Overview
Type 2 diabetes can be challenging, primarily leading to elevated blood glucose levels due to insulin resistance. This condition may result in serious long-term complications, including:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Kidney damage
- Diabetic neuropathy
It's understandable to feel concerned about these potential outcomes. These complications arise from prolonged hyperglycemia, which emphasizes the importance of making lifestyle modifications and engaging in regular monitoring. By taking these steps, you can significantly mitigate health risks and improve your quality of life. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; there are resources and support available to help you navigate these challenges.
Introduction
Type 2 Diabetes has emerged as a significant health concern, affecting millions worldwide and transforming lives in profound ways. This chronic metabolic disorder, characterized by insulin resistance, poses serious risks that extend beyond elevated blood sugar levels. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed as you grapple with the implications of this condition. Understanding its physiological effects, lifestyle adjustments, and potential long-term complications is critical.
With the prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes on the rise, the need for effective management strategies and community support is more urgent than ever. This article delves into the intricacies of Type 2 Diabetes, offering insights into its definition and the physiological ramifications of prolonged high blood sugar. It also discusses the lifestyle changes necessary for effective management. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; ongoing education and support can make a significant difference as you navigate this complex path. We are here to support you every step of the way.
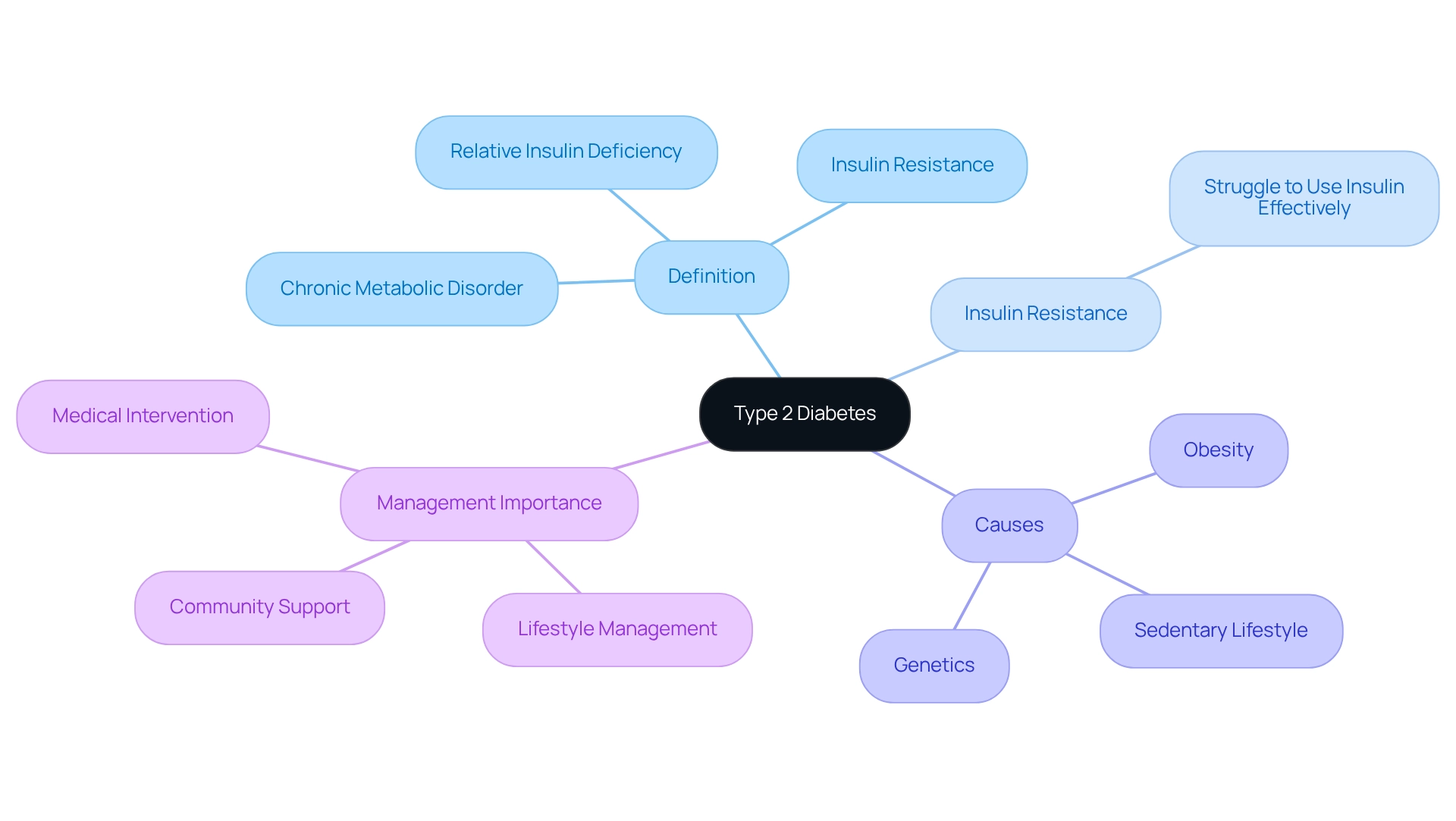
Define Type 2 Diabetes: An Overview
To understand what does type 2 diabetes do, it is important to recognize that it is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency, which leads to elevated blood glucose levels. Unlike Type 1 Diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin, what Type 2 Diabetes does is allow individuals to generate insulin, but their bodies struggle to use it effectively. This condition, often linked to factors such as obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetics, prompts the question of what does type 2 diabetes do. It’s important to recognize what does type 2 diabetes do, as it is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90-95% of all cases. Understanding this definition is essential, as it emphasizes the significance of lifestyle management and medical intervention in controlling the disease.
At T2DSolutions, we genuinely care about your journey with Type 2 Diabetes. We are committed to empowering individuals like you by providing comprehensive resources and community support. You're not alone in this journey; together, we can help you manage your condition effectively and improve your quality of life. Remember, seeking support is a vital step, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Examine the Physiological Effects of Type 2 Diabetes
