Overview
An A1C of 6.7 indicates that your average blood glucose levels have been consistently elevated. This suggests a diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes and an increased risk for related health complications. It’s understandable to feel concerned about this result, but it’s important to know that you are not alone in this journey.
Understanding this metric is crucial for effective diabetes management. By making proactive lifestyle changes and regularly consulting with your healthcare provider, you can lower your A1C levels and reduce the risk of serious health issues. Remember, every small step counts, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Consider reaching out to a support group or a healthcare professional to discuss your feelings and options. Sharing your experiences can foster connection and help you feel less isolated. You have the power to take control of your health, and there are resources available to guide you through this process.
Introduction
In the journey of managing diabetes, understanding the importance of A1C testing is crucial. This essential measurement not only reflects your average blood sugar levels over the past few months but also serves as a key tool for both diagnosing and managing diabetes. With diabetes becoming increasingly common, grasping the implications of A1C levels can empower you to take control of your health.
From lifestyle changes to medication options, the path to effective diabetes management is multifaceted, intertwining your physical health with emotional well-being. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed, but remember that healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of regular monitoring and personalized care. A supportive network and informed strategies are vital for navigating the complexities of this chronic condition.
This article explores the nuances of A1C testing, offering insights into its role in diabetes management and the resources available for those affected. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key Metric for Diabetes
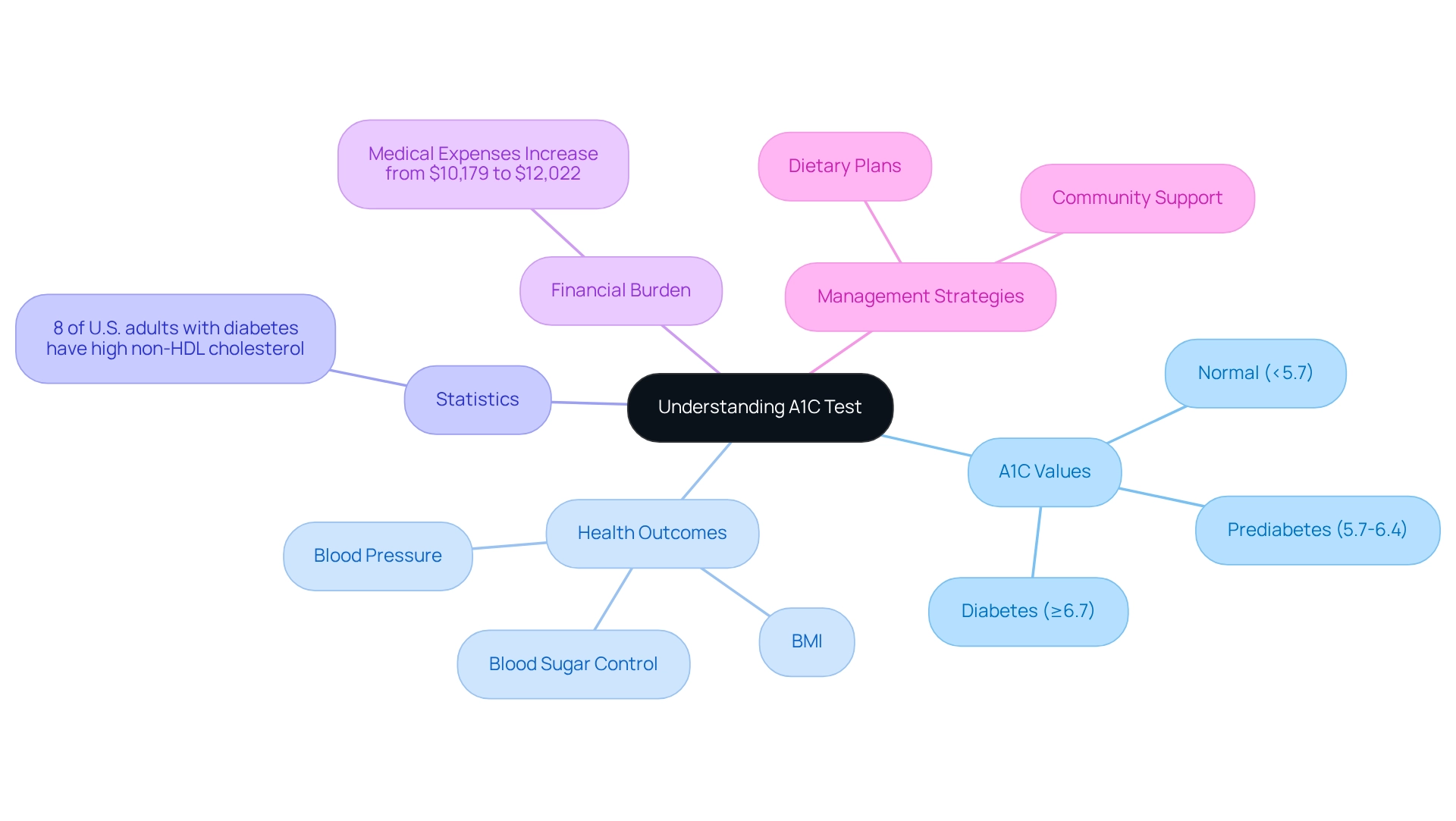
The A1C test, often referred to as the hemoglobin A1C test, is vital for assessing average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. This evaluation serves as a cornerstone for diagnosing and managing diabetes, offering crucial insights into how well blood sugar levels have been controlled over time. A1C values are expressed as a percentage, indicating the proportion of hemoglobin molecules in the blood that have glucose attached.
