Overview:
An A1C level of 5.9 indicates prediabetes, which signifies elevated blood sugar levels that necessitate lifestyle changes to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes. The article emphasizes this classification by referencing guidelines from the American Diabetes Association, which categorize A1C values between 5.7% and 6.4% as prediabetes, underscoring the importance of proactive health management, dietary adjustments, and regular monitoring to mitigate health risks.
Introduction
Understanding an A1C level of 5.9% is crucial for individuals navigating the early stages of prediabetes. This reading serves as a warning sign, indicating that blood sugar levels are elevated yet not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
With nearly 97.6 million U.S. adults affected by prediabetes, recognizing the implications of this measurement is vital for fostering proactive health management. The article delves into effective strategies for addressing this condition, emphasizing the importance of:
- Lifestyle modifications
- Regular monitoring
- Community support
By exploring:
- Dietary changes
- Physical activity
- The significance of follow-up care
Individuals can take informed steps toward improving their health and reducing the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes.
Interpreting an A1C Level of 5.9: What It Means for Your Health
An A1C measurement of 5.9 means that it suggests prediabetes, indicating increased blood sugar values that are not sufficient to be categorized as a serious condition. The A1C test assesses average blood glucose readings over the preceding two to three months. According to guidelines from the American Diabetes Association, a1c 5.9 means that the individual has a reading that falls within the prediabetes range, as A1C levels ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes.
This classification is crucial as it enables individuals to recognize their risk factors and emphasizes the need for lifestyle changes to prevent the progression to type 2. The financial implications of managing this condition are significant, with excess medical costs per person rising from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022, highlighting the importance of early intervention. Recent studies highlight the alarming prevalence of prediabetes, with approximately 97.6 million U.S. adults aged 18 years and older affected as of 2021.
Moreover, information from 2017 to 2020 indicated that 38.0% of adults had prediabetes based on fasting glucose or A1C measurements. Acknowledging these statistics highlights the urgency for proactive wellness management, including the adoption of healthier lifestyle choices, which can significantly reduce the risk of developing a serious condition. For example, case studies have demonstrated that individuals who include regular physical activity and a balanced diet can reduce their A1C levels and enhance overall well-being.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to offering extensive resources, such as educational materials, workshops, and online forums, to assist those navigating their health journey. This community support helps empower patients with the knowledge they need for effective management. Furthermore, the crude rate for major cardiovascular disease hospital admissions declined from 82.0 per 1,000 in 2019 to 71.6 per 1,000 in 2020, indicating the positive influence of effective management of blood sugar levels on broader wellness outcomes.
Managing Your Health: Steps to Take After Receiving an A1C of 5.9
An A1C result of 5.9 means that there is a need for proactive health management. The first crucial step is to schedule a follow-up appointment with a healthcare provider to discuss the implications of this result and outline an appropriate action plan. It's important to note that risk factors for diabetes include:
- An HDL cholesterol concentration of less than 35 mg/dL
- A triglyceride measurement greater than 250 mg/dL
Implementing effective lifestyle changes is crucial; adopting a balanced diet that emphasizes whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can significantly impact blood sugar. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly is also recommended, as physical activity plays a vital role in glycemic control. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels allows individuals to track how their lifestyle choices impact their A1C results, fostering a better understanding of personal health dynamics.
T2DSolutions aims to support newly diagnosed patients by providing resources and education on understanding what A1C 5.9 means and its implications. Involvement in education programs related to blood sugar conditions can provide essential emotional support and practical strategies, easing the transition into proactive prediabetes management. As Chuck Henderson, the ADA’s chief executive officer, states, 'At the ADA, we are focused on improving the quality of care for anyone who lives with diabetes, prediabetes, or who is at risk of developing diabetes.'
These steps are not only aligned with the latest recommendations for managing prediabetes but also contribute to sustainable health improvements. Additionally, individuals with impaired glucose tolerance should consider the insights from case studies like the treatment of CFRD, where insulin therapy is crucial for achieving individualized glycemic goals.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up Testing
Upon receiving an A1C result of 5.9, it is important to understand what A1C 5.9 means and engage in consistent blood glucose monitoring. This can be accomplished through self-monitoring at home with a glucose meter or using continuous glucose monitoring systems, both of which offer valuable insights into daily fluctuations in blood sugar. Regular follow-up testing is generally suggested every three to six months to effectively monitor changes in A1C values.
