Overview
This article gently guides you through understanding how to convert a 6.0 A1C measurement into blood glucose levels, indicating an average blood glucose of approximately 126 mg/dL. This information is crucial for effectively managing diabetes and can feel overwhelming at times. Regular A1C testing is emphasized as an essential tool for monitoring your blood sugar control. By grasping this conversion, you can make informed treatment decisions and embrace lifestyle changes that lead to better health outcomes.
It's completely understandable to feel uncertain about these numbers and what they mean for your health. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Many people share similar concerns, and it’s important to reach out for support. Understanding your A1C levels can empower you to take charge of your health, and we are here to support you every step of the way. Sharing your experiences with others can foster a sense of community and connection, making this journey a little easier.
Introduction
In the journey of diabetes management, the A1C test emerges as a vital ally in understanding your long-term blood sugar control. This essential tool not only assists in diagnosing diabetes but also plays a crucial role in monitoring and adjusting treatment strategies for those navigating this condition. With the rising prevalence of diabetes, especially among younger individuals, recognizing the importance of A1C levels has never been more crucial.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, but by exploring the nuances of the A1C test—from how to interpret the results to the factors that influence its accuracy—you can empower yourself to take charge of your health. This article will guide you through the workings of the A1C test, its implications for your health management, and practical strategies for lowering A1C levels. Together, we can foster a deeper understanding of how to effectively navigate the complexities of diabetes care, ensuring you feel supported every step of the way.
What is the A1C Test and Why is it Important?
The A1C test, often known as the hemoglobin A1C test, is a vital diagnostic tool that assesses how average blood sugar levels have fluctuated over the past two to three months. This test is crucial for both diagnosing and managing blood sugar conditions, as it provides a comprehensive view of blood sugar control over time. An A1C measurement below 5.7% is considered normal, while values from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes.
When the rate reaches 6.5% or higher, it confirms a blood sugar condition. Regular A1C testing is essential for both individuals and healthcare providers, as it allows for the evaluation of glucose control strategies, particularly in understanding how to convert a 6.0 A1C to glucose, and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
Recent studies highlight the significance of the A1C test in managing blood sugar conditions. For instance, it has been reported that 8.0% of U.S. adults aged 18 years or older diagnosed with diabetes had a non-HDL level of 190 mg/dL or higher. This statistic underscores the need for effective monitoring and control of blood sugar levels. Regular A1C testing can be a proactive approach in managing blood sugar levels, enabling timely actions to prevent complications.
The financial burden of diagnosed blood sugar conditions in the United States reached an estimated $413 billion in 2022, with direct costs rising significantly over the past decade. This financial impact emphasizes the necessity of proactive care for individuals with blood sugar issues, where regular A1C testing plays a critical role in reducing long-term healthcare expenses and improving patient outcomes.
Experts in the field, including Roopa Naik, affirm that the A1C test can assist in determining the conversion from a 6.0 A1C to glucose levels. It can be conducted as a point of care (POC), a STAT test, or through laboratory analysis, making it accessible for timely decision-making in blood sugar management. This accessibility is vital, as it empowers healthcare providers to make informed decisions swiftly, enhancing patient care.