For those without diabetes, a normal A1C level is below 5.7%. Values ranging from 5.7% to 6.4% suggest prediabetes, while an A1C of 6.7% typically confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
Understanding what an A1C of 6.7% signifies is essential for effectively managing diabetes. For instance, a recent study titled 'Outcomes Assessment in Diabetes Care' involved 431 patients and examined various health outcomes related to blood sugar management, including changes in A1C values, blood pressure, and body mass index (BMI). This thorough investigation highlighted the importance of A1C testing in monitoring treatment effectiveness, while also considering demographic factors, medical history, health literacy, and emotional distress—all crucial for a comprehensive understanding of health care.
Current statistics indicate that approximately 8.0% of U.S. adults aged 18 and older with diagnosed diabetes have a non-HDL cholesterol level of 190 mg/dL or higher. This underscores the interconnectedness of diabetes management and cardiovascular health. Moreover, the financial burden of diabetes has risen, with average medical expenses per individual increasing from $10,179 in 2012 to $12,022 in 2022. This emphasizes the necessity for effective management strategies that encompass not only medical treatment but also lifestyle changes and mental health support, in line with 2 Solutions' comprehensive approach to education and community support.
At At&T Solutions, we are committed to providing a variety of resources, including informative articles, dietary plans, and community support groups, to help individuals manage their diabetes effectively. Experts recognize that understanding an A1C of 6.7% is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. Eyth E. states, 'Hemoglobin A1C is a valuable tool in managing metabolic disorders and other glycemic control issues, but it functions best in a collaborative healthcare team environment to be effective.'
This highlights the collaborative nature of blood sugar control, which is essential for guiding treatment decisions and lifestyle adjustments. Recent studies show that comprehending what an A1C of 6.7% means emphasizes the significance of A1C testing in accurately and reliably monitoring long-term glucose control. By understanding and consistently tracking A1C readings, individuals can make informed choices about their health, ultimately leading to better diabetes management and improved overall well-being.
Together, we can foster a supportive network that promotes resilience, hope, and an enhanced quality of life for all affected by diabetes.
What Does an A1C of 6.7 Indicate About Your Health?
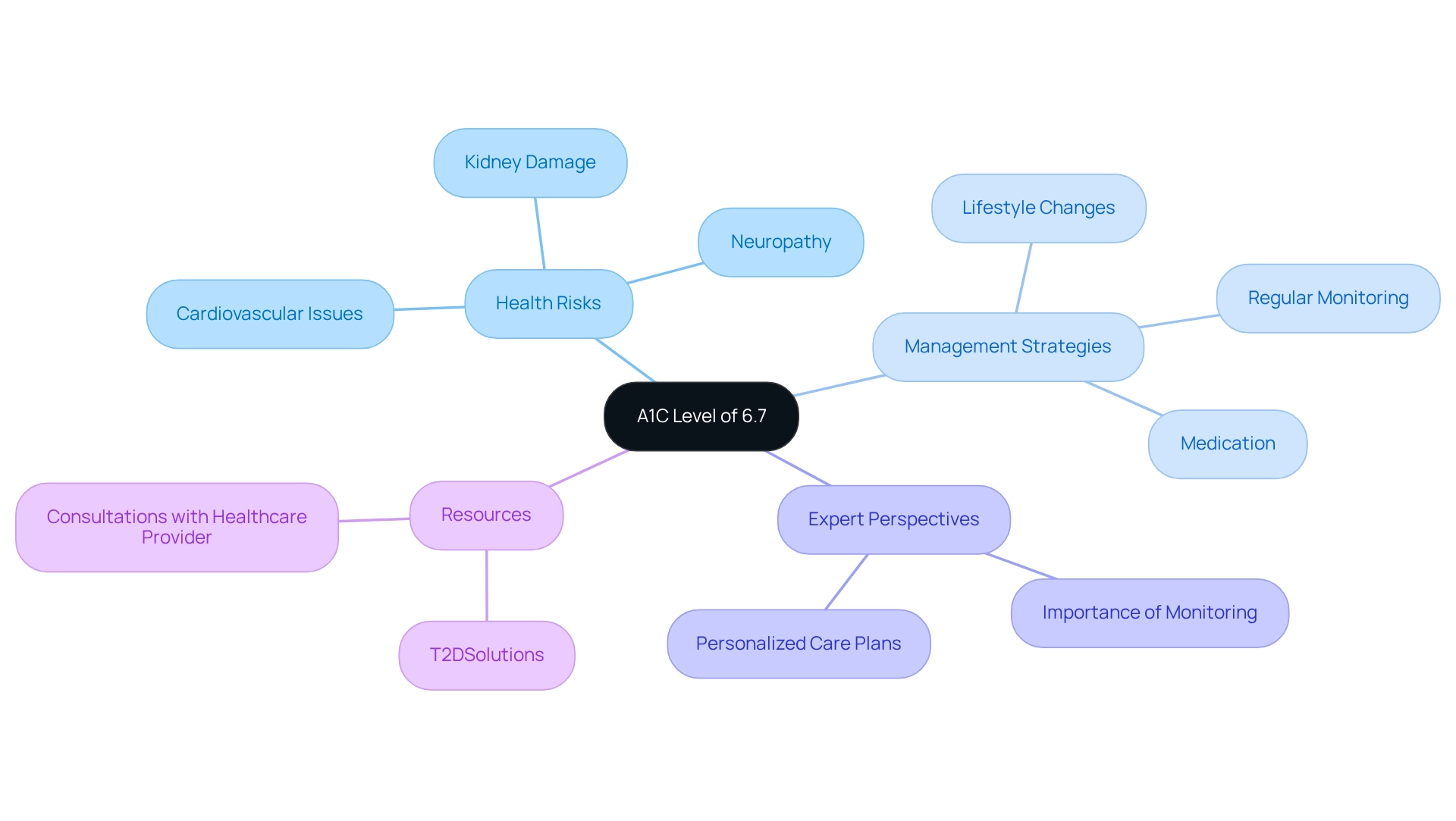
An A1C of 6.7 indicates that your average blood glucose levels have been consistently elevated over the past few months. This measurement falls within the glucose threshold, suggesting an increased risk for related complications if proactive measures are not taken. Specifically, an A1C of 6.7 signifies Type 2 conditions, requiring careful oversight through lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and possibly medication.