This proactive strategy not only enables individuals to evaluate the effectiveness of their lifestyle modifications but also facilitates timely adjustments, illustrating what A1C 5.9 means. Regular blood glucose monitoring promotes a sense of control and awareness over one’s well-being, which is essential for managing prediabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, regular monitoring is a critical component in the ongoing assessment and management of blood sugar levels, reinforcing the importance of this practice in achieving long-term health outcomes.
Furthermore, individuals with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) should undergo lifelong screening for the development of prediabetes or related conditions at least every three years, as emphasized by the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee in their 2024 Standards of Care. Additionally, while community screening for this condition is generally not recommended due to follow-up challenges, it may be considered in specific situations with established referral systems, highlighting the complexities involved in screening and the need for targeted approaches.
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for diabetes education and community support, it aims to provide newly diagnosed patients with essential information and tools for effective A1C management and blood glucose monitoring, fostering a supportive environment for managing their health.
Dietary Changes to Support Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
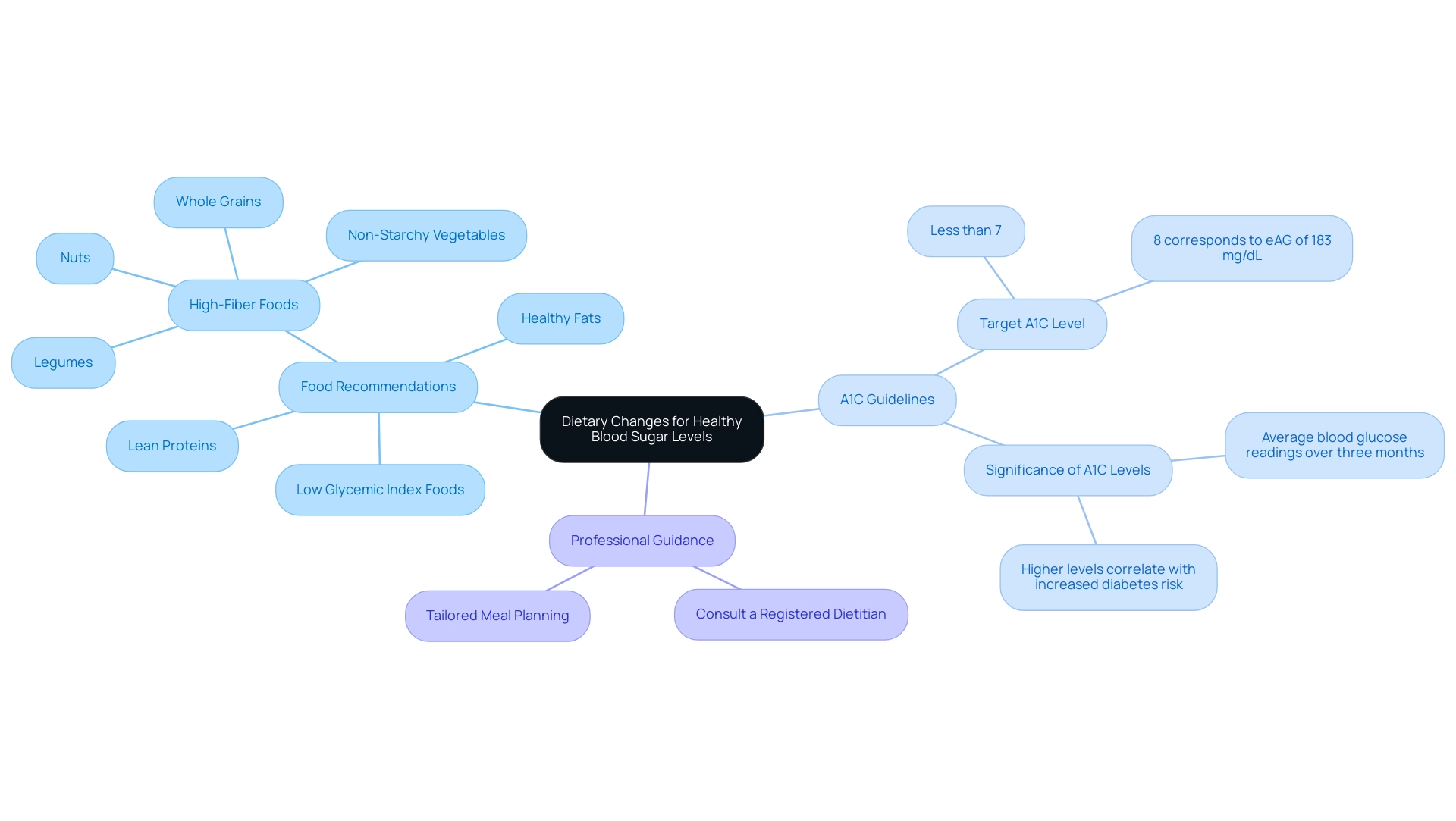
Dietary modifications play a crucial role in understanding what A1C 5.9 means for managing blood sugar levels. A well-rounded diet should emphasize high-fiber foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats while minimizing refined sugars and processed foods. Incorporating low glycemic index foods is especially advantageous for stabilizing blood sugar.