Furthermore, nurses and pharmacists who specialize in managing blood sugar levels are increasingly recognized for their essential roles in interpreting A1C results and communicating changes to treating clinicians. Their involvement ensures effective oversight of metabolic disorders and glycemic control issues, highlighting the collaborative nature of care.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of the A1C test in effectively managing these conditions. Our platform is dedicated to providing comprehensive resources and support for newly diagnosed patients, empowering them to take charge of their health. The proportion of individuals with high blood sugar utilizing A1C testing illustrates its importance in managing the condition, especially regarding the conversion from a 6.0 A1C to glucose.
As healthcare professionals continue to advocate for regular testing, the A1C test remains a cornerstone in the journey of managing blood sugar levels. It helps translate a 6.0 A1C to glucose insights, empowering individuals to take control of their health. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
How the A1C Test Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
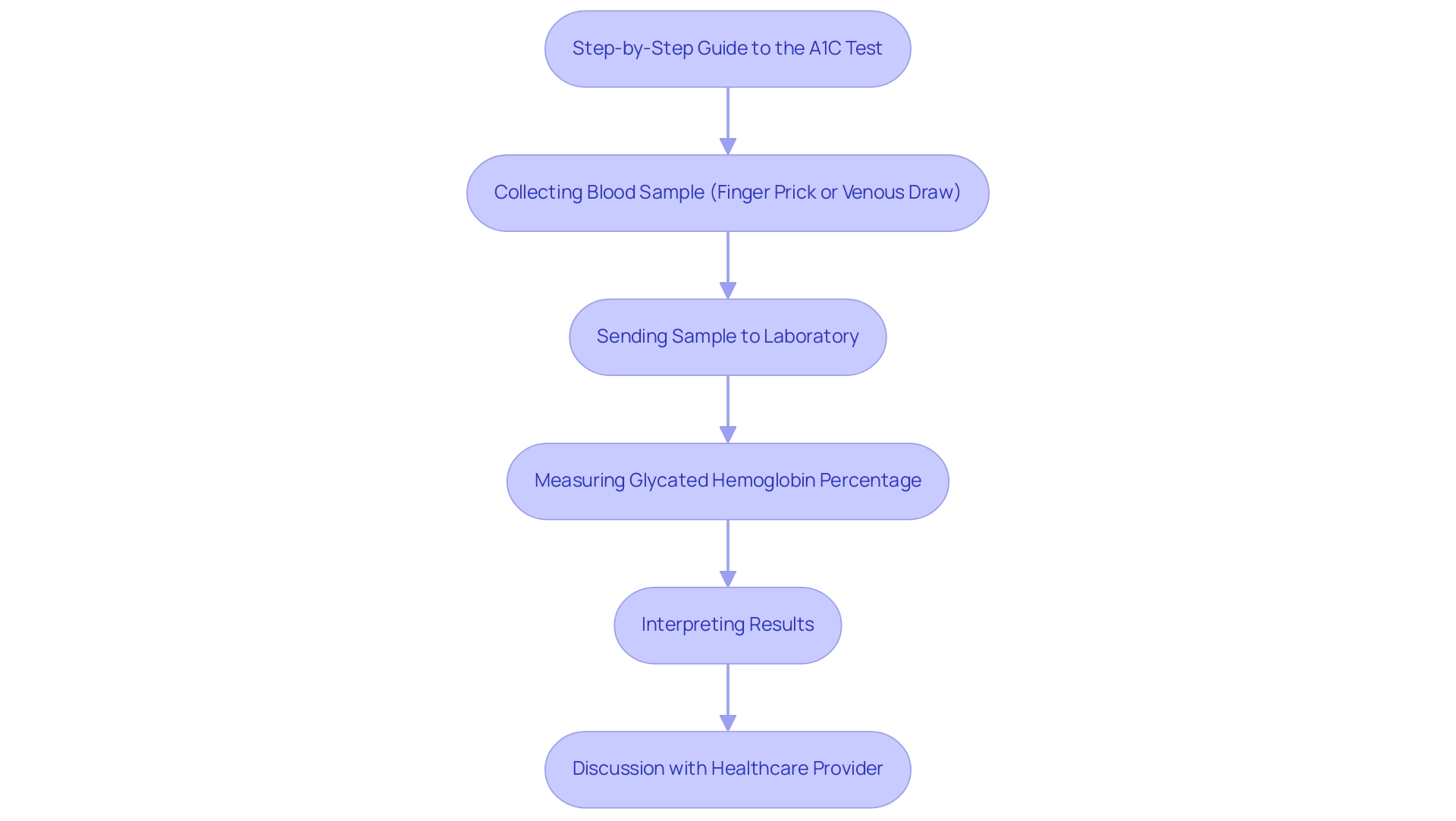
The A1C test is a vital tool in managing blood sugar levels, especially when it comes to understanding how a 6.0 A1C translates to glucose levels. This important test is performed by collecting a blood sample, either through a finger prick or a venous draw, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Here, it measures the percentage of hemoglobin that has become glycated, providing an indication of average blood glucose readings over the past two to three months. Typically, results are ready within a few days, allowing for timely discussions with your healthcare provider.
One of the significant advantages of the A1C test is that it doesn't require fasting, making it a convenient option for many patients. This accessibility is crucial, as studies indicate that adherence to A1C testing recommendations can vary widely based on factors like insurance status and educational attainment. For instance, uninsured individuals have a 12.4% lower completion rate for A1C tests compared to those who are insured.
As Vishnu Nepal from the Houston Department of Health and Human Services notes, "Population-based management programs for blood sugar conditions should consider educational achievement and insurance status when creating interventions to improve adherence to A1C testing recommendations among diabetic patients."
Understanding the A1C testing process can help ease anxiety and empower you to engage more effectively with your healthcare team. During the test, you can expect a straightforward procedure, and knowing what to anticipate can enhance your comfort level. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise—particularly among specific demographics such as Hispanic and Latino adults, who show rates between 5.0% and 7.3%—the importance of regular A1C testing, especially for converting a 6.0 A1C to glucose, becomes even more pronounced.
In recent years, the incidence of diabetes among children and adolescents has also increased, highlighting the need for effective management strategies. During 2017-2018, an estimated 18,169 children and adolescents under the age of 20 were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, and 5,293 children and adolescents aged 10 to 19 were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. This concerning trend is further supported by data from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, which indicated a significant rise in the incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents from 2002 to 2018.
Given these statistics, it is essential for young patients and their families to understand the significance of the A1C test, particularly how converting a 6.0 A1C to glucose is crucial for effectively monitoring and managing blood sugar levels. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Interpreting Your A1C: What Does a 6.0 Mean for Your Glucose Levels?