If you have this A1C measurement, it's important to prioritize consultations with your healthcare provider. Together, you can create a customized strategy aimed at lowering your A1C and reducing the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. Research shows that keeping an A1C under 7% can greatly reduce the risk of these complications, highlighting the significance of effective strategies for managing your condition. Ann L Albright, PhD, RD from the CDC notes, "Our findings suggest that an A1C range of 5.5 to 6.5% will capture a large portion of people at high risk, and if interventions can be employed to this target population, it may bring about significant absolute risk reduction."
Moreover, statistics reveal that a substantial percentage of individuals with an A1C of 6.7% face increased health risks, including a higher likelihood of developing serious conditions. For instance, studies show that individuals with an A1C of 6.7 are at a greater risk for cardiovascular issues, with the potential for long-term damage if not addressed promptly. The A1C test does not require fasting and can be conducted at any time during the day, assessing average blood sugar amounts over the previous three months. This makes it a useful tool for tracking your blood sugar management.
Real-life examples illustrate the challenges faced by those managing an A1C of 6.7. Many individuals have shared their experiences of making lifestyle modifications, such as improving eating habits and increasing physical activity. These changes have demonstrated success in lowering their A1C figures, leading to better blood sugar control. These strategies not only enhance blood sugar management but also contribute to your overall well-being.
The case study named "Understanding the A1C Test" emphasizes how this diagnostic tool assesses average blood sugar readings and helps identify individuals at risk of developing complications, as well as tracking treatment effectiveness for those already diagnosed.
Expert perspectives highlight the essential importance of understanding A1C values in blood sugar control. Endocrinologists advocate for regular monitoring and personalized care plans, emphasizing that early intervention can lead to significant health improvements. By taking proactive measures, you can effectively manage your condition and decrease the risk of complications associated with an A1C of 6.7.
Furthermore, T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource for individuals managing blood sugar levels. They provide educational materials, community support, and tools to help regulate A1C values effectively. We encourage you to explore T2 Solutions for more information and resources tailored to your diabetes care needs.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting A1C Levels: Diet, Exercise, and More
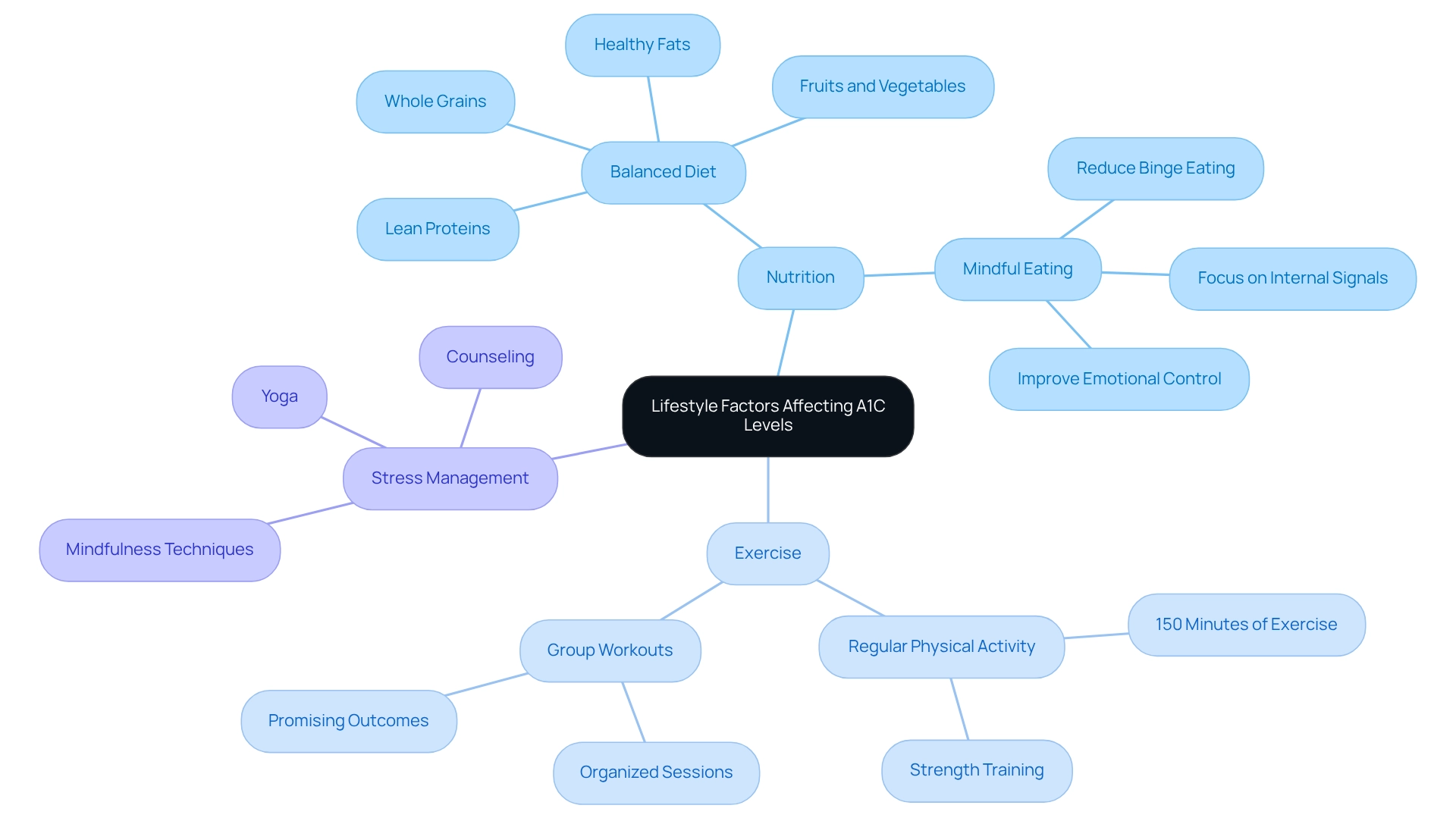
A range of lifestyle influences can significantly affect A1C readings, particularly nutrition, exercise, and stress management. Embracing a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables is crucial for stabilizing blood sugar. Studies show that dietary choices can greatly influence A1C; for instance, mindful eating habits have been linked to reduced binge eating and improved emotional control, both of which are beneficial for diabetes care.
