Overview
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a chronic metabolic condition that can feel overwhelming. It is characterized by insulin resistance and insufficient insulin production, which leads to elevated blood glucose levels. This condition is often linked to lifestyle factors like obesity and inactivity. Understanding diabetes is crucial, as increased awareness can lead to earlier diagnosis and better management strategies. By taking action, we can work together to reduce the significant health and economic burdens associated with diabetes.
It's understandable to feel concerned about this diagnosis. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. There are resources and support options available to help you navigate your path. Increased awareness not only empowers you but also fosters a community where individuals can share their experiences and support one another. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
As we confront a rapidly rising epidemic, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) stands out as a significant public health concern, impacting millions around the globe. This chronic condition, marked by insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels, brings not only serious health risks but also places a burden on our healthcare systems and economies. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed as the prevalence of T2DM continues to rise. Therefore, gaining a deeper understanding of its origins, risk factors, and the broader diabetes spectrum is essential for effective prevention and management.
From genetic predispositions that heighten susceptibility to lifestyle choices that can reduce risk, the multifaceted nature of T2DM calls for comprehensive education and proactive strategies. We want you to know that you are not alone in this journey. This article explores the complexities of Type 2 Diabetes, emphasizing the importance of awareness, early intervention, and community support. Together, we can empower individuals to navigate their health journeys with confidence and resilience.
Define Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
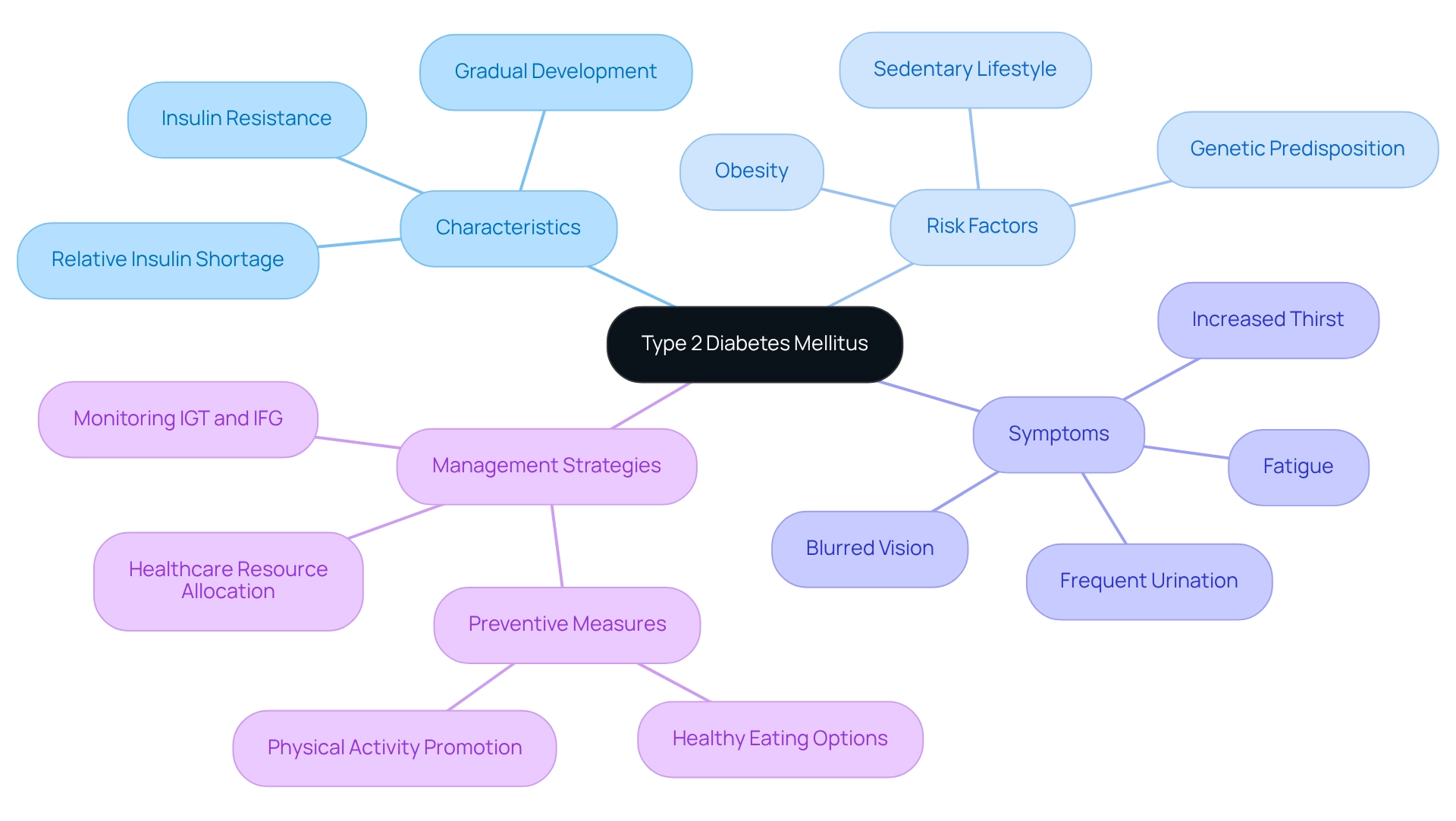
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a persistent metabolic condition that many people face, characterized by insulin resistance and a relative shortage of insulin production. This results in increased blood glucose levels. Unlike Type 1 Diabetes, where insulin production is absent, individuals with type 2 diabetes can produce insulin, but their bodies struggle to use it effectively.
