Overview
If you're navigating diabetes, you may wonder about alcohol options that are safe for you. Generally, low-sugar choices like dry wines, light beers, and distilled spirits can help minimize the risk of blood sugar spikes. It's understandable to feel concerned about how these choices might affect your health.
Moderation is key. Monitoring your blood glucose levels is essential, and it's a good idea to consult with your healthcare provider. They can help tailor your alcohol consumption to your individual health needs, ensuring that you can enjoy safe drinking practices.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Many people share similar concerns, and reaching out for support can make a difference. We are here to support you every step of the way, providing the guidance you need to navigate your choices confidently.
Introduction
Navigating the complex relationship between alcohol and diabetes is essential for those managing this condition. It’s understandable to feel uncertain about how different types of alcohol can affect your blood sugar levels. This article explores the potential for both beneficial and harmful effects, helping you make informed decisions. From the risks of hypoglycemia to the nuances of moderate consumption, we will delve into the multifaceted impact of alcohol on diabetes management.
By sharing expert insights, real-life strategies, and the latest research findings, you will gain valuable knowledge to safely incorporate alcohol into your life while prioritizing your health. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way. Together, we can navigate these challenges and foster a healthier lifestyle.
The Connection Between Alcohol and Diabetes
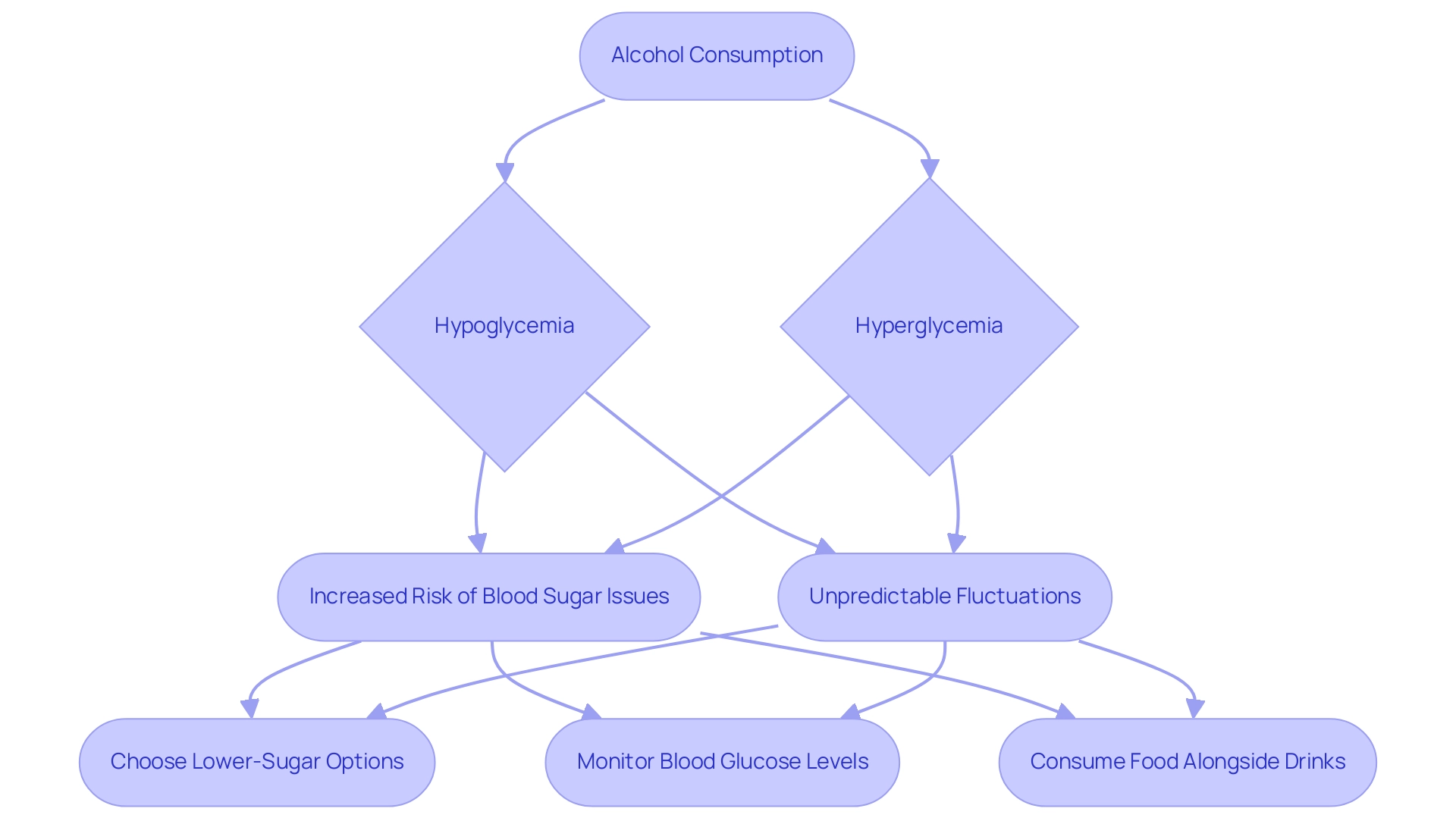
Alcohol intake can significantly impact individuals managing diabetes, making it essential to understand which types of alcohol are safe for diabetics. This is crucial as it influences the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels and can potentially lead to serious complications. Notably, beverages containing ethanol can trigger both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Therefore, identifying alcohol options that are safe for diabetics is vital, as the outcomes can vary based on factors such as the type of drink consumed and whether it is taken with food. This duality highlights the importance of understanding how alcohol interacts with blood sugar management.