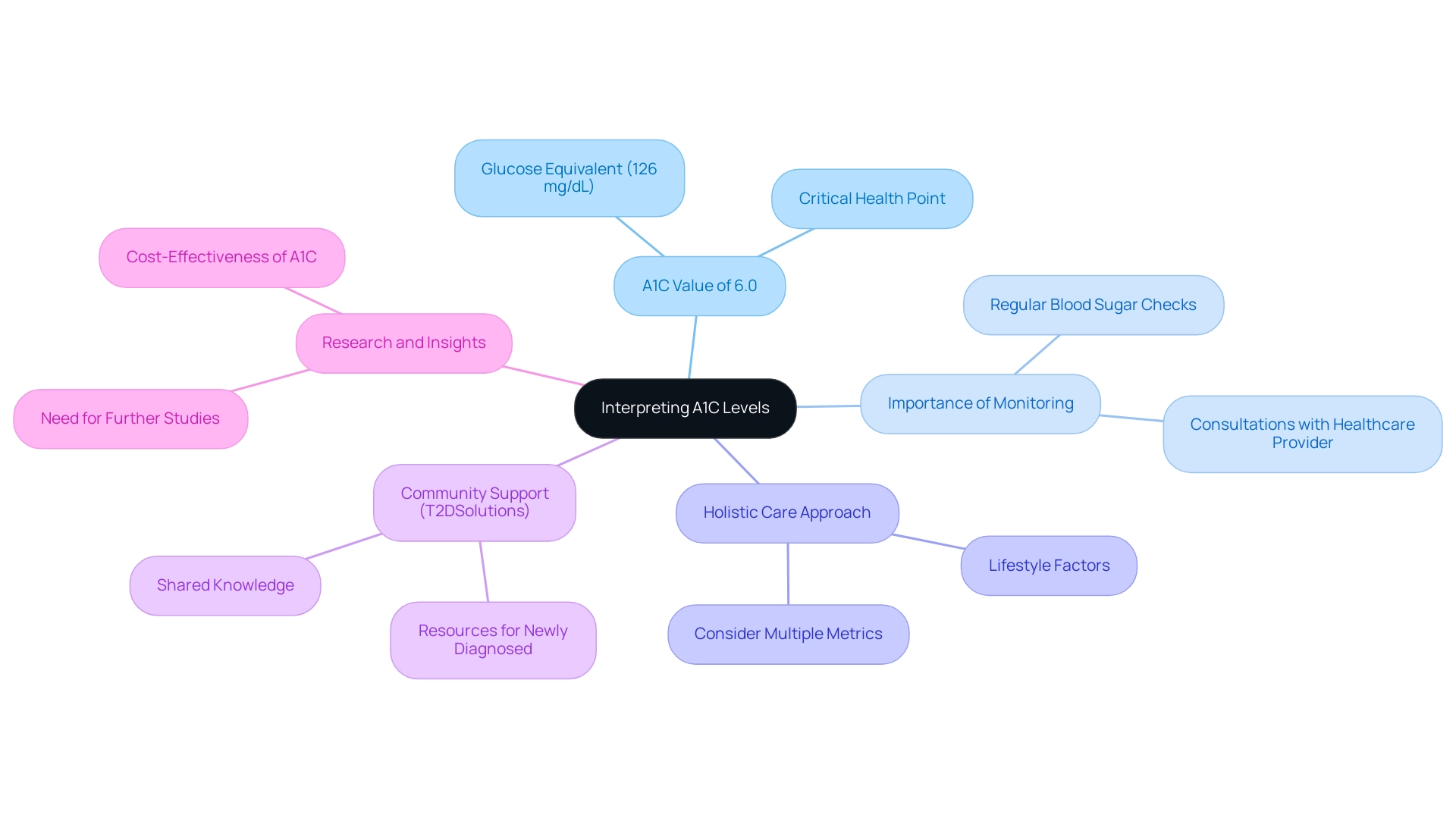
An A1C value of 6.0% translates to approximately 126 mg/dL when converting A1C to glucose. This stage indicates that, on average, blood sugar readings are at the limit for glucose control, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring. If your A1C is at this level, it's essential to engage in consistent blood sugar checks and work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized care plan that meets your unique needs.
Understanding the connection between A1C and glucose readings is vital for effectively managing your condition. Research shows that the area under the curve (AUC) for fasting plasma glucose (FPG) is 0.937, indicating a strong relationship between these metrics. This connection emphasizes the need for patients to consider their A1C results within the broader context of their overall health.
Healthcare professionals remind us that "therapy decisions should not be based on just one metric," like A1C. Instead, a holistic approach that considers various factors, including lifestyle and individual health conditions, is crucial for optimal diabetes care. For example, some laboratories now provide A1C results alongside estimated average glucose (eAG), translating A1C percentages into familiar glucose meter units. This dual reporting helps you understand your blood sugar measurements over time, enabling more effective management strategies.
Maintaining a 6.0 A1C level carries significant implications. It suggests that you are at a critical point in your health journey, where proactive measures can lead to improved health outcomes. Regular consultations with your healthcare provider can empower you to navigate your care plan effectively, ensuring you remain informed and in control of your treatment.
As we continue to learn about A1C levels and their correlation with glucose, staying updated on the latest research and insights is essential for those managing blood sugar. Moreover, the ongoing need for more research on the cost-effectiveness and practical application of A1C in diabetes treatment highlights the importance of continuous learning in this field.
T2DSolutions serves as a supportive community for individuals affected by diabetes, promoting shared knowledge and improved health outcomes, which are crucial for effective management. By offering resources and education, T2DSolutions helps newly diagnosed patients understand their A1C readings and develop effective strategies for managing their condition. Remember, you're not alone in this journey—we are here to support you every step of the way.