Typically, this condition develops gradually and is linked to various risk factors, including obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition. It's understandable to feel concerned when learning that recent studies show 8.0% of U.S. adults diagnosed with this condition have a non-HDL cholesterol level of 190 mg/dL or higher. This statistic highlights how interconnected diabetes is with cardiovascular health.
Common symptoms of diabetes mellitus type 2 include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. However, many individuals may remain asymptomatic in the early stages. Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG) are critical warning signs indicating a high risk of progressing to diabetes mellitus type 2. Recognizing these conditions can empower you to take preventive actions to postpone or even avert the development of this illness.
As the prevalence of type 2 diabetes continues to rise, understanding what it entails is crucial. The medical costs per person have increased significantly from $10,179 to $12,022 between 2012 and 2022, making it essential to prioritize both prevention and effective management strategies.
The call for a shift in healthcare resource allocation towards the prevention of blood sugar-related conditions underscores the importance of addressing lifestyle factors. As one specialist observed, "Unless immediate actions are implemented to decrease poor dietary habits, inactive living, swift urban growth, and other elements associated with economic progress, the load of this condition is anticipated to keep increasing."
This highlights the need for policies that support healthy eating options while discouraging unhealthy foods, which are crucial for effectively managing diabetes mellitus type 2.
T2DSolutions aims to be a comprehensive resource hub for individuals newly diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2, providing educational materials and community support initiatives to empower you in your management journey. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Contextualize Type 2 Diabetes in the Diabetes Spectrum
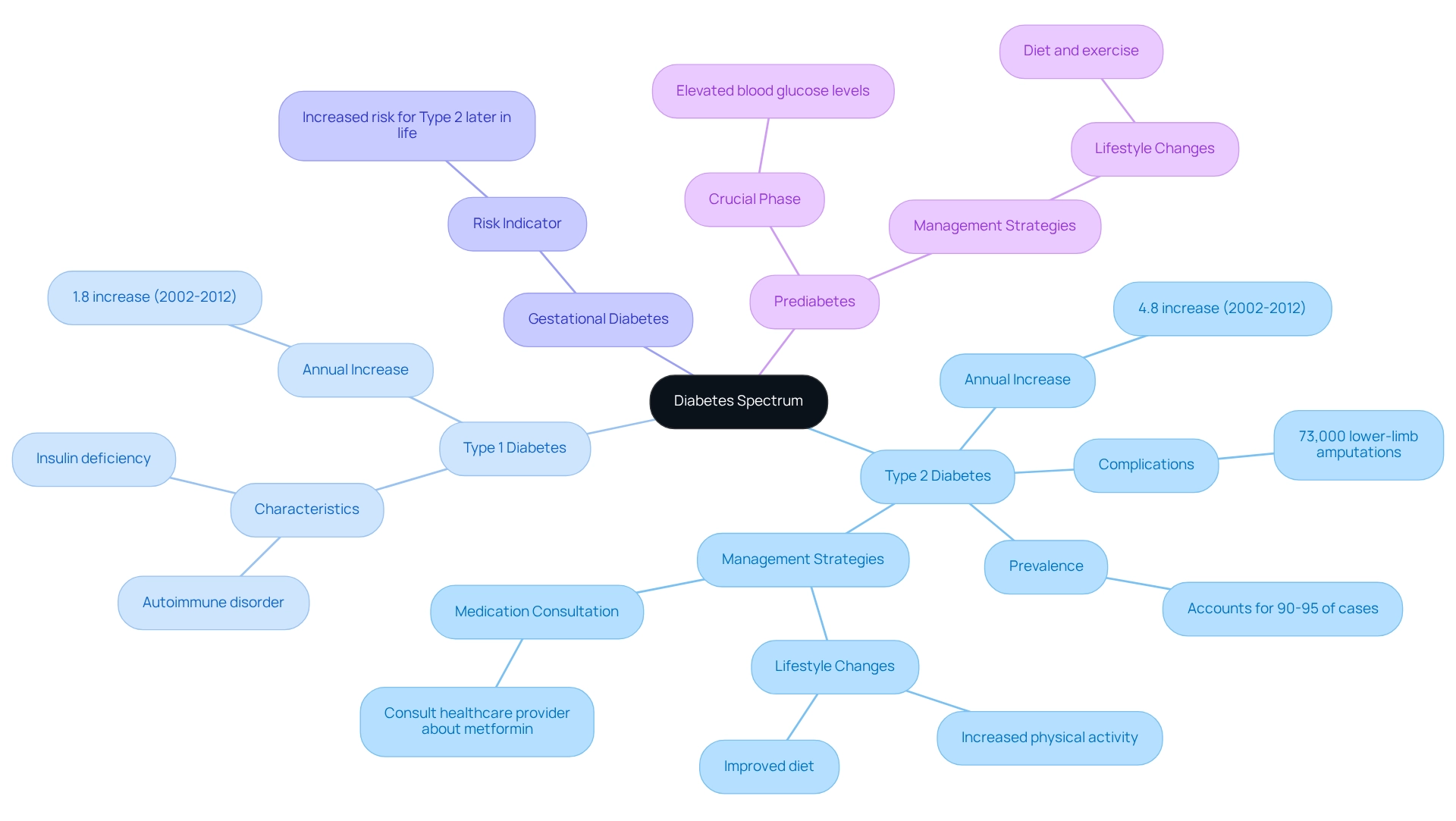