Consider a case study on mindful eating: focusing on dining experiences and internal signals can lead to better diabetes management.
Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, not only enhances insulin sensitivity but also supports effective weight management—both essential for lowering A1C levels. Current exercise guidelines recommend aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, along with strength training on two or more days.
Managing stress is equally important, as heightened stress can cause blood sugar spikes. Techniques like mindfulness, yoga, and counseling can help alleviate these effects. By adopting a holistic approach that integrates these lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage their condition and achieve improved A1C results, reflecting what an A1C of 6.7 means for their health.
In real-world scenarios, exercise programs tailored for patients with this health issue have shown promising outcomes. For example, organized group workout sessions have led to significant improvements in A1C levels among participants, illustrating the tangible benefits of physical activity in managing blood sugar. As Nichola J. Davis, MD, MS, concluded in her study, there was no notable difference in weight or A1C change between participants following low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets over 12 months, highlighting the importance of personalized dietary recommendations.
Moreover, national and global guidelines emphasize the significance of these individualized approaches, underscoring that a comprehensive plan addressing nutrition, physical activity, and stress management is vital for optimal care. This is particularly relevant in the context of Type 3 Diabetes, which underscores the intricate relationship between this condition and cognitive health. T2DSolutions serves as a valuable resource for newly diagnosed patients, offering educational materials and community support to help them navigate these lifestyle changes effectively.
When to Consider Medication: Understanding Treatment Options
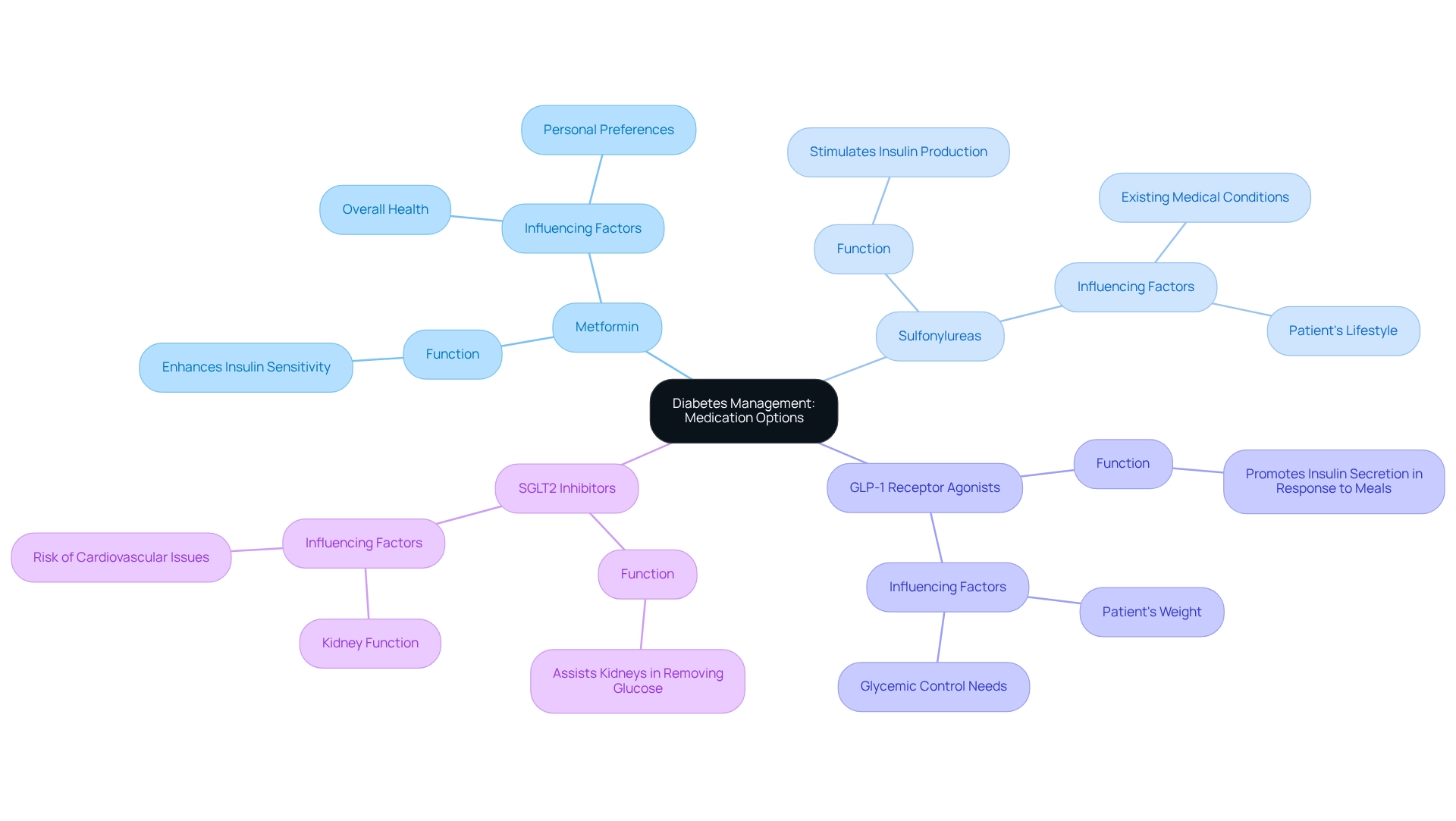
An A1C measurement of 6.7 can feel overwhelming, and it often indicates that lifestyle changes alone may not be enough for effective diabetes management. In these situations, healthcare providers typically recommend starting medication to help control blood sugar levels more effectively. Metformin is often the first-line treatment because it enhances insulin sensitivity, but there are other options available as well.