Translating A1C to Average Blood Sugar: The Conversion Process
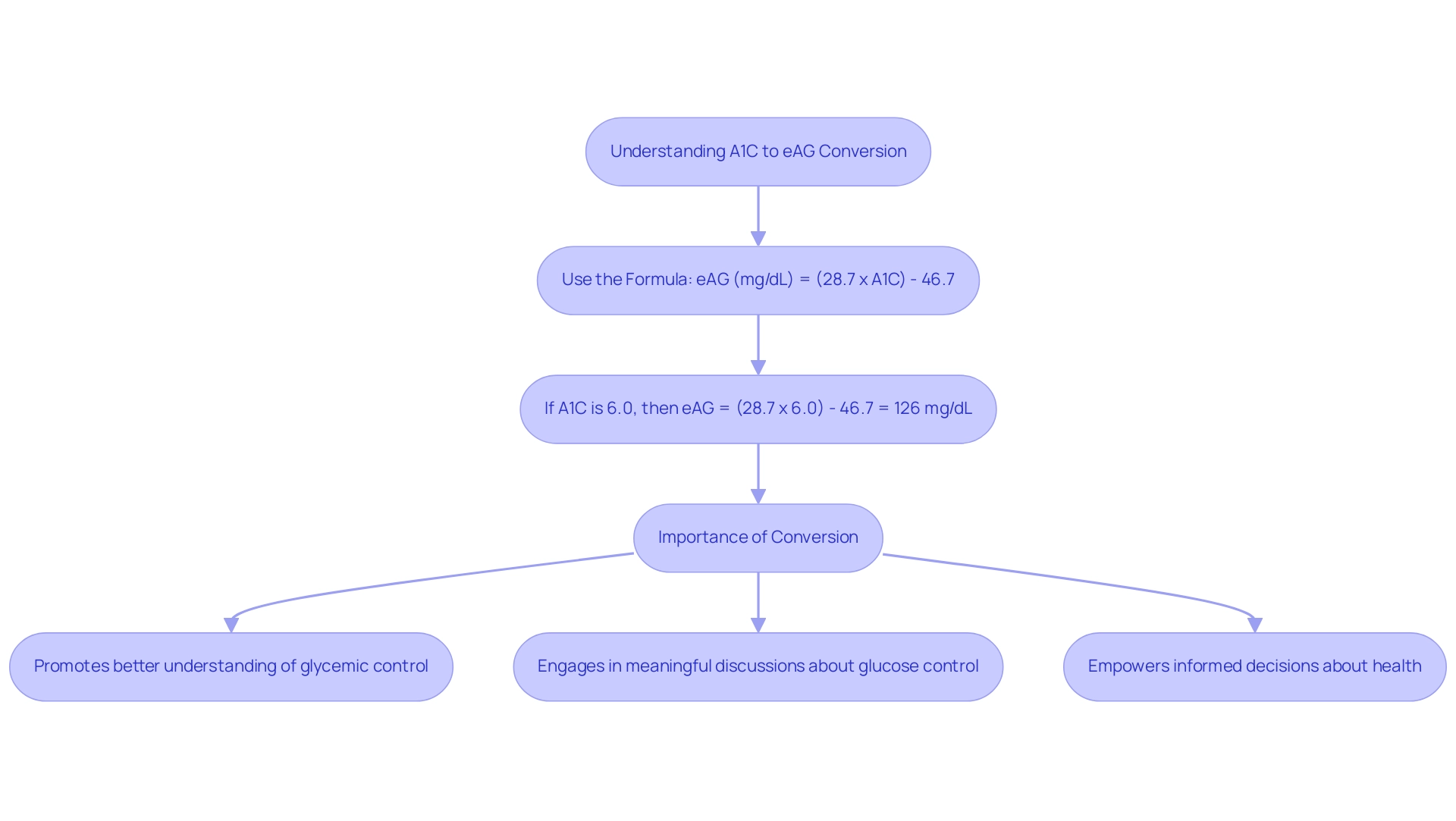
Understanding how to convert A1C to average blood sugar levels can feel overwhelming, but it’s an important step in managing your health. The formula used is:
- eAG (mg/dL) = (28.7 x A1C) - 46.7.
For example, if your A1C is 6.0%, you would calculate it as follows:
- eAG = (28.7 x 6.0) - 46.7, which gives you an estimated average glucose (eAG) of about 126 mg/dL.
This conversion is vital because it helps you relate your A1C results to your daily blood sugar monitoring, promoting a better understanding of your glycemic control.
At t D Solutions, we recognize how significant this conversion is for your health journey. Our platform is dedicated to providing newly diagnosed patients with the resources they need to navigate their health more effectively. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has introduced the eAG/A1C conversion calculator, which enhances communication between healthcare providers and patients.
When A1C results are reported in the same units as routine blood glucose measurements, it allows you to engage more meaningfully in discussions about your glucose control. This initiative has shown to improve patient understanding, which may lead to better outcomes in managing blood sugar levels. However, research indicates that many patients struggle to grasp the importance of A1C results and their conversion to eAG.
This gap in understanding underscores the need for educational resources that clarify these concepts. For instance, a recent survey revealed that only a portion of patients could accurately interpret their A1C results in relation to their daily blood sugar levels.
The formula for converting A1C to eAG is not just a mathematical exercise; it carries significant implications for your health management. By understanding this relationship, you empower yourself to take charge of your health, making informed decisions about your lifestyle and treatment options. Health educators emphasize that regular monitoring and comprehension of these metrics are crucial for achieving optimal health outcomes.
The ADA recommends having an A1C test at least twice a year for those who are consistently meeting their blood sugar management goals.
Moreover, patient-specific models play a valuable role in managing glycemic status, especially in cases where HbA and average glucose values differ. This highlights the importance of personalized approaches to managing diabetes. Additionally, it’s noteworthy that 70.8% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions have a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or higher, which reflects the broader health challenges faced by individuals with such conditions.
We invite you to explore T2D Solutions for more information on effectively managing your diabetes and accessing educational materials tailored to your needs. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Factors Influencing A1C Accuracy: What You Need to Know
The accuracy of A1C test results is influenced by several critical factors that are important to understand.
- Hemoglobin variants, which are genetic alterations in the hemoglobin molecule, can lead to misleading A1C readings.
- For instance, individuals with conditions such as sickle cell disease or thalassemia may experience discrepancies in their A1C results.
