Overview:
The A1C test, also known as glycated hemoglobin, is a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months, which is essential for diagnosing diabetes and monitoring long-term glycemic control. The article emphasizes that understanding A1C values and their classifications—normal, prediabetes, and diabetes—enables individuals to manage their blood sugar effectively and informs treatment decisions, thus highlighting its importance in diabetes management.
Introduction
The A1C test stands as a cornerstone in the management and diagnosis of diabetes, providing essential insights into an individual's blood glucose levels over time. This critical tool not only aids in identifying diabetes and prediabetes but also plays a pivotal role in monitoring long-term glycemic control for those already diagnosed.
With the increasing prevalence of diabetes and its associated complications, understanding A1C levels has never been more vital. As healthcare providers and patients navigate the complexities of diabetes management, the significance of personalized care strategies, informed by A1C results, becomes paramount.
This article delves into the intricacies of the A1C test, exploring its implications for diagnosis, treatment, and the factors that can influence its accuracy, ultimately equipping readers with the knowledge necessary for effective diabetes management.
Understanding the A1C Test: A Key Indicator of Diabetes
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support. Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes is an essential aspect of managing blood sugar effectively. The A1C test, clinically known as glycated hemoglobin or HbA1c, is an essential diagnostic instrument that assesses the average blood glucose amounts over the prior two to three months.
This test is essential for diagnosing both blood sugar disorders and prediabetes, as well as for monitoring long-term glycemic control in individuals already diagnosed with these conditions. By providing a percentage that reflects the proportion of hemoglobin molecules with glucose attached, the A1C test offers a clear indication of how effectively blood sugar concentrations have been managed. As highlighted by the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, 'Higher A1C values are associated with health complications, so achieving and sustaining your target is essential for living well with this condition.'