Diabetes mellitus type 2 represents Form 2 of this condition, which is the dominant type of this illness, accounting for roughly 90-95% of all identified instances. It exists within a broader spectrum of glucose-related conditions that includes Type 1, an autoimmune disorder characterized by insulin deficiency, and gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy. Additionally, the spectrum encompasses prediabetes, a crucial phase where blood glucose levels are elevated but not yet sufficient for a diagnosis. Understanding this spectrum is vital for both healthcare professionals and patients, as it influences prevention strategies and tailored treatment plans.
Recent statistics reveal a concerning trend regarding diabetes mellitus type 2, with an annual increase in cases noted at 4.8%, significantly higher than the 1.8% rise for Type 1 Diabetes from 2002 to 2012. This emphasizes the urgent need for improved awareness and education about diabetes mellitus type 2, especially since many individuals remain unaware of their condition. For instance, approximately 73,000 lower-limb amputations were performed in diabetics aged 20 and older, underscoring the serious complications that can arise from uncontrolled blood sugar. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights that the rise in diabetes mellitus type 2 is particularly evident around puberty across all ethnic groups, further stressing the importance of targeted educational efforts.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the critical need for education and support for newly diagnosed patients. Our platform aims to serve as a comprehensive resource hub for individuals navigating their health journey. Experts emphasize the interconnectedness of the conditions within this spectrum. While Class 1 and Class 2 diabetes differ in their pathophysiology, they share common risk factors and complications, necessitating a thorough approach to management. Furthermore, gestational diabetes serves as an important indicator, as women who experience it are at an increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus type 2 later in life.
Understanding the spectrum of this condition not only aids in early detection but also guides effective management strategies. Real-life case studies illustrate that individuals diagnosed with prediabetes can significantly lower their risk of progressing to diabetes mellitus type 2 through lifestyle changes, such as improved diet and increased physical activity. This proactive approach is essential, considering that diabetes mellitus type 2 accounts for a significant share of diabetic cases worldwide. Enhanced educational initiatives can lead to earlier detection and better management of the condition, ultimately improving health outcomes.