- This highlights the importance of understanding the conversion from 6.0 A1C to glucose for accurate blood glucose monitoring.
It's understandable to feel concerned about how recent blood loss—whether from surgery or injury—can distort results, as can certain medical conditions like anemia or chronic kidney disease, which influence hemoglobin amounts. Laboratory errors also play a role in the reliability of A1C tests. Therefore, it's essential for patients to engage in open discussions with their healthcare providers regarding any concerns about their A1C results. This conversation is vital, especially since the A1C test is classified into ranges: normal, prediabetes, and a higher condition.
A case study titled "Interpreting A1C Results" illustrates that the A1C test must be conducted in a lab using NGSP-certified methods for accurate diagnosis, highlighting its diagnostic limitations. Understanding these ranges, including the conversion of 6.0 A1C to glucose, can empower patients to recognize the implications of their results on their health journey.
Recent research emphasizes that higher A1C levels, particularly those indicating a conversion of 6.0 A1C to glucose, significantly increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Therefore, being aware of potential discrepancies in A1C results is vital for effective management. For example, a study indicated that the mean total daily dose of insulin was nearly double in patients with discordant low A1C results (32 units) compared to those with discordant high results (17 units). This underscores the importance of accurate testing in treatment planning.
Healthcare professionals emphasize that while the A1C test is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar levels, it functions best within an interprofessional healthcare team environment. As Eyth E. states, "Hemoglobin A1C is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar conditions and other glycemic control disorders, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective." This collaborative approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their unique circumstances.
By understanding the factors that can influence A1C accuracy, individuals can better navigate their health conditions and make informed choices about their well-being. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Patients are encouraged to discuss their A1C results and approaches with their healthcare providers to formulate a plan for improvement.
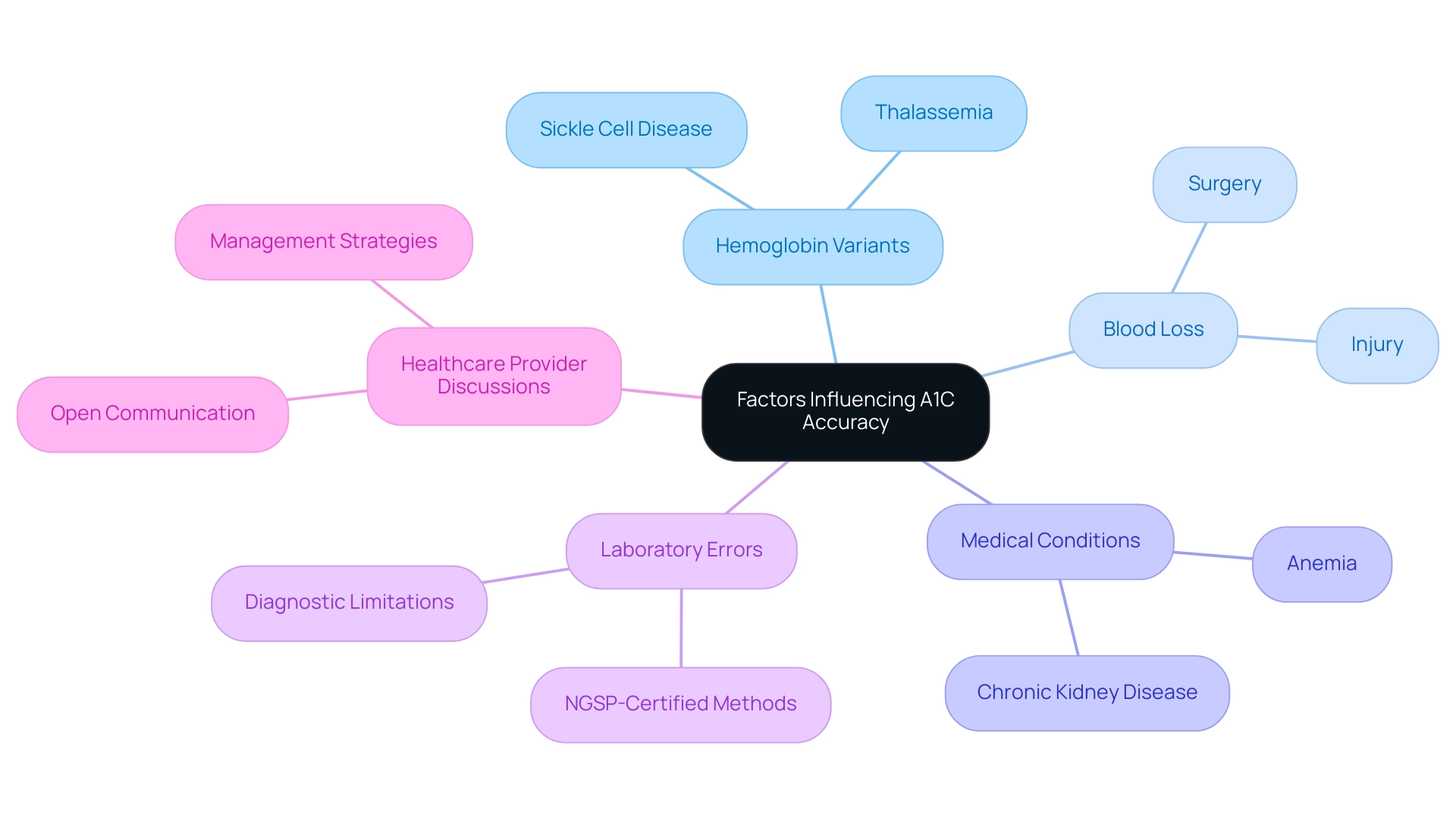
Strategies for Lowering Your A1C: Practical Tips and Lifestyle Changes
To effectively lower your A1C levels, consider adopting the following strategies with the support of Td Solutions, your comprehensive resource for diabetes education and community support:
-
Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet abundant in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. It’s essential to restrict processed foods and sugars, as research shows that around 50% of individuals with this condition find it challenging to follow dietary guidelines, which can impede their control efforts. T2DSolutions offers resources and meal planning tips to help you make healthier choices.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Engaging in physical activity not only aids in weight management but also significantly contributes to enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar. T2DSolutions provides guidance on suitable exercise routines tailored for individuals with diabetes.