These alternatives include:
- Sulfonylureas, which stimulate insulin production
- GLP-1 receptor agonists that promote insulin secretion in response to meals
- SGLT2 inhibitors that assist the kidneys in removing glucose from the bloodstream
Choosing the right medication is influenced by several factors, including your overall health, any existing medical conditions, and personal preferences. For example, if your A1C is 6.7, you might benefit from a combination of metformin and a GLP-1 receptor agonist to achieve better glycemic control. Regular consultations with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your A1C levels and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Current statistics show that many individuals with diabetes are prescribed medications to manage their health effectively. As we look to 2025, the landscape of blood sugar management is evolving, with new medications and therapies emerging that offer improved outcomes for patients. Understanding what an A1C of 6.7 means is crucial for initiating medication at this level to prevent complications linked to the condition, such as vision loss and foot issues, which can lead to serious consequences like ulcers and amputations.
Indeed, those with high blood sugar levels face an increased risk of lasting vision impairment and foot problems, underscoring the importance of proper care.
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of these treatment plans. For instance, one patient with an A1C of 6.7% found that by starting a regimen that included metformin along with lifestyle modifications, they were able to reduce their A1C to 6.0% within six months. This highlights the significance of a personalized strategy for blood sugar control, where medication and lifestyle changes work together to improve health outcomes.
As Megan M Weemer noted, while the quality of care appears consistent across healthcare providers, there are notable differences in prescribing practices that can affect treatment effectiveness. Furthermore, the case study titled 'Diabetes as a Cause of Death' emphasizes that diabetes was the eighth leading cause of mortality in the United States in 2021, highlighting the urgent need for improved oversight and preventive strategies. The American Diabetes Association stresses that ongoing support and education are vital in navigating the complexities of blood sugar management.
At T2DSolutions, we are here for you. We strive to provide newly diagnosed individuals with the resources and assistance needed to understand their A1C figures and manage their condition effectively. Our platform offers educational materials, community support, and access to healthcare professionals to help you navigate your treatment options and make informed decisions about your health.
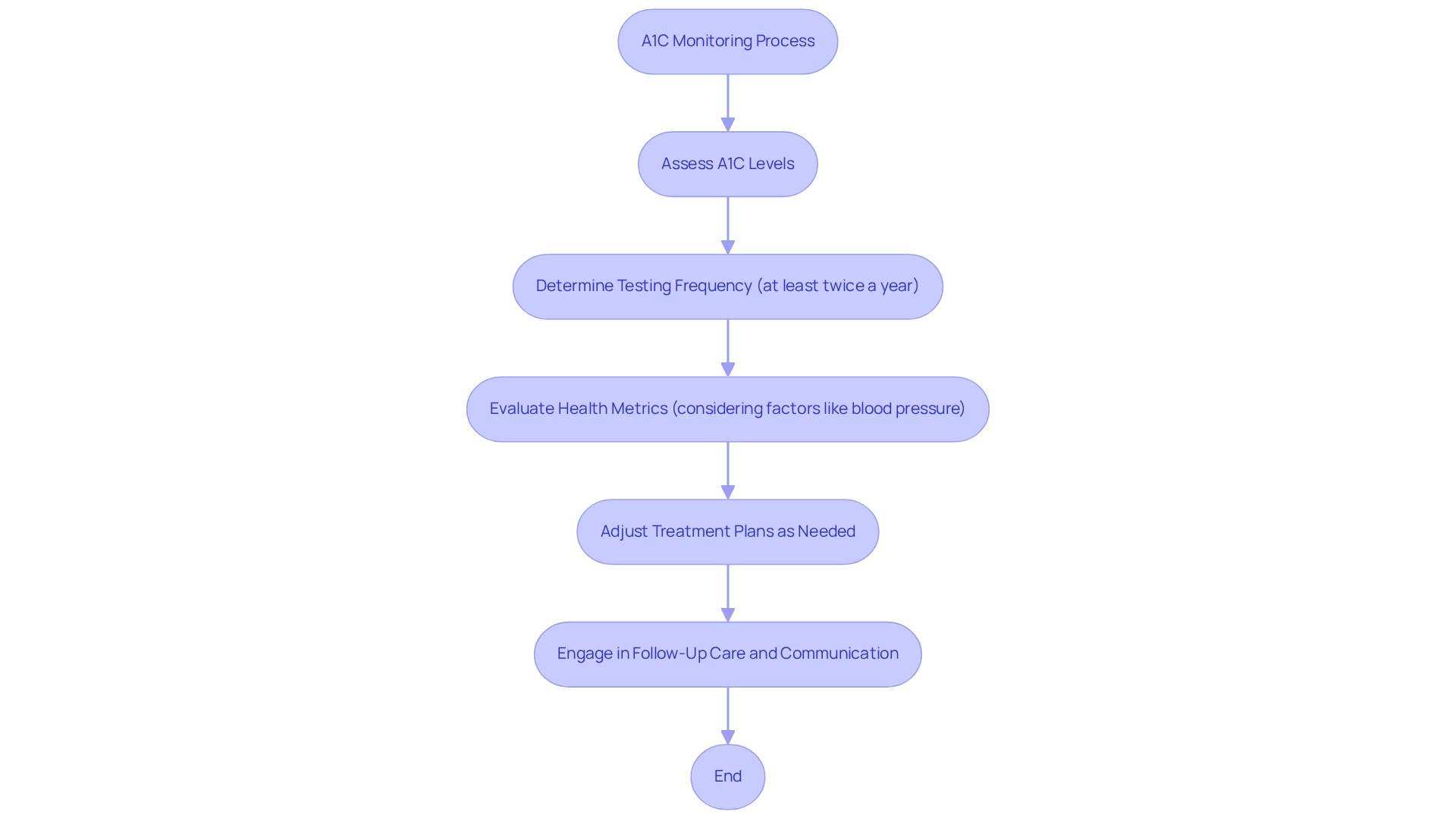
The Importance of Regular Monitoring and Healthcare Follow-Up
Consistent tracking of A1C values is essential for effective blood sugar control. An A1C of 6.7 indicates a critical level that requires attention. It's recommended that individuals facing blood sugar challenges undergo A1C testing at least twice a year. More frequent assessments may be necessary if treatment strategies change or if A1C readings fall outside the target range. This ongoing evaluation allows healthcare professionals to understand what an A1C of 6.7 signifies for the effectiveness of the current approach and make necessary adjustments to improve care.