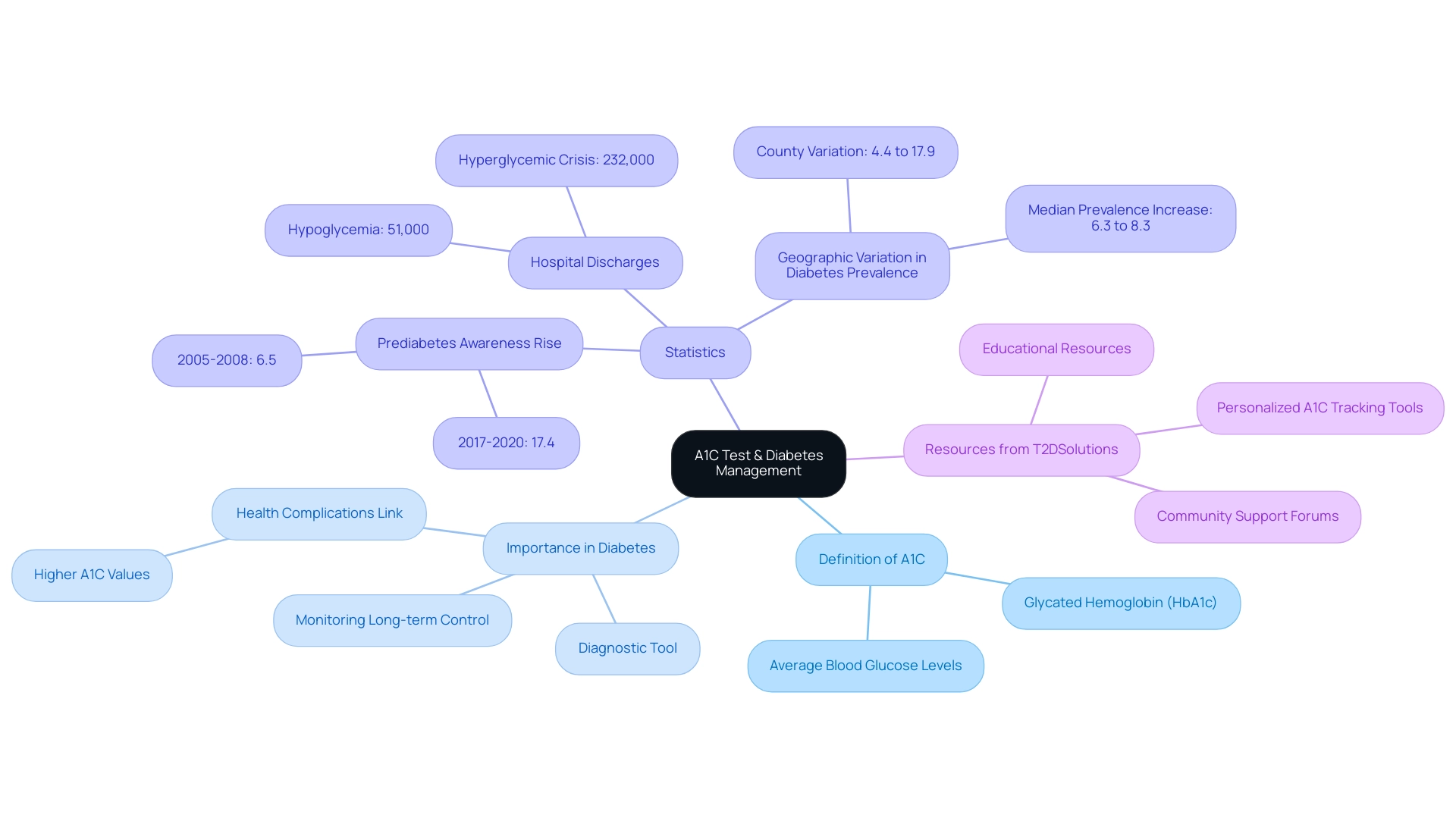
Therefore, achieving and maintaining target A1C levels is vital for living well with this condition. Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes is essential for anyone engaged in managing blood sugar conditions since it not only acts as a key metabolic health indicator but also informs treatment effectiveness. T2DSolutions will provide a range of features, including educational resources, community support forums, and personalized A1C tracking tools, to help patients in managing their condition effectively.
Recent statistics suggest that the awareness of prediabetes has significantly risen from 6.5% in 2005-2008 to 17.4% in 2017-2020, emphasizing the increasing acknowledgment of the significance of monitoring A1C values in managing this condition. Additionally, the case study titled 'Geographic Variation in Diagnosed Diabetes Prevalence (2021)' illustrates how diagnosed condition prevalence varies by county, underscoring the need for localized public health interventions. Furthermore, the urgency of monitoring A1C readings is emphasized by the fact that in 2020, there were 232,000 hospital discharges for hyperglycemic crisis and 51,000 for hypoglycemia.
T2DSolutions aims to assist patients in navigating these critical aspects of managing their condition.
Interpreting A1C Levels: What They Mean for Diabetes Diagnosis
The a1c definition of diabetes includes specific thresholds into which A1C values are classified, playing an essential role in diagnosing and managing blood sugar conditions. According to the American Diabetes Association, the A1C definition of diabetes states that:
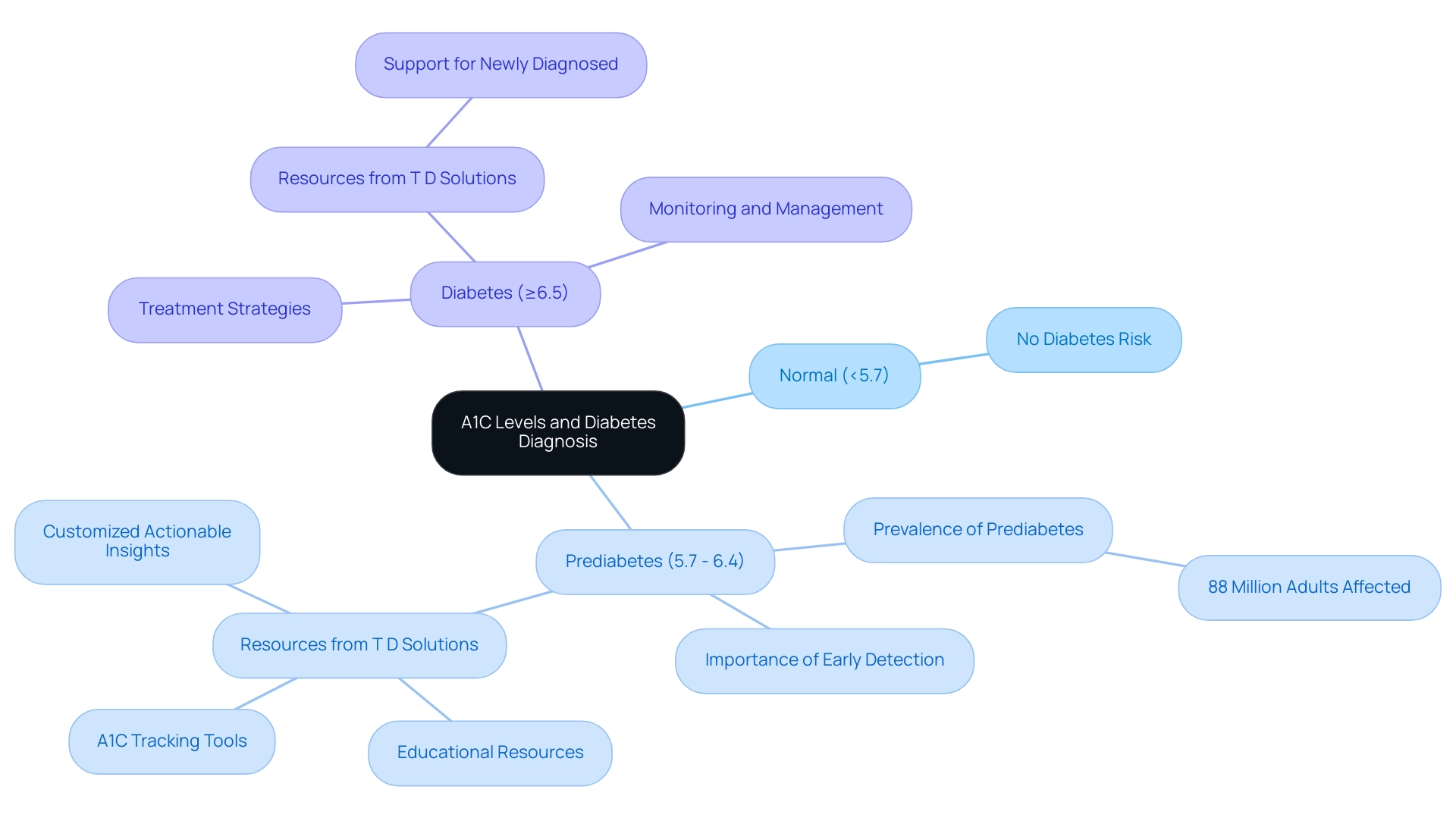
- An A1C below 5.7% is categorized as normal
- Values between 5.7% and 6.4% signify prediabetes
- 6.5% or above indicates the condition
These established thresholds are essential for understanding the a1c definition of diabetes and its relation to glucose metabolism disorders.
Approximately 88 million adults in the United States have prediabetes, underscoring the importance of early detection and intervention. At T D Solutions, we strive to offer recently diagnosed individuals with extensive resources and assistance to help them comprehend their A1C values and manage their condition efficiently. This encompasses:
- Educational resources
- Tools for tracking A1C measurements
- Actionable insights customized to personal needs
Regular monitoring is vital, not only for diagnosing these conditions but also for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment strategies over time. By comprehending and analyzing the A1C definition of diabetes, individuals and healthcare professionals can adopt essential lifestyle adjustments and measures to effectively manage or prevent the condition. T D Solutions is dedicated to being a valuable asset in this journey, assisting individuals in managing their condition with confidence.
Factors Affecting A1C Accuracy: Understanding Limitations
Welcome to T2DSolutions, a brand new resource hub that is currently in development, dedicated to educating and supporting individuals diagnosed with Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar conditions. We invite you to subscribe to our updates and stay informed as we prepare to launch our comprehensive information and community support platform. Our mission is to empower patients as they navigate their management journey for the condition.
Understanding the A1C definition of diabetes is essential for efficient management of blood sugar. The accuracy of A1C test results is influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Hemoglobin variants
- Specific medical conditions like anemia and kidney disease
- Ethnic backgrounds
Research indicates that individuals with sickle cell disease may exhibit falsely low A1C levels due to alterations in hemoglobin structure.
Moreover, conditions that affect red blood cell turnover can significantly skew A1C results, leading to inaccurate assessments of glycemic control. A recent study demonstrated that 74.6% of Non-Hispanic Whites failed to achieve the A1C target of less than 7%, highlighting the necessity for careful interpretation of these results. Healthcare providers must consider these influencing factors and may employ additional diagnostic tests, such as fasting blood glucose measurements, to ensure an accurate diagnosis based on the A1C definition of diabetes.