Moreover, individuals using metformin should consult their healthcare provider regarding their medication, as it plays a vital role in managing the second form of diabetes. By fostering a deeper understanding of these connections, T2DSolutions strives to empower individuals to take control of their wellness and navigate their journey with confidence. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Examine the Origins and Development of Type 2 Diabetes
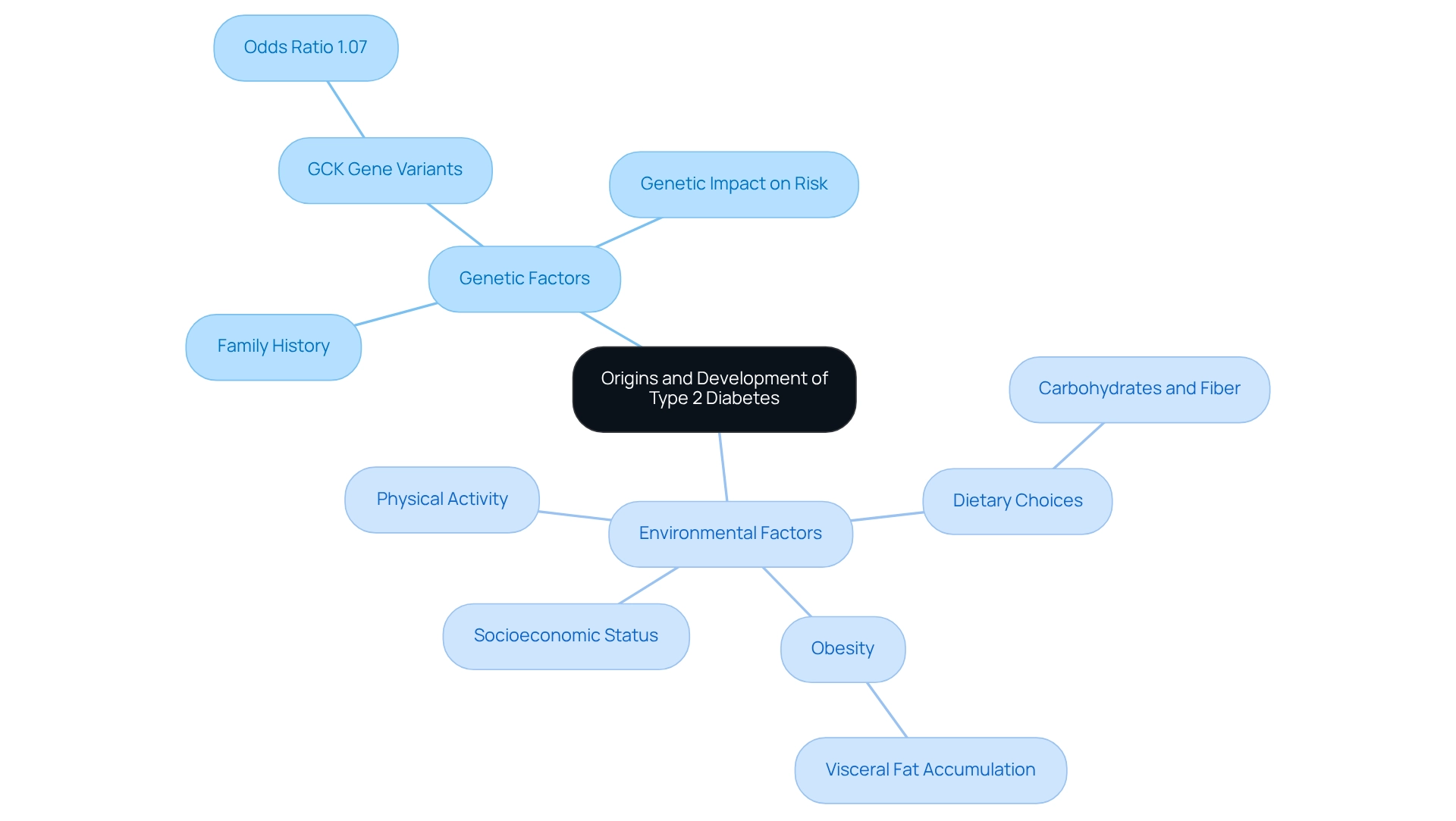
The development of diabetes mellitus type 2 involves a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors, and it’s important to understand how these elements affect your health. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role; if you have a family history of this condition, your risk may be higher. Recent findings have shown that specific genetic variants, such as those linked to the GCK gene, can influence susceptibility to diabetes, with an odds ratio of 1.07 underscoring this genetic connection. Even small genetic differences can impact your chances of developing this condition, highlighting the importance of understanding your genetic history. Moreover, studies indicate that dietary carbohydrates and fiber can modify the effects of these genetic variants, emphasizing the vital role of nutrition in managing diabetes.