Statistics reveal that many adults with elevated blood sugar levels experience high A1C figures, underscoring the importance of vigilant monitoring and tailored treatment plans. Among adults with this condition, 80.6% also have high blood pressure, emphasizing the interconnectedness of these health issues and the need for comprehensive care. Additionally, it’s crucial to recognize that falsely elevated HbA1c levels can result from factors such as iron deficiency anemia, hemoglobinopathies, and certain medications, which can influence the interpretation of an A1C of 6.7.
Routine follow-up visits present vital opportunities for patients to discuss challenges, gain insights into managing their condition, and stay updated on new treatment options. Experts stress that maintaining open communication with healthcare providers is key to achieving and sustaining optimal A1C levels. Health educators highlight that follow-up care is essential for ensuring patients remain engaged in their wellness journey and can effectively manage their health.
Gregory J. Norman points out that using personal continuous glucose monitoring (p-CGM) in adults not on insulin therapies is linked to improved glycemic control. This suggests it could be a valuable resource for healthcare providers to assist patients in reaching their glycemic objectives. Real-life stories illustrate the benefits of regular A1C monitoring. Patients who adhere to consistent testing schedules often report better outcomes, including improved glycemic control and a deeper understanding of their health metrics. As we approach 2025, the consensus remains that an A1C of 6.7 should prompt testing at least twice a year, with adjustments tailored to individual health needs and treatment responses.
This proactive approach not only enhances health oversight but also empowers individuals to take charge of their well-being. Furthermore, with 5,293 children and adolescents aged 10 to 19 newly diagnosed with type 2 conditions, the importance of early and consistent monitoring for all age groups cannot be overstated. As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for education and community support, it will offer essential tools and information for newly diagnosed patients.
By integrating A1C tracking into their management strategies, patients can leverage the resources provided by T2D Solutions to enhance their understanding and management of their condition. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
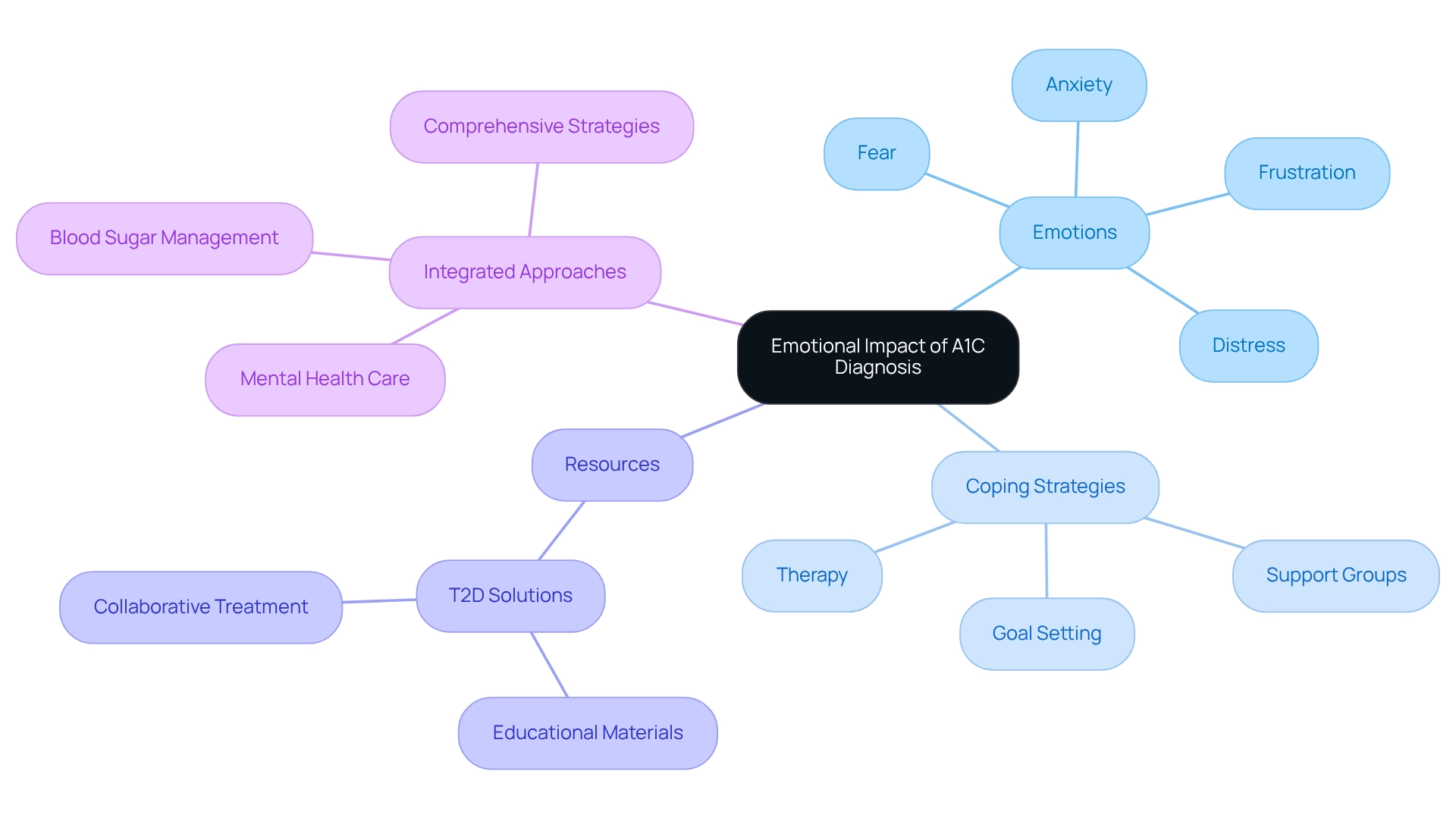
Coping with the Emotional Impact of an A1C Diagnosis
Receiving an A1C diagnosis can trigger a spectrum of emotions. An A1C of 6.7 often brings feelings such as fear, anxiety, and frustration. It's important to acknowledge and affirm these emotions as vital steps in managing your health journey. Research shows that between 33% to 50% of individuals with this condition experience distress, which can lead to unhealthy behaviors and neglect of self-care.