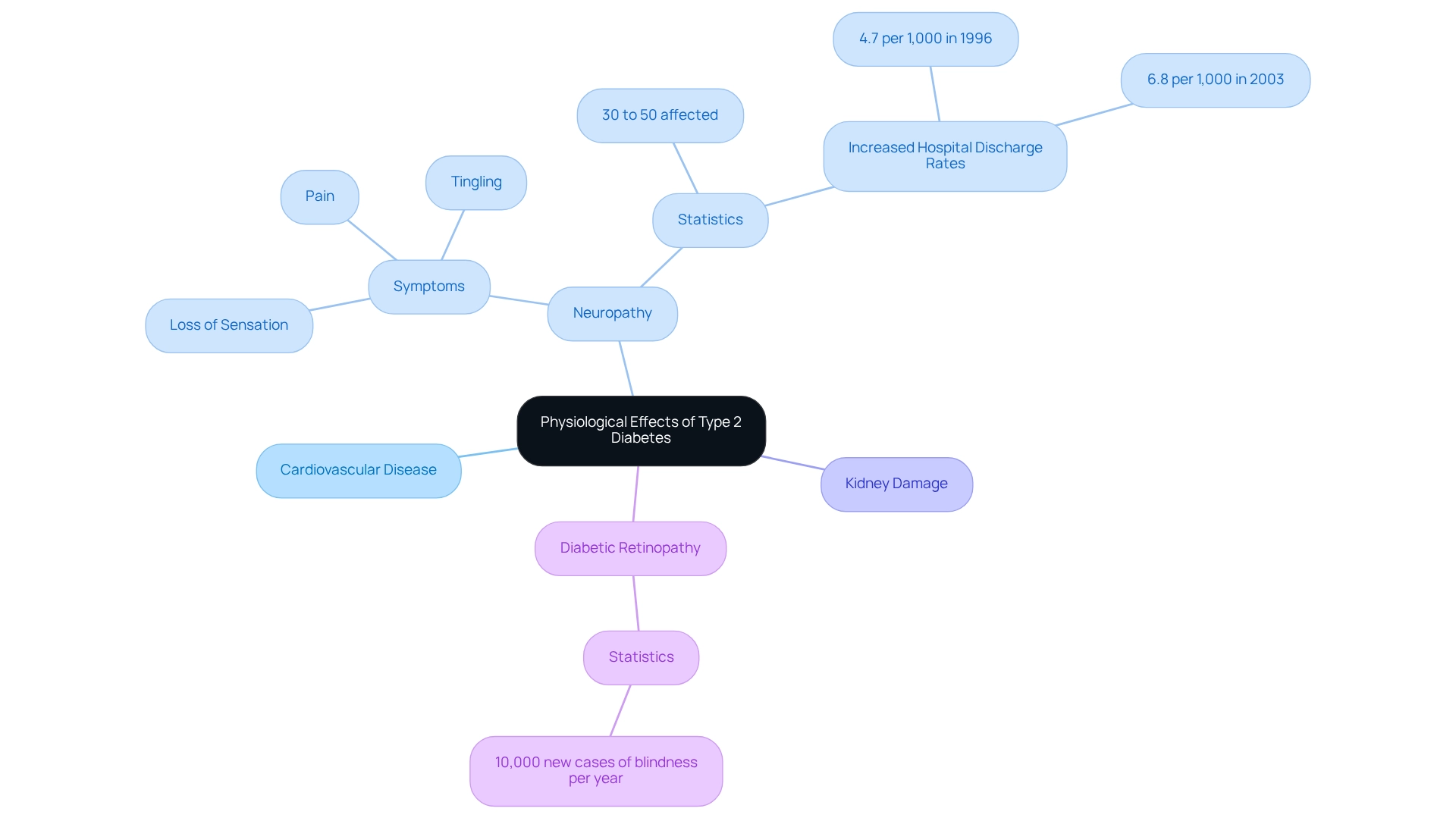
There are concerning physiological effects related to what does type 2 diabetes do, which primarily arise from prolonged elevated sugar levels. These levels can harm vessels and nerves throughout the body, leading to various health issues. For instance, cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage are common complications. Elevated glucose levels can cause the blood vessels in the eyes to swell, resulting in diabetic retinopathy. This is the most prevalent microvascular issue among those with high blood sugar, leading to over 10,000 new cases of blindness each year.
Additionally, nerve damage, known as diabetic neuropathy, affects around 30% to 50% of individuals with this condition. Symptoms can include pain, tingling, or loss of sensation in the extremities. It's understandable to feel worried about these symptoms, as they are primarily caused by hyperglycemia and can increase the risk of foot ulcers and amputations. The disability from lower extremity amputations can be a serious outcome of these complications.
Hospital discharge rates for diabetic peripheral neuropathy have risen from 4.7 per 1,000 individuals with the condition in 1996 to 6.8 per 1,000 in 2003. This increase indicates a growing awareness of this complication and the need for improved management strategies. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise—from 16.2 million diagnosed cases in 2005 to a projected 48.3 million by 2050—it becomes increasingly vital to understand what does type 2 diabetes do and its physiological effects. By recognizing the implications of elevated glucose levels, you can appreciate the importance of keeping your sugar within target ranges. This proactive approach can help reduce serious health risks. The impact of elevated glucose levels on health is profound, with complications extending beyond immediate symptoms to long-term consequences that can significantly influence your quality of life. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Discuss the Lifestyle Implications of Living with Type 2 Diabetes
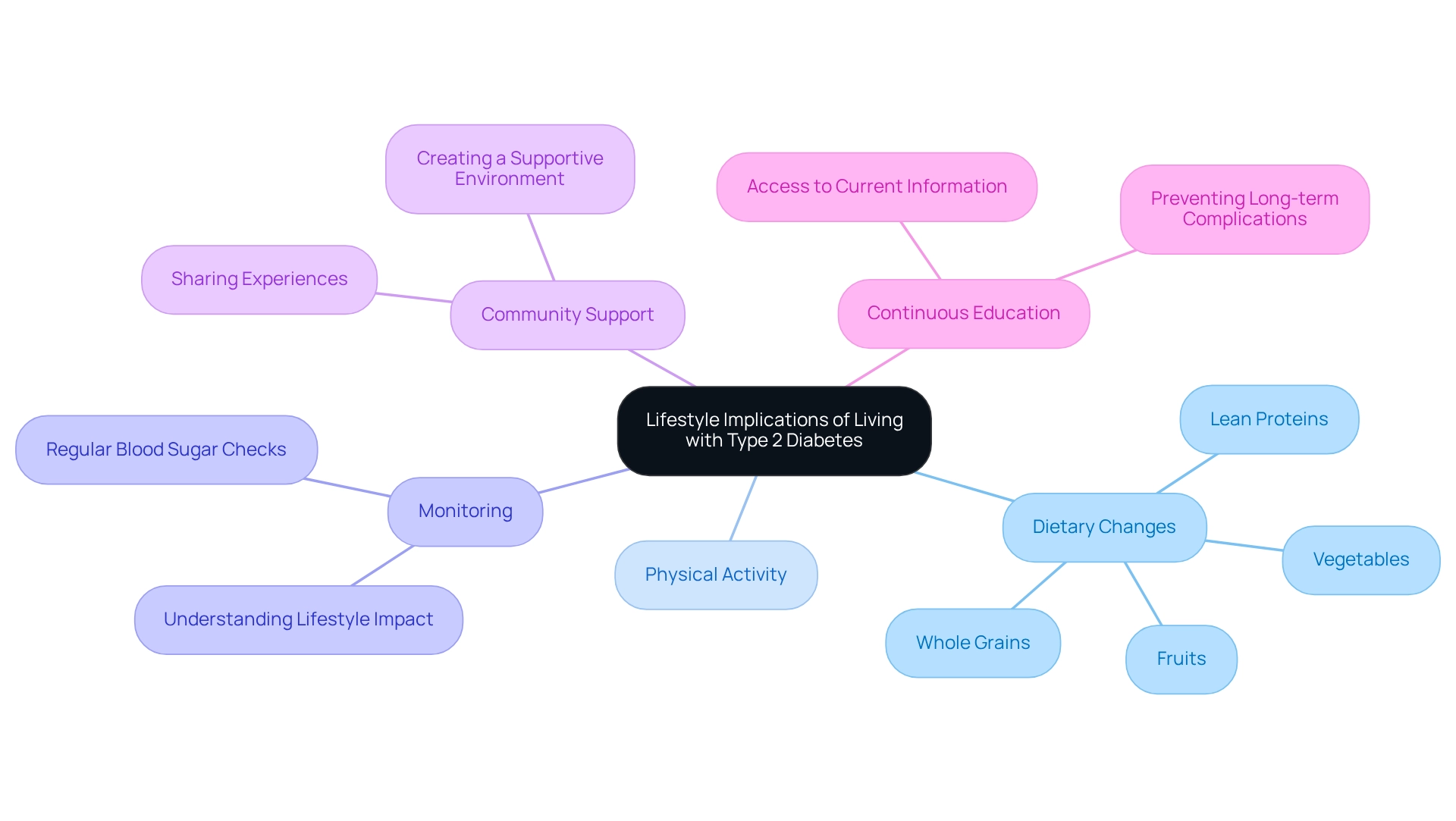
Living with Type 2 Diabetes can feel overwhelming, and it's important to understand what does type 2 diabetes do, but remember that you're not alone in this journey. Making substantial lifestyle modifications is essential, including dietary changes, regular physical activity, and continuous monitoring of glucose levels. In recent years, the occurrence of this condition has risen significantly, largely due to the increase in obesity and inactive lifestyles. This highlights the need for embracing healthier habits together.
Patients are encouraged to adopt a balanced diet rich in:
- Whole grains
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Lean proteins
while minimizing processed foods and sugars. It's understandable to feel challenged by these changes, but regular exercise is also crucial. It helps improve insulin sensitivity and aids in weight management, making a positive impact on your health.