Environmental factors are equally crucial in understanding diabetes mellitus type 2. Lifestyle choices, particularly your diet and physical activity levels, significantly influence your risk of developing this condition. For instance, obesity, especially visceral fat accumulation, is strongly linked to increased insulin resistance, which is often a precursor to diabetes. A study examining the long-term effects of intensive glycemic control revealed that while short-term results did not show a significant reduction in cardiovascular mortality, long-term follow-up indicated a potential decrease in major cardiovascular events. This suggests that lifestyle changes can offer delayed benefits, reinforcing the need for ongoing management strategies.
Additionally, recent research highlights the importance of understanding diabetes mellitus type 2 and how environmental factors, such as socioeconomic status and access to nutritious foods, can affect your risk of developing diabetes-related complications. These insights are essential for creating effective prevention strategies and emphasize the need for a comprehensive approach to managing this condition, considering both genetic and environmental influences. You're not alone in this journey, and understanding these factors can empower you to take proactive steps toward better health. Recent statistics also show that the integrated-discrimination-improvement method significantly enhances the prediction of future diabetes risk in various individuals, further illustrating the intricate relationship between genetics and environment in diabetes risk.
Discuss the Importance of Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
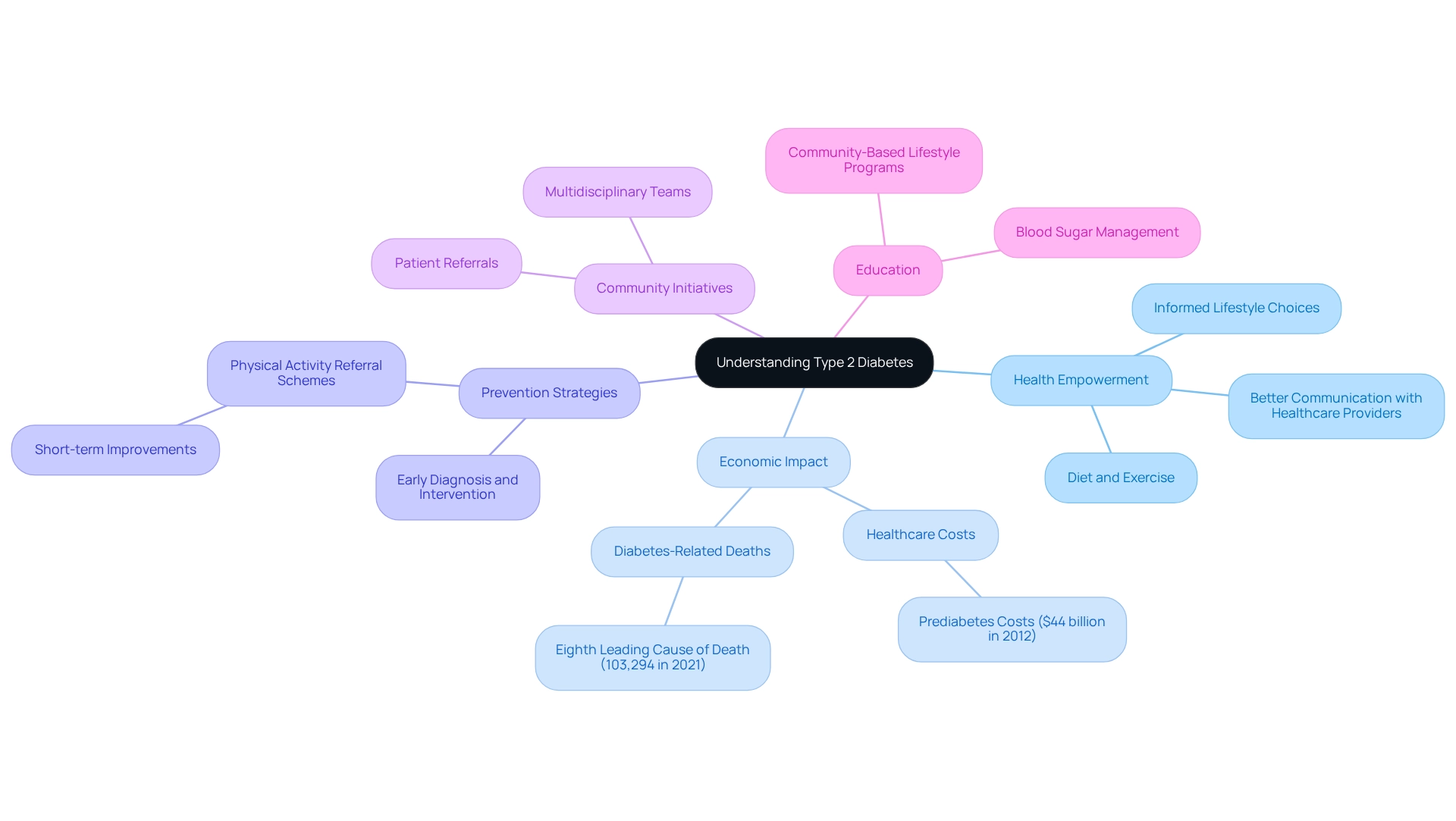
Understanding diabetes mellitus type 2 is essential for many reasons. It empowers individuals to take charge of their health through informed lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise. When people have knowledge of this condition, it can lead to earlier diagnosis and intervention, crucial steps in preventing complications like cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. By understanding diabetes mellitus type 2, which involves insulin resistance, patients can communicate better with healthcare providers, facilitating tailored treatment plans that meet their unique needs.