This emotional turmoil is distinct from depression and anxiety, highlighting the need for tailored approaches. Consulting with mental health professionals and establishing attainable goals can be beneficial.
Coping strategies can significantly enhance your emotional well-being. Joining support groups, engaging in therapy, or connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide invaluable support. T2D Solutions offers resources like support groups and educational materials to assist individuals in managing distress related to their condition.
For instance, collaborative treatment methods that combine mental health care with blood sugar management have shown promising results. By working alongside mental health experts, care teams can develop comprehensive strategies that address both physical and emotional health, fostering resilience and enhancing overall well-being. A case study titled "Collaborative Treatment for Diabetes and Mental Health" illustrates how such integrated approaches can effectively address both conditions, leading to improved patient outcomes.
The emotional impact of an A1C diagnosis is profound, especially when a 6.7 A1C means that individuals need to pay closer attention to their mental health and blood sugar control. Statistics indicate that the indirect impact of diabetes-related distress on depression is significant, with a partial mediation effect of -0.10 for the entire sample. This underscores the importance of addressing emotional challenges. Recognizing stress patterns can also aid in managing both blood sugar levels and mental health effectively.
By actively addressing these emotions, you can cultivate a more optimistic perspective on your health journey, ultimately leading to better management of your condition and an enhanced quality of life. As the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion emphasizes, "You're not alone—help is available!" This message reinforces the significance of seeking assistance and utilizing available resources, such as those offered by T2D Solutions, to navigate the challenges related to your condition.
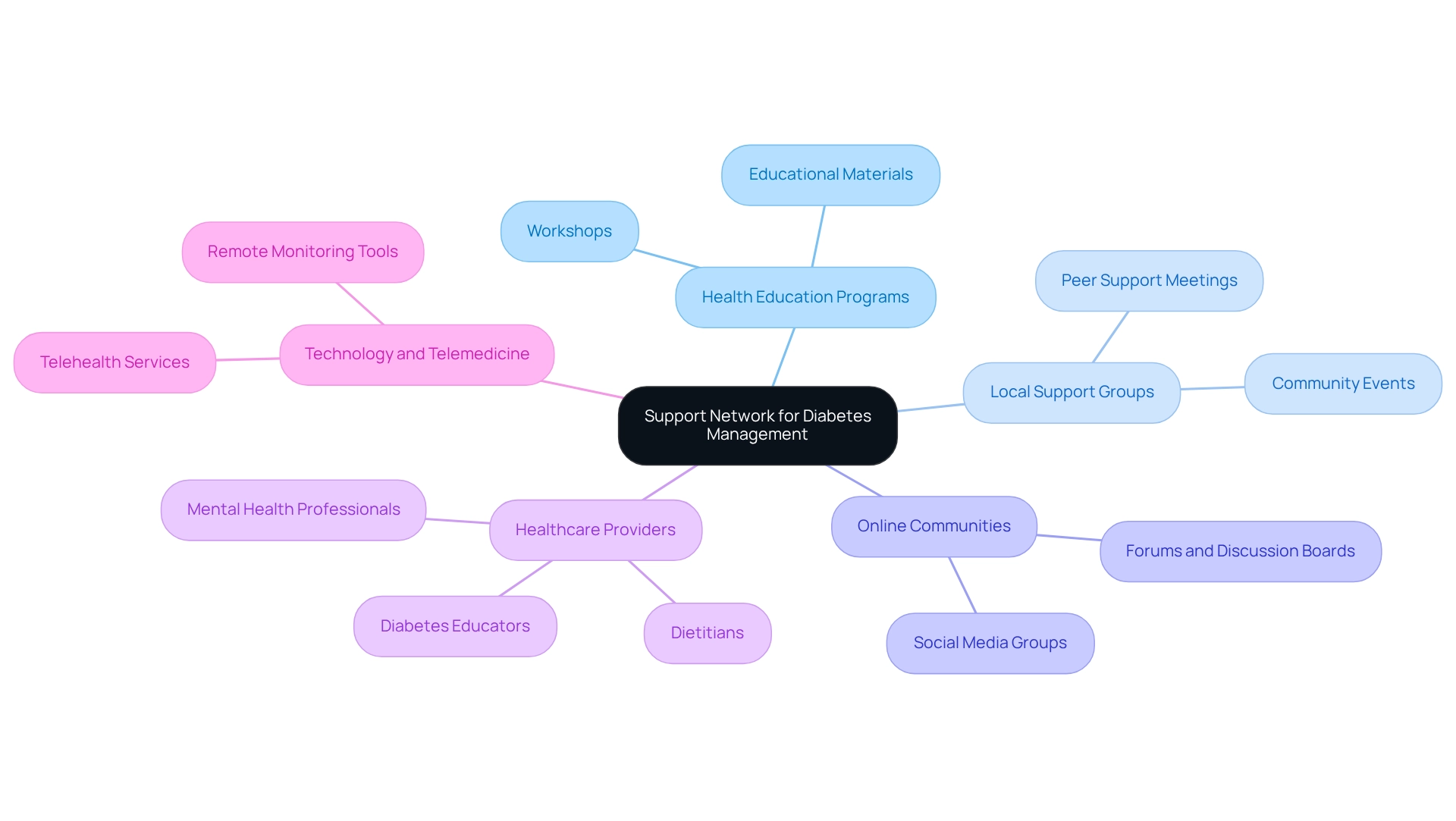
Building a Support Network: Resources for Diabetes Management
Creating a strong support system is vital for individuals navigating the challenges of diabetes. This network can encompass a variety of resources, such as health education programs, local support groups, and online communities where individuals can share their experiences and advice. Organizations like the American Diabetes Association, in collaboration with local health departments, often provide educational resources, workshops, and events specifically tailored to improve skills in managing this condition.