Recommended options include:
- Whole grains
- Legumes
- Nuts
- A variety of non-starchy vegetables
It's important to note that an A1C value of 8% or less corresponds to an estimated average glucose (eAG) value of 183 mg/dL or less, which provides a benchmark for understanding A1C levels in managing blood sugar. Furthermore, practicing portion control is vital to avoid overeating; individuals are encouraged to consume smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day.
As the American Diabetes Association states, 'the goal for most adults with diabetes is an A1C of less than 7%.' For tailored meal planning that aligns with personal health goals and preferences, consulting with a registered dietitian is advisable. Such professional guidance can ensure adherence to the latest dietary guidelines for effectively managing what A1C 5.9 means.
Furthermore, comprehending A1C test outcomes, as emphasized in the case study 'Understanding A1C and eAG Measurements,' indicates average blood glucose readings over three months, with elevated amounts relating to heightened risk of the condition, underscoring the significance of proper dietary management. As T2DSolutions launches as a comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management, it will provide valuable information and support for those navigating their dietary choices.
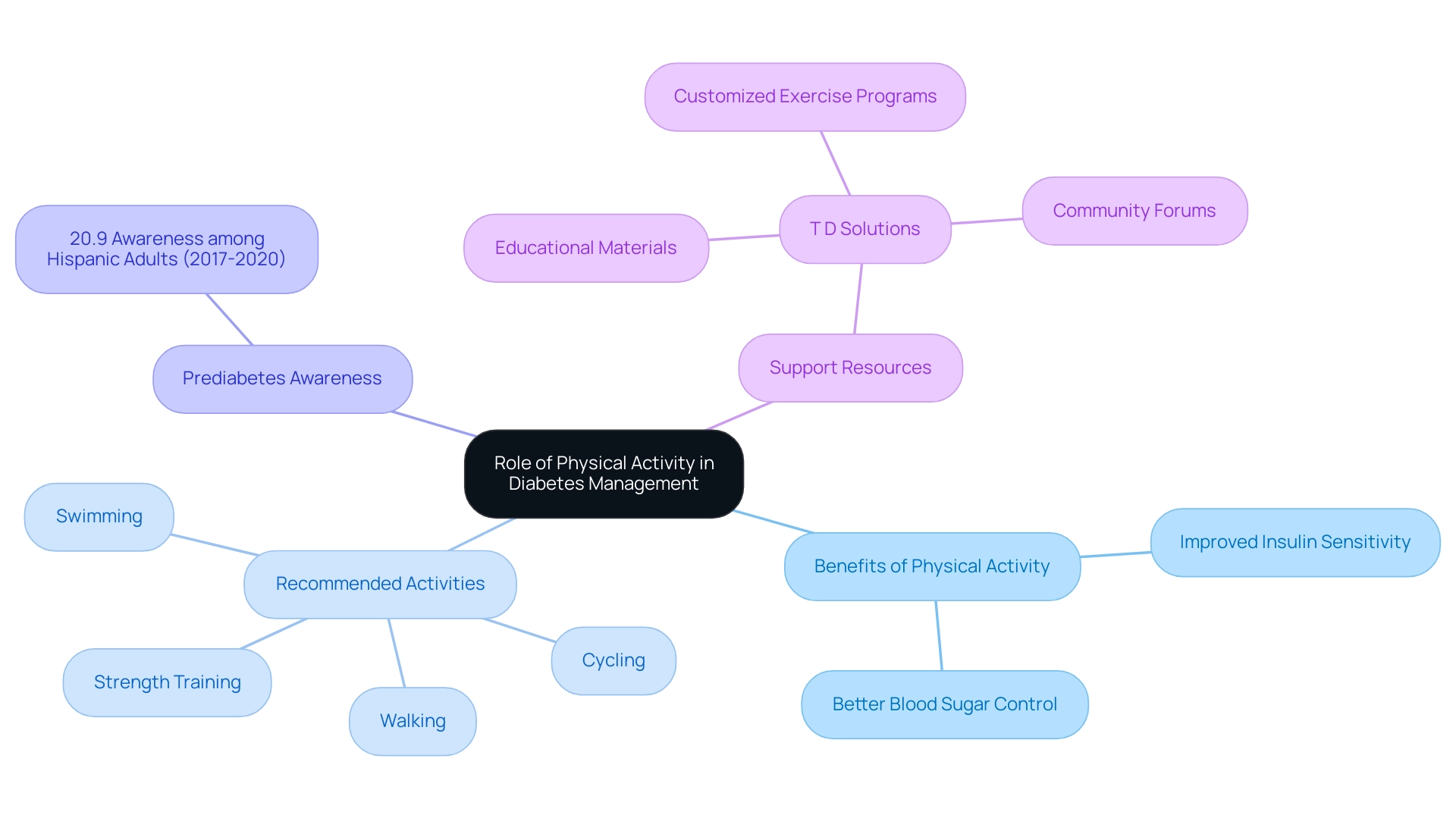
The Role of Physical Activity in Diabetes Management
Physical activity stands as a fundamental component in understanding what a1c 5.9 means for managing blood sugar levels. Engaging in regular exercise significantly enhances insulin sensitivity, enabling the body to utilize insulin more effectively, which ultimately contributes to improved blood sugar control. Notably, prediabetes awareness among Hispanic adults was reported at 20.9% from 2017 to 2020, underscoring the critical need for effective management strategies in this demographic.
Recommended activities include:
- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Strength training