Understanding the limitations of A1C testing is crucial, particularly when considering the A1C definition of diabetes and the prevalence of hemoglobin variants within diverse populations. For instance, certain medical conditions and medications can result in falsely elevated A1C readings, creating challenges in assessment and management of blood sugar. As emphasized by Mårtensson J., 'Hemoglobin A1c and Permissive Hyperglycemia in Patients in the Intensive Care Unit with Diabetes,' recognizing these nuances is essential for delivering effective patient care.
Additionally, a case study on the causes of falsely high A1C results illustrates how conditions such as anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency can impact A1C readings, underscoring the importance of precise assessment of blood sugar management.

Managing Diabetes: The Role of A1C in Treatment Strategies
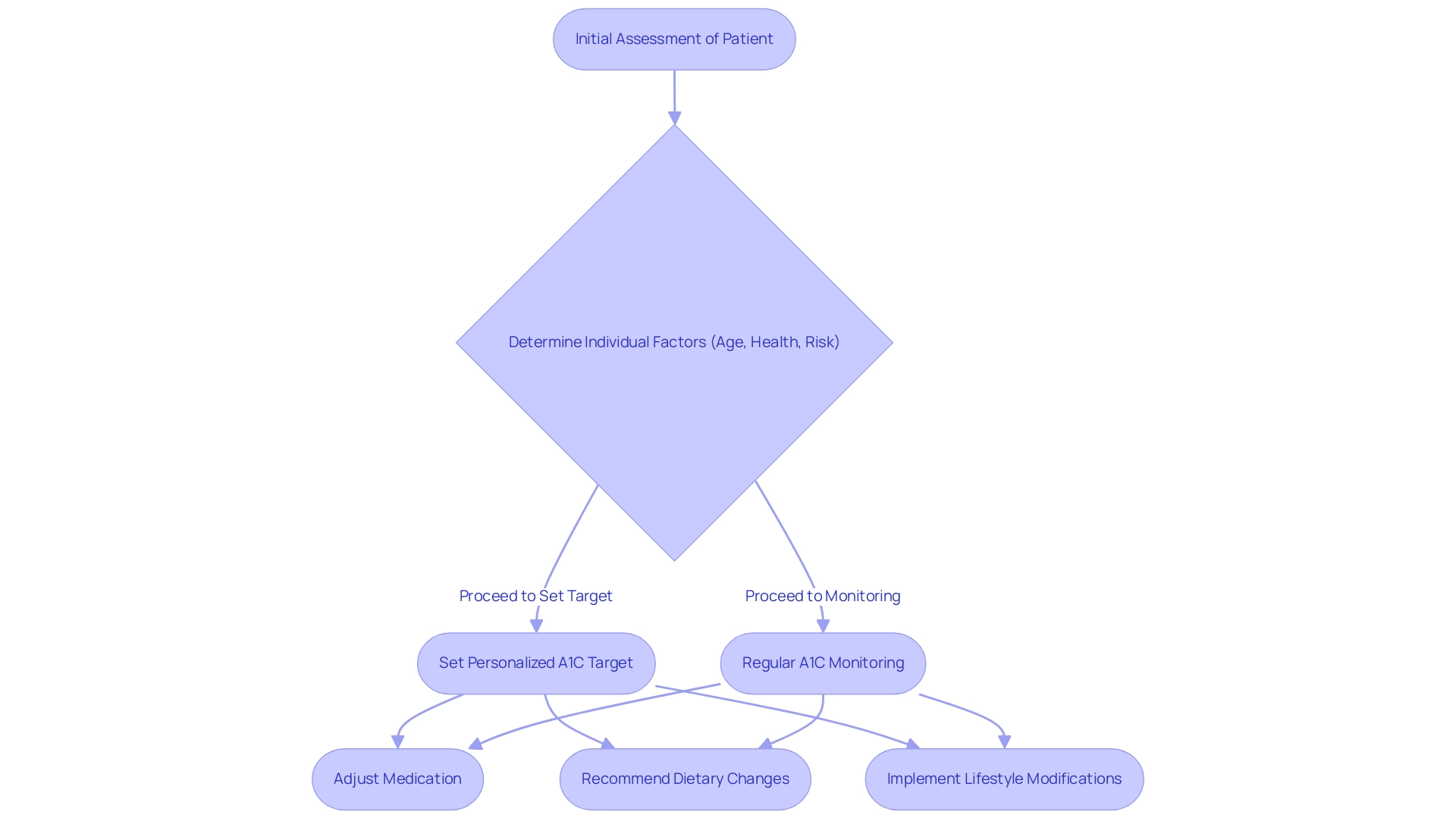
As T2DSolutions gets ready to launch as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support, understanding the A1C definition of diabetes remains essential to developing effective diabetes management strategies. Healthcare providers typically establish individualized A1C targets that take into account the A1C definition of diabetes, considering factors such as an individual's age, overall health, and their risk of developing complications. These tailored targets play a crucial role in informing treatment decisions, including medication adjustments, dietary recommendations, and necessary lifestyle changes.