-
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly checking your blood sugar readings can help you identify patterns and make necessary adjustments. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, which can lead to better glycemic control. T2DSolutions encourages users to share their monitoring experiences to foster community learning.
-
Stress Management: Incorporate relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation into your routine. Managing stress is essential, as high stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels and overall health. T2DSolutions provides resources on stress reduction methods that can be advantageous for controlling blood sugar.
-
Adherence to Treatment Plans: Following your healthcare provider's recommendations regarding medications and treatment plans is crucial. A rigorous lifestyle intervention has proven to be more effective than standard care in sustaining glycemic control, emphasizing the significance of a customized approach to health. As noted by Mathias Ried-Larsen, "the main finding was that an intensive lifestyle intervention was nonequivalent compared with standard care in relation to maintaining glycemic control, with the modest reduction in HbA favoring the lifestyle group."
Implementing these lifestyle changes can lead to significant improvements in your health, particularly in the conversion of 6.0 A1C to glucose levels. Community support, including sharing experiences with others encountering similar challenges, can further enhance your journey, fostering resilience and hope as you navigate health care. T2DSolutions emphasizes the importance of building a supportive community, which can significantly improve health outcomes through shared knowledge and support.
Furthermore, it's essential to consider the financial consequences of diabetes care; excess medical expenses related to diabetes rose from $10,179 to $12,022 from 2012 to 2022, highlighting the necessity for effective strategies. Additionally, with 70.8% of individuals having a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or being on medication for high blood pressure, comprehensive health oversight is crucial in conjunction with A1C control.
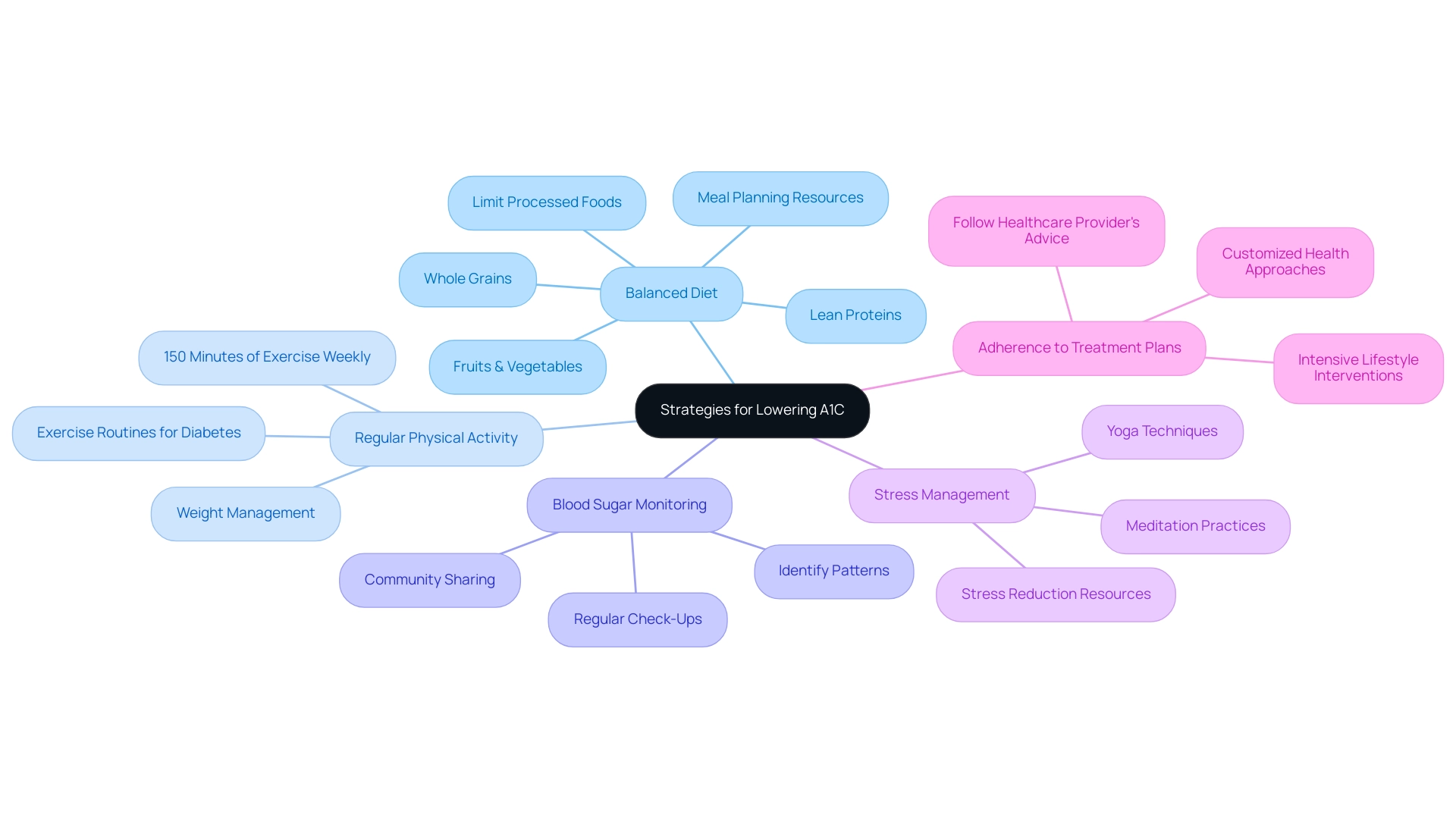
Health Implications of a 6.0 A1C: Understanding Risks and Management
An A1C measurement of 6.0 a1c to glucose indicates a heightened risk of developing diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney issues. It's important to understand that individuals with this A1C measurement may face serious health conditions. Therefore, proactive health management is crucial. For instance, statistical analyses reveal that 70.8% of U.S. adults with diagnosed blood sugar issues also experience elevated blood pressure, which increases the risks associated with higher A1C levels.