All of which have demonstrated efficacy in managing diabetes. As wellness authorities advocate for a target of at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, complemented by muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days weekly, it is vital to emphasize that 'the role of physical activity in blood glucose control should be stressed to care providers and their patients.' Furthermore, integrating physical activity into daily life—such as opting for stairs over elevators or participating in active hobbies—can lead to substantial wellness benefits.
T D Solutions will act as a comprehensive resource center for newly diagnosed patients, providing educational materials on physical activity, community forums for support, and customized exercise programs to assist individuals in incorporating physical activity into their management plans. A systematic search process identified 6,346 potential records related to physical activity and diabetes, resulting in 126 studies included in a meta-analysis, which confirms the positive impact of consistent physical activity on diabetes management and overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
Recognizing an A1C level of 5.9% is a critical first step in addressing prediabetes. This measurement signals elevated blood sugar levels, prompting individuals to take proactive measures to prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes. Emphasizing lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and community support can significantly influence health outcomes.
Implementing dietary changes, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining consistent blood glucose monitoring are essential strategies for improving A1C levels. By focusing on a balanced diet rich in fiber and healthy fats, along with at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar and reduce health risks.
Furthermore, the importance of follow-up care and community resources cannot be overstated. Access to educational materials and support networks, such as those offered by T2DSolutions, empowers individuals to take control of their health journey. With nearly 100 million adults in the U.S. affected by prediabetes, understanding and acting on an A1C level of 5.9% is not just a personal health matter; it is a public health imperative. Taking informed steps today can pave the way for a healthier tomorrow, significantly reducing the risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications.