Additionally, learning to monitor blood sugar levels regularly can empower you to understand what does type 2 diabetes do and how your lifestyle choices affect your condition. These lifestyle modifications not only assist in controlling blood sugar levels but also illustrate what does type 2 diabetes do by enhancing your overall well-being and reducing the chances of complications. As Peter M. House aptly stated, "Diabetes is not a burden, but a lesson in perseverance and self-care."
Community support plays a vital role in managing this condition. Sharing experiences and strategies can create a nurturing atmosphere where individuals feel connected and supported. By cultivating this sense of community, we can reinforce the idea of what does type 2 diabetes do in terms of being a shared path toward better health outcomes.
Continuous education is crucial, ensuring that you have access to the most current information and resources to manage your condition effectively. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way, and together we can navigate this journey toward a healthier life.
Identify Long-Term Complications Associated with Type 2 Diabetes
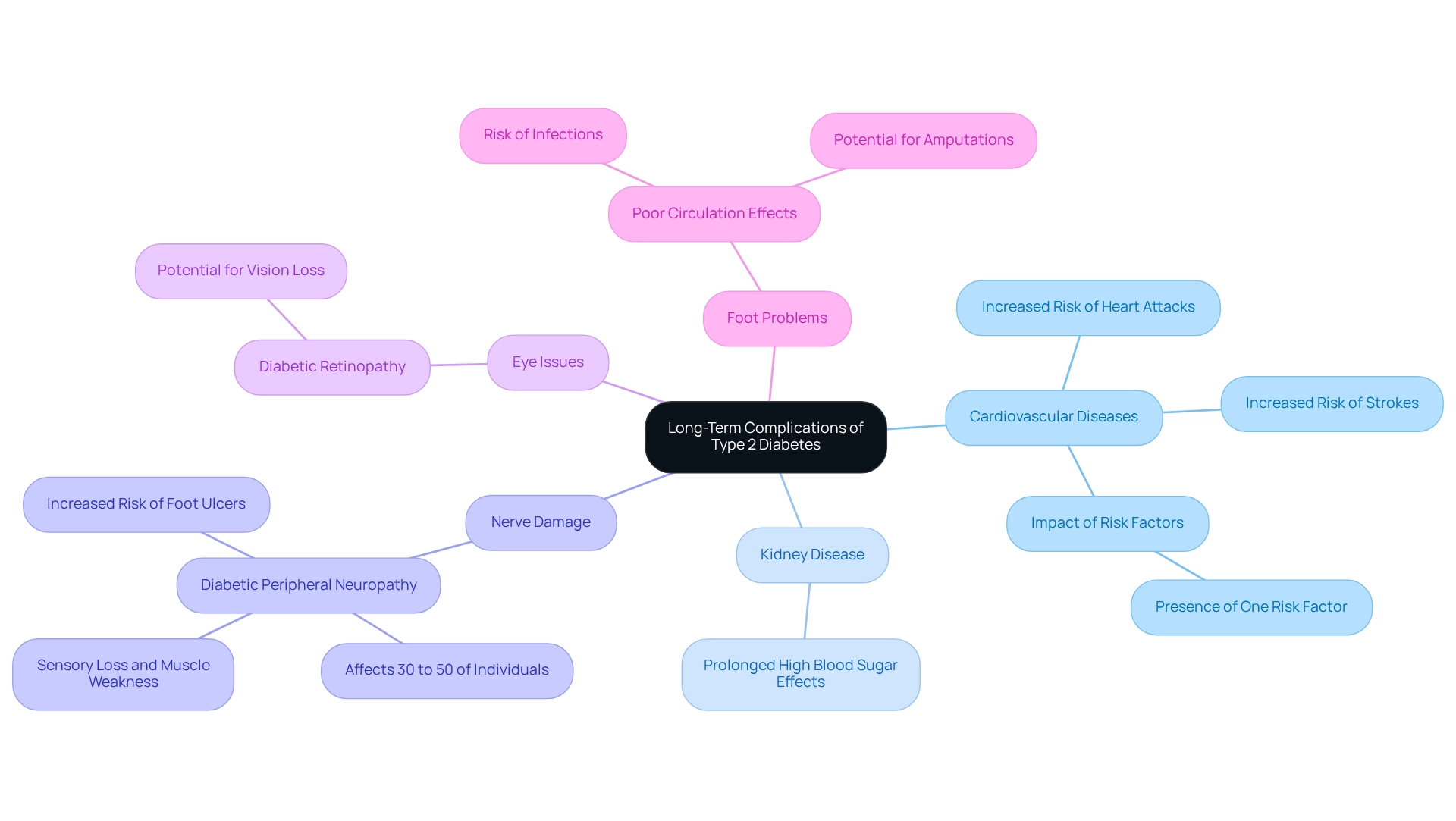
Long-term issues associated with Type 2 Diabetes can be both severe and life-altering, leading to the question of what does type 2 diabetes do to significantly affect your quality of life. Among the most critical complications are cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, which are common among individuals with blood sugar issues. It’s understandable to feel concerned, especially considering that statistics suggest individuals with this condition face an increased risk for these ailments. Recent discoveries emphasize that having even one cardiovascular risk factor can lead to worse health outcomes compared to those without this illness.