Regular monitoring of A1C levels is essential in understanding the A1C definition of diabetes, enabling timely interventions that empower newly diagnosed patients to maintain their blood glucose within the desired range. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of long-term complications associated with the condition, underscoring the importance of personalized management strategies. In fact, the crude rate of hospital discharges for hypoglycemia was 2.2 per 1,000 adults with blood sugar issues, highlighting the need for careful A1C monitoring.
Recent studies have further highlighted the necessity for personalized A1C targets, aligning with the A1C definition of diabetes, and suggesting that high-risk individuals with type 2 glycemic issues who fail to achieve A1C levels below 8% face an increased risk of cardiovascular events. A study titled 'Impact of Glycemic Control on Cardiovascular Risk' found that individuals with this condition are at a heightened risk, raising questions about the ideal A1C target for minimizing these risks. This reinforces the necessity for careful monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans.
As R. James Dudl, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Southern California observed, 'Establishing personalized A1C goals is essential in enhancing management and improving patient outcomes, particularly when considering the A1C definition of diabetes.' To remain updated on T2D Solutions and its forthcoming features, subscribe for notifications and join our community focused on education and support.
Personalizing Diabetes Care: Beyond the A1C Test
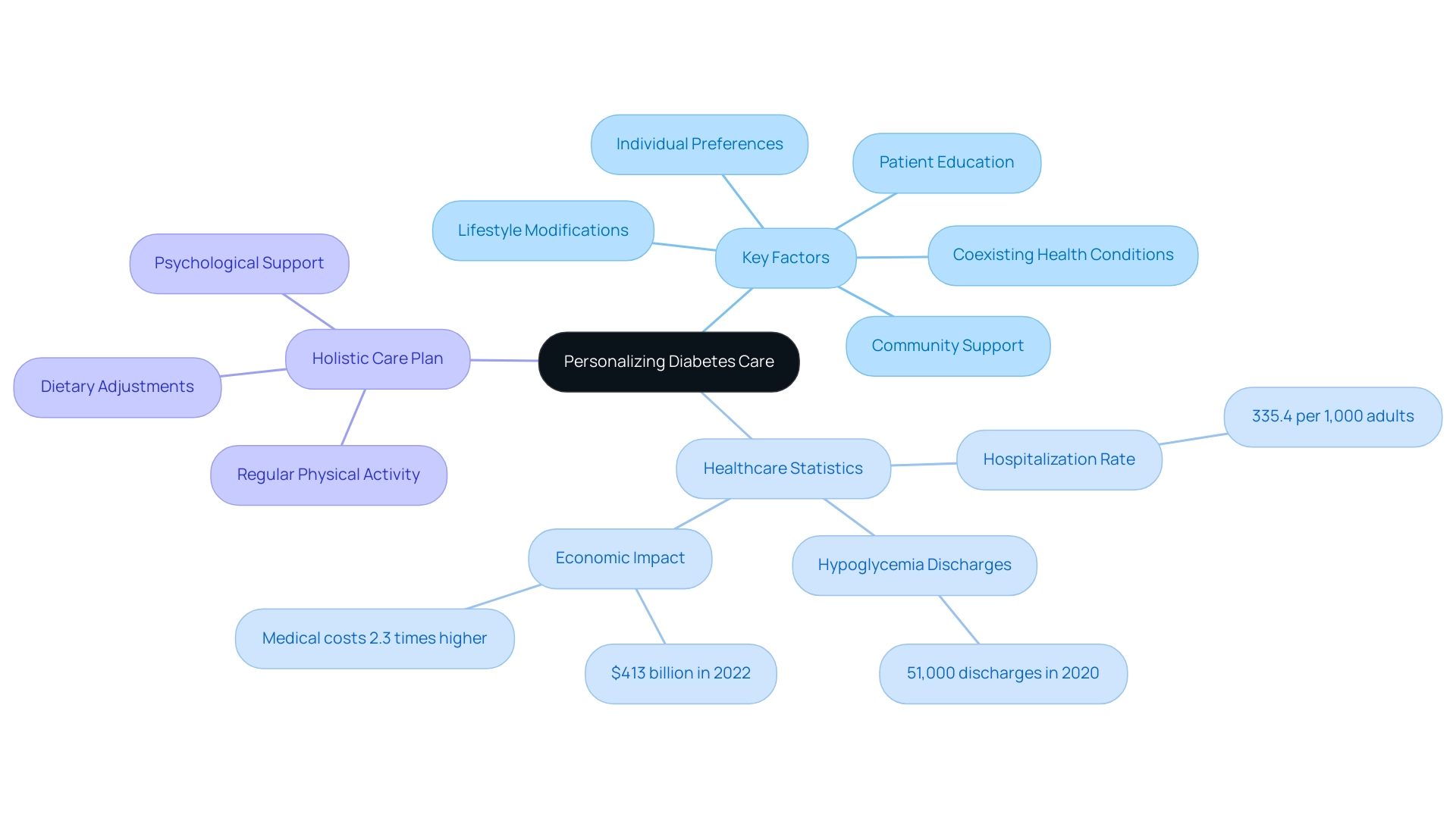
While the A1C test serves as a crucial metric in managing blood sugar levels, the A1C definition of diabetes should not exclusively dictate treatment decisions. Personalizing care for those with blood sugar issues necessitates a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Patient education
- Community support
- Consideration of individual preferences
- Lifestyle modifications
- Coexisting health conditions
Recent data indicates that in 2020, the crude hospitalization rate for diabetes-related diagnoses was 335.4 per 1,000 adults, reflecting the substantial healthcare burden associated with this condition.
Additionally, there were 51,000 hospital discharges for hypoglycemia among adults with high blood sugar, highlighting the complications that can arise from managing the condition. The total projected expenses of diagnosed health conditions in the United States reached $413 billion in 2022, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive healthcare strategies. A holistic care plan may encompass:
- Regular physical activity
- Dietary adjustments
- Psychological support
All tailored to the individual's needs.
The suggestion for the continuation of personal continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in hospitalized individuals with blood sugar issues is vital for effective treatment plans. As emphasized by North Dakota Health, the medical costs for individuals with the condition are 2.3 times higher than those without the illness. By adopting a holistic approach, healthcare providers can facilitate improved health outcomes and enhance patients' quality of life, ultimately leading to more effective management of Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes.
T D Solutions is dedicated to empowering individuals through education and support, fostering a community that improves management of the condition. Stay tuned for upcoming events and resources from T D Solutions that will further support your journey in managing diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding A1C levels is crucial for effective diabetes management, serving as a key indicator for diagnosing and monitoring both diabetes and prediabetes. This article has explored the fundamental aspects of the A1C test, including its role in interpreting glucose metabolism, the significance of maintaining target levels, and the necessity of personalized treatment strategies. By recognizing the established A1C thresholds, individuals can better understand their health status and take proactive steps towards managing their condition.
Moreover, the accuracy of A1C results can be influenced by various factors, including medical conditions and genetic variances. This highlights the importance of healthcare providers considering these nuances when interpreting test results and formulating treatment plans. Regular monitoring and tailored interventions are essential, particularly for high-risk patients, to minimize complications and optimize health outcomes.
Ultimately, while the A1C test is a vital tool in diabetes care, it should be part of a broader, holistic management approach. Incorporating patient education, lifestyle modifications, and community support ensures a comprehensive strategy that addresses individual needs. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, understanding and leveraging A1C results will remain integral to improving patient care and enhancing quality of life for those living with diabetes.