The financial burden of prediabetes in the U.S. was significant, amounting to $44 billion in direct healthcare expenses in 2012. This underscores the economic impact of managing this illness and the urgent need for effective strategies. In 2021, diabetes was the eighth leading cause of death in the United States, with 103,294 death certificates listing it as the underlying cause. Such statistics highlight the serious health risks associated with this condition, emphasizing that education and awareness are vital components of prevention strategies.
Recent public health initiatives have focused on improving awareness and understanding of diabetes mellitus type 2. Patients who are informed about their condition are more likely to adopt lifestyle changes that can significantly impact their health. For instance, physical activity referral schemes have shown promise in encouraging short-term improvements in patients' activity levels, illustrating the effectiveness of organized interventions.
Experts emphasize the importance of education regarding blood sugar management. Community-based lifestyle initiatives and multidisciplinary groups have been recognized as effective in fostering behavior change. As Karla I. Galaviz from the Emory Global Diabetes Research Center notes, partnering with community initiatives and establishing patient referrals are among the most promising approaches to enhance the management of this illness. By fostering a deeper understanding of diabetes mellitus type 2, individuals can make proactive choices leading to better health outcomes, ultimately contributing to the reduction of the chronic disease burden on society. You're not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
The complexities of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) highlight an urgent need for increased awareness and proactive management strategies. This chronic condition, characterized by insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels, is not merely a personal health issue; it’s a significant public health concern that impacts millions worldwide. Understanding the origins of T2DM—encompassing both genetic predispositions and environmental factors like lifestyle choices—is essential for effective prevention and management.
Education plays a vital role in empowering individuals to take charge of their health. By fostering a deeper understanding of T2DM and its risk factors, individuals can make informed choices regarding their diet and physical activity, ultimately reducing their risk of developing the disease. It’s also crucial to recognize the diabetes spectrum, which includes prediabetes and gestational diabetes, as this awareness enables early intervention strategies that can profoundly improve health outcomes.
As the prevalence of T2DM continues to rise, we must not overlook the economic burden associated with managing the condition. The necessity for community support and educational resources, such as those provided by T2DSolutions, underscores the importance of collaboration in addressing this epidemic. By prioritizing awareness, early diagnosis, and lifestyle modifications, we can navigate the challenges posed by T2DM with resilience and confidence.
In conclusion, the fight against Type 2 Diabetes requires a collective effort, emphasizing the importance of education, early intervention, and community support. By taking proactive steps and fostering a supportive environment, you can significantly impact your health and well-being. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; together, we can contribute to a healthier society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is diabetes mellitus type 2?
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a persistent metabolic condition characterized by insulin resistance and a relative shortage of insulin production, leading to increased blood glucose levels. Unlike Type 1 Diabetes, individuals with type 2 diabetes can produce insulin, but their bodies struggle to use it effectively.
What are the common risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes?
Common risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition.
What are some common symptoms of diabetes mellitus type 2?
Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. However, many individuals may not exhibit symptoms in the early stages.
What are impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG)?
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG) are critical warning signs indicating a high risk of progressing to diabetes mellitus type 2.
How has the medical cost for managing diabetes changed over the years?
The medical costs per person for managing diabetes have increased significantly from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022.
Why is there a call for a shift in healthcare resource allocation regarding diabetes?
There is a call for a shift in healthcare resource allocation towards the prevention of blood sugar-related conditions, emphasizing the importance of addressing lifestyle factors to manage and prevent diabetes mellitus type 2 effectively.
What role does T2DSolutions play for individuals diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2?
T2DSolutions aims to be a comprehensive resource hub for individuals newly diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2, providing educational materials and community support initiatives to empower them in their management journey.