These findings highlight A1C as an effective tool for identifying those at risk. As noted by Xuanping Zhang from the CDC, this understanding can help advance efforts to connect individuals at risk for type 2 diabetes with appropriate preventive interventions.
To mitigate these risks, it's essential for individuals to grasp the correlation between a 6.0 a1c to glucose and work closely with their healthcare providers. Regular check-ups and screenings are vital for early detection of potential complications. Timely interventions can significantly improve health outcomes. Experts emphasize that maintaining an A1C below this threshold can help lower the likelihood of cardiovascular events and other serious health issues.
Moreover, concerning trends in the prevalence of diabetes-related conditions among youth, particularly non-Hispanic Black children, underscore the urgent need for targeted interventions. Data from 2017-2018 showed that 18,169 children and adolescents under 20 were diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, while 5,293 were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. The rising prevalence of both types among young people emphasizes the importance of education and preventive actions, especially for those at greater risk.
Management approaches should focus on lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments and increased physical activity. These changes can help lower A1C values and decrease the likelihood of complications. By understanding the health risks associated with a 6.0 a1c to glucose measurement and implementing effective control strategies, individuals can make meaningful strides toward enhancing their overall health and well-being. You're not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you every step of the way.
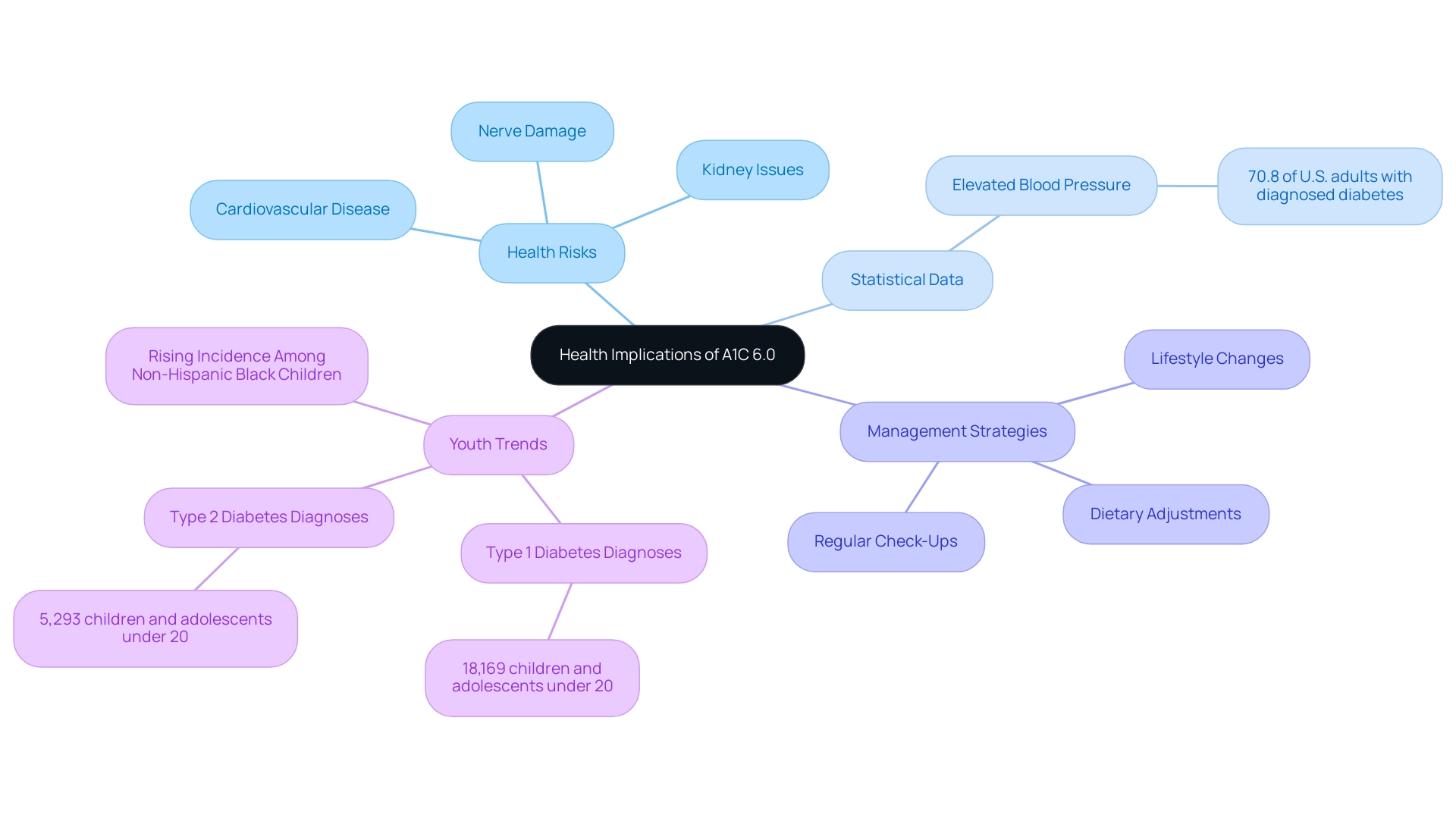
The Importance of Regular Monitoring: Keeping Track of Your A1C
Regular A1C testing is essential for individuals managing their condition. It offers a comprehensive overview of blood sugar control over time, such as translating a 6.0 A1C to glucose levels. Healthcare providers typically recommend that patients with stable treatment goals undergo testing at least twice a year. However, if you're experiencing fluctuations in blood sugar, more frequent assessments may be necessary to ensure optimal management.