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource hub for education on diabetes-related conditions, it aims to provide the support and information you need to manage these risks effectively. Kidney disease is another serious issue, often resulting from prolonged high blood sugar levels. Additionally, nerve damage, or diabetic neuropathy, impacts 30% to 50% of people with the condition, leading to sensory loss, muscle weakness, and a heightened risk of foot ulcers. The increase in hospital discharge rates—from 4.7 per 1,000 individuals with the condition in 1996 to 6.8 per 1,000 in 2003—indicates a growing awareness of its impact on healthcare usage.
Eye issues, such as diabetic retinopathy, can also arise, potentially leading to vision loss. Foot problems due to poor circulation and nerve damage can result in infections and, in severe cases, amputations. As we consider what does type 2 diabetes do, it's important to note that the likelihood of experiencing these issues increases with the length of the condition and inadequate blood sugar management. Therefore, awareness of these potential complications underscores the necessity for effective management strategies and regular medical check-ups to monitor and mitigate risks. It’s crucial to take a proactive approach to diabetes care.
At T2DSolutions, we are here to support you every step of the way, providing resources and guidance to help you navigate these challenges. Remember, you're not alone in this journey.
Conclusion
Type 2 Diabetes is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive understanding of its effects, management, and long-term implications. This article has explored the definition of Type 2 Diabetes, highlighting its prevalence and the critical role of lifestyle management in controlling the disease. The physiological effects of prolonged high blood sugar levels can lead to severe complications, including cardiovascular issues, neuropathy, and kidney damage. It's essential to maintain blood sugar within target ranges to prevent these outcomes.
Living with Type 2 Diabetes necessitates significant lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity. These adjustments not only help manage the condition but also improve overall well-being. Remember, community support and ongoing education are vital components of effective diabetes management. Sharing experiences reinforces the notion that you are not alone in your journey.
Awareness of the long-term complications associated with Type 2 Diabetes, such as heart disease and vision loss, is crucial for proactive care. By prioritizing effective management strategies and regular check-ups, you can mitigate risks and enhance your quality of life. The journey with Type 2 Diabetes may be challenging, but with the right resources, support, and knowledge, it is possible to lead a healthy and fulfilling life. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
How does Type 2 Diabetes differ from Type 1 Diabetes?
Unlike Type 1 Diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin, individuals with Type 2 Diabetes can generate insulin but struggle to use it effectively.
What are the common causes of Type 2 Diabetes?
Common causes of Type 2 Diabetes include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors.
What percentage of diabetes cases does Type 2 Diabetes account for?
Type 2 Diabetes accounts for approximately 90-95% of all diabetes cases.
Why is it important to understand Type 2 Diabetes?
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes is essential as it emphasizes the significance of lifestyle management and medical intervention in controlling the disease.
How can individuals manage their Type 2 Diabetes?
Individuals can manage their Type 2 Diabetes through lifestyle changes and medical intervention, with support from resources and community groups like T2DSolutions.



