably in the Healthy Buddies group, while scores in the control group declined (p = 0.05), underscoring the psychosocial benefits of such community interventions.
As we look ahead to 2025, the emphasis on effective interventions remains crucial. Successful case studies, such as 'Resources for Managing Diabetes in Young People,' highlight the importance of collaboration among schools, healthcare providers, and community organizations in establishing a robust support system for individuals at risk of type 2 diabetes prevalence. T2DSolutions aims to be a vital resource center in this initiative, offering valuable information and assistance for the education and management of the condition. By utilizing these resources, we can work together to reverse the trend and secure a healthier future for our younger generation. As Joel Fuhrman wisely states, 'The more greens you consume, the more weight you will shed,' emphasizing the essential role of nutrition in managing blood sugar levels.
Results and Insights: Evaluating the Impact of Interventions on Diabetes Prevalence
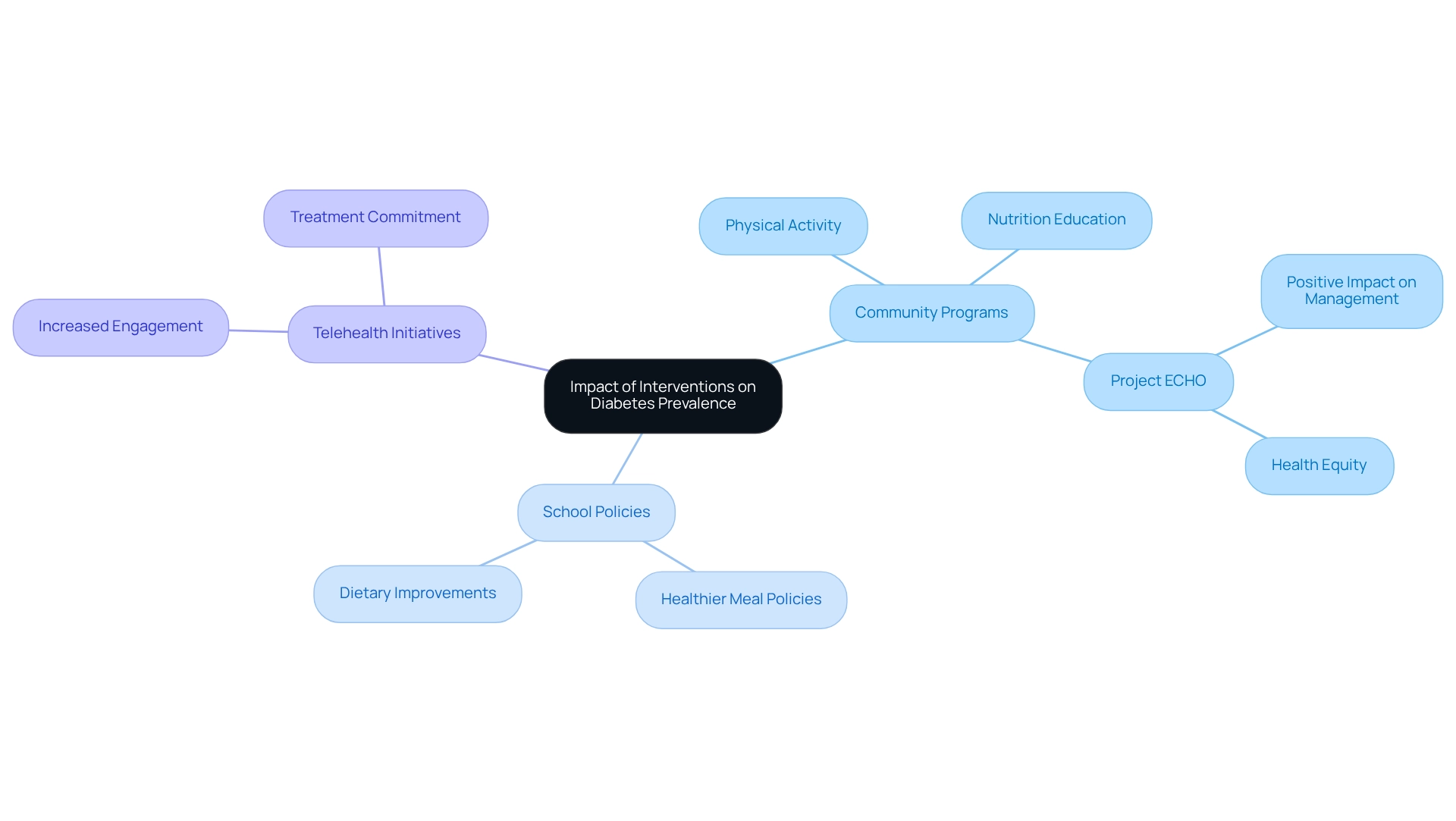
Recent assessments of interventions aimed at reducing the type 2 diabetes prevalence in young individuals have produced promising results. Community programs that focus on physical activity and nutrition education have shown a significant reduction in obesity rates among participants. Schools that have implemented healthier meal policies are reporting notable improvements in students' dietary habits, fostering a culture of better nutrition. Moreover, telehealth initiatives have increased involvement in managing diabetes-related health, with many young individuals expressing that they feel more committed to their treatment plans.