Monitoring A1C results, including the conversion of 6.0 A1C to glucose, is crucial for making informed decisions about your treatment plans and lifestyle modifications. For instance, a study revealed that among adults with this condition, 47.4% had an A1C value of 7.0% or higher, indicating a significant prevalence of poor glycemic control. This highlights the importance of regular monitoring to identify and address potential issues early.
The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with the condition have their A1C readings assessed at least twice a year if they are achieving their treatment objectives. Conversely, if you are not meeting your targets or experiencing changes in therapy, testing should occur quarterly. This proactive approach is vital, allowing for timely adjustments to treatment strategies and ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
Real-world examples illustrate the impact of A1C testing frequency on patient outcomes. A significant percentage of individuals with blood sugar issues actively track their A1C levels, which correlates with better management of their condition. In fact, adherence to testing guidelines is crucial; recent findings indicate that 70.8% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions had elevated blood pressure, a common complication associated with poor glycemic control.
This connection emphasizes the need for regular A1C testing to mitigate risks related to converting 6.0 A1C to glucose.
As of 2025, updates to A1C testing frequency recommendations stress the importance of personalized care, considering individual patient circumstances and health status. It's also important to note that the accuracy of the HbA1c test can be affected by various conditions, necessitating confirmation with plasma glucose samples in certain cases. Regular A1C monitoring not only assists in effectively managing your condition but also empowers you to take charge of your health journey.
Eyth E. aptly states, "Hemoglobin A1c is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar disorders and other glycemic control issues, but it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment to be effective." This highlights the collaborative effort needed in blood sugar control. Overall, regular A1C monitoring is crucial for effective diabetes management and improving health outcomes. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the A1C test is crucial for anyone managing diabetes. This essential tool not only serves as a diagnostic marker but also provides valuable insights into long-term blood sugar control. By regularly monitoring A1C levels, you can gain a comprehensive view of your glycemic management, enabling timely interventions and adjustments to your treatment plan. It's important to interpret A1C results in conjunction with other health metrics, and to seek collaborative care involving healthcare providers, diabetes educators, and support networks.
Practical strategies for lowering A1C levels include:
- Dietary changes
- Regular physical activity
- Effective stress management
Adopting these lifestyle modifications can significantly enhance your overall health and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. With the increasing prevalence of diabetes among younger populations, there's an urgent need for proactive management and education regarding A1C testing.
Ultimately, staying informed about your A1C levels and their implications empowers you to take control of your diabetes management. By prioritizing regular testing, engaging with your healthcare team, and implementing recommended lifestyle changes, you can foster a healthier future and mitigate the risks associated with diabetes. You're not alone in this journey; as the landscape of diabetes care continues to evolve, the A1C test remains a cornerstone of effective health management. It guides you toward improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, assesses average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, making it essential for diagnosing and managing blood sugar conditions.
What do the A1C test results indicate?
An A1C measurement below 5.7% is considered normal, values from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, and a result of 6.5% or higher confirms a blood sugar condition.
Why is regular A1C testing important?
Regular A1C testing is crucial for evaluating glucose control strategies, understanding treatment effectiveness, and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans, thereby preventing complications.
How can the A1C test help in managing diabetes?
The A1C test helps translate a 6.0 A1C to glucose insights, aiding healthcare providers in making timely decisions regarding blood sugar management and improving patient care.
What is the financial impact of blood sugar conditions in the U.S.?
In 2022, the financial burden of diagnosed blood sugar conditions in the U.S. reached an estimated $413 billion, emphasizing the necessity for proactive care and regular A1C testing to reduce long-term healthcare expenses.
How is the A1C test performed?
The A1C test is performed by collecting a blood sample through a finger prick or a venous draw, which is then analyzed in a laboratory to measure the percentage of glycated hemoglobin.
Do patients need to fast before the A1C test?
No, the A1C test does not require fasting, making it a convenient option for many patients.
What factors can affect adherence to A1C testing recommendations?
Adherence to A1C testing can vary based on factors such as insurance status and educational attainment, with uninsured individuals showing lower completion rates.
What trends have been observed regarding diabetes in children and adolescents?
There has been a significant rise in the incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents, highlighting the need for effective management strategies.
How can understanding the A1C testing process benefit patients?
Knowing what to expect during the A1C testing process can ease anxiety and empower patients to engage more effectively with their healthcare team.