Healthcare providers play an essential role in connecting patients with specialists, including dietitians, educators, and mental health professionals focused on care. Engaging with a supportive community not only boosts motivation but also provides practical tips and fosters a sense of belonging. This collective involvement can greatly enhance outcomes related to blood sugar control.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed. For instance, between 2017 and 2018, approximately 5,293 children and teenagers were identified with type 2 blood sugar issues in the U.S. This underscores the pressing need for effective education and support systems, especially in at-risk groups. Moreover, the overall expense of blood sugar disorders in the United States reached $412.9 billion in 2022, highlighting the financial impact of care and the essential role of community resources in easing these challenges. Furthermore, statistics show that 8.0% of U.S. adults aged 18 years or older with diagnosed conditions had a non-HDL level of 190 mg/dL or higher, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive management strategies.
Real-life examples of community support networks illustrate their effectiveness in improving care. These networks provide not only emotional support but also practical resources that empower individuals to take charge of their health. As organizations focused on blood sugar regulation stress, the accessibility of educational programs and community resources is essential for promoting resilience and enhancing health outcomes for individuals managing the condition.
Finally, researchers are exploring the application of technology and telemedicine to help deliver care at a distance for rural communities, further enhancing the support available to individuals managing diabetes. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing diabetes effectively hinges on the pivotal role of A1C testing. This crucial metric not only provides insight into average blood sugar levels but also serves as a guiding tool for both diagnosis and ongoing management. Regular monitoring of A1C levels allows individuals to track their progress, make informed decisions about their health, and adapt lifestyle changes that are essential for effective diabetes care.
The journey toward better health is multifaceted, involving lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, as well as the potential need for medication. Emphasizing a holistic approach, including emotional well-being and community support, can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with diabetes. Resources like T2DSolutions provide valuable educational materials and support networks, enabling individuals to navigate their diabetes journey with confidence.
It's understandable to feel a range of emotions when faced with an A1C diagnosis. Acknowledging the feelings of distress that can accompany such a diagnosis is vital for fostering resilience. By building supportive networks and engaging in proactive management strategies, individuals can cultivate a healthier mindset, ultimately leading to improved diabetes management and overall well-being.
In conclusion, the importance of A1C testing and a collaborative approach to diabetes care cannot be overstated. With the right tools, resources, and support, you're not alone in this journey. Individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their health, reducing the risk of complications, and living fulfilling lives despite the challenges of diabetes. Embracing this journey with knowledge and community support lays the foundation for a brighter, healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the A1C test and why is it important?
The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, is essential for assessing average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is crucial for diagnosing and managing diabetes, providing insights into how well blood sugar levels have been controlled over time.
How are A1C values interpreted?
A1C values are expressed as a percentage. A normal A1C level is below 5.7%. Values from 5.7% to 6.4% indicate prediabetes, and an A1C of 6.7% typically confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
What does an A1C of 6.7% signify?
An A1C of 6.7% indicates that average blood glucose levels have been consistently elevated, suggesting an increased risk for complications associated with diabetes. It typically signifies Type 2 diabetes, requiring careful management through lifestyle changes, monitoring, and possibly medication.
What are the health risks associated with an A1C of 6.7%?
Individuals with an A1C of 6.7% are at a higher risk for serious health issues, including cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. Keeping an A1C under 7% can significantly reduce these risks.
How often should A1C testing be conducted?
Regular A1C testing is recommended to monitor blood sugar management effectively. It does not require fasting and can be performed at any time during the day, assessing average blood sugar levels over the previous three months.
What lifestyle changes can help lower A1C levels?
Making lifestyle modifications such as improving eating habits and increasing physical activity can help lower A1C levels. Many individuals have successfully reduced their A1C figures through these changes, leading to better blood sugar control.
What resources are available for individuals managing diabetes?
Resources such as educational materials, dietary plans, community support groups, and tools for regulating A1C values are available through organizations like At&T Solutions and T2DSolutions. These resources aim to assist individuals in managing their diabetes effectively.
What role do healthcare providers play in managing an A1C of 6.7%?
It is important for individuals with an A1C of 6.7% to consult with healthcare providers to create a customized management strategy aimed at lowering their A1C and reducing the risk of complications. Regular monitoring and personalized care plans are essential for effective diabetes management.