As Ashby F. Walker from the University of Florida Diabetes Institute poignantly noted, "I've actually had a mentee of mine [who] passed away," highlighting the urgent need for effective management strategies for this condition. Additionally, the assessment of the Project ECHO Program has revealed initial results indicating a beneficial impact on blood sugar management and health equity, reinforcing the efficacy of community interventions.
Despite these positive trends, it’s crucial to continue monitoring and adapting these programs to ensure their long-term effectiveness, especially as new challenges arise in our evolving post-pandemic world. Recognizing the genetic determinants of Type 2 diabetes, as Dr. Hivert emphasizes, can also shed light on the risk factors affecting our youth.
Looking ahead, future studies are recommended to evaluate the long-term sustainability of community-based interventions like Mebane on the Move. This emphasizes the importance of ongoing evaluation and adaptation of these programs. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. It's important to align future content with the themes of T2DSolutions to provide comprehensive insights and support for the target audience. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
The alarming rise in Type 2 diabetes among our youth, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, reveals a significant public health crisis that truly needs our immediate attention. With a staggering increase of 77.2% in new cases, the pandemic has intensified existing health disparities, particularly among minority populations who are already facing higher risks due to obesity and sedentary lifestyles. It's crucial that we address the root causes—such as decreased physical activity, poor dietary choices, and heightened stress—through urgent and targeted interventions.
Fortunately, efforts to combat this trend have begun to show promise. Community-based programs focused on nutrition and physical activity, alongside school initiatives promoting diabetes education, are vital in fostering healthier habits. Telehealth services have also enhanced access to diabetes management resources, providing essential support to families navigating this challenging landscape. Successful case studies highlight the importance of collaboration among schools, healthcare providers, and community organizations in creating a strong support system for at-risk youth.
As we move forward, it will be critical to continuously evaluate and adapt these interventions to ensure their effectiveness in our evolving post-pandemic environment. Together, we can educate, support, and empower young individuals, paving the way for a healthier future. By prioritizing these initiatives, our communities can unite to reverse the rising tide of Type 2 diabetes among youth and build a solid foundation for lifelong health. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the trend in type 2 diabetes prevalence among youth before the COVID-19 pandemic?
Before the pandemic, type 2 diabetes prevalence was increasingly common among youth, particularly in communities with high obesity rates and inactive lifestyles.
How many cases of type 2 diabetes were reported in U.S. children and adolescents?
The CDC reported approximately 5,293 cases of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents aged 10 to 19 years in the U.S.
What percentage of children and teens suffered from obesity between 2017 and 2020?
Between 2017 and 2020, roughly 14.7 million children and teens, nearly 20%, suffered from obesity, which is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Which demographic groups experienced the highest rates of type 2 diabetes prevalence?
Hispanic and Black children experienced the highest rates of type 2 diabetes prevalence.
How did the COVID-19 pandemic impact type 2 diabetes prevalence among youth?
The pandemic led to increased screen time and reduced physical activity, resulting in a notable rise in type 2 diabetes prevalence, particularly among Black and Hispanic adolescents.
What was the financial impact of type 2 diabetes on families from 2012 to 2022?
Excess medical expenses linked to type 2 diabetes rose from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022, indicating a significant financial burden on families.
What is being emphasized as a necessary response to the rise in type 2 diabetes among youth?
Focused measures and education are essential to tackle the problem, and support is available for those affected as we work towards a healthier future for our youth.