Research indicates a strong connection between excessive intake of spirits and an increased risk of developing blood sugar issues. A study revealed a remarkable 73% rise in the risk of developing conditions linked to high beverage intake. This emphasizes the need for individuals with blood sugar concerns to monitor their intake closely. Furthermore, the effect of ethanol on blood sugar levels is not consistent; it can lead to unpredictable fluctuations that complicate diabetes management.
Real-world examples show how individuals with diabetes navigate the consumption of these drinks. Many diabetics adopt strategies such as:
- Choosing lower-sugar options
- Monitoring their blood glucose levels before and after drinking
- Ensuring they consume food alongside beverages to mitigate risks
These practical approaches can help maintain stable blood sugar levels while allowing for social engagement.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed, and expert opinions stress the necessity of moderation and informed choices. Healthcare professionals often advise patients to be mindful of the carbohydrate content in alcoholic drinks and consider how different varieties may affect their blood sugar, particularly when selecting alcohol that is safe for diabetics. For instance, sweet wines and cocktails can lead to higher blood sugar spikes compared to spirits mixed with calorie-free mixers. Case studies further illuminate the relationship between beverages and blood sugar management.
A thorough examination of research from 1980 to 2008 uncovered 20 pertinent articles investigating the relationship between beverage intake and the risk of blood sugar disorders. This rigorous methodology began with a literature search producing 1,615 results, ensuring that the findings were based on high-quality data. This contributes to a deeper understanding of how beverages can influence health outcomes. The study adhered to ethical principles and received approval from relevant ethics committees, reinforcing the credibility of the research findings.
In summary, the effect of ethanol on blood sugar levels for diabetics is multifaceted and requires careful consideration. By remaining informed and adopting mindful drinking habits, those with blood sugar issues can better manage their condition while enjoying social occasions. As noted by the authors of the study, JPC, SP, and AAH, their responsibilities included study design and writing of the first draft of the manuscript, ensuring a thorough analysis and interpretation of the data.
For additional details on handling blood sugar issues, including methods concerning beverage intake, visit T2D Solutions, your complete resource for diabetes education and community support.
Understanding the Risks of Alcohol for Diabetics
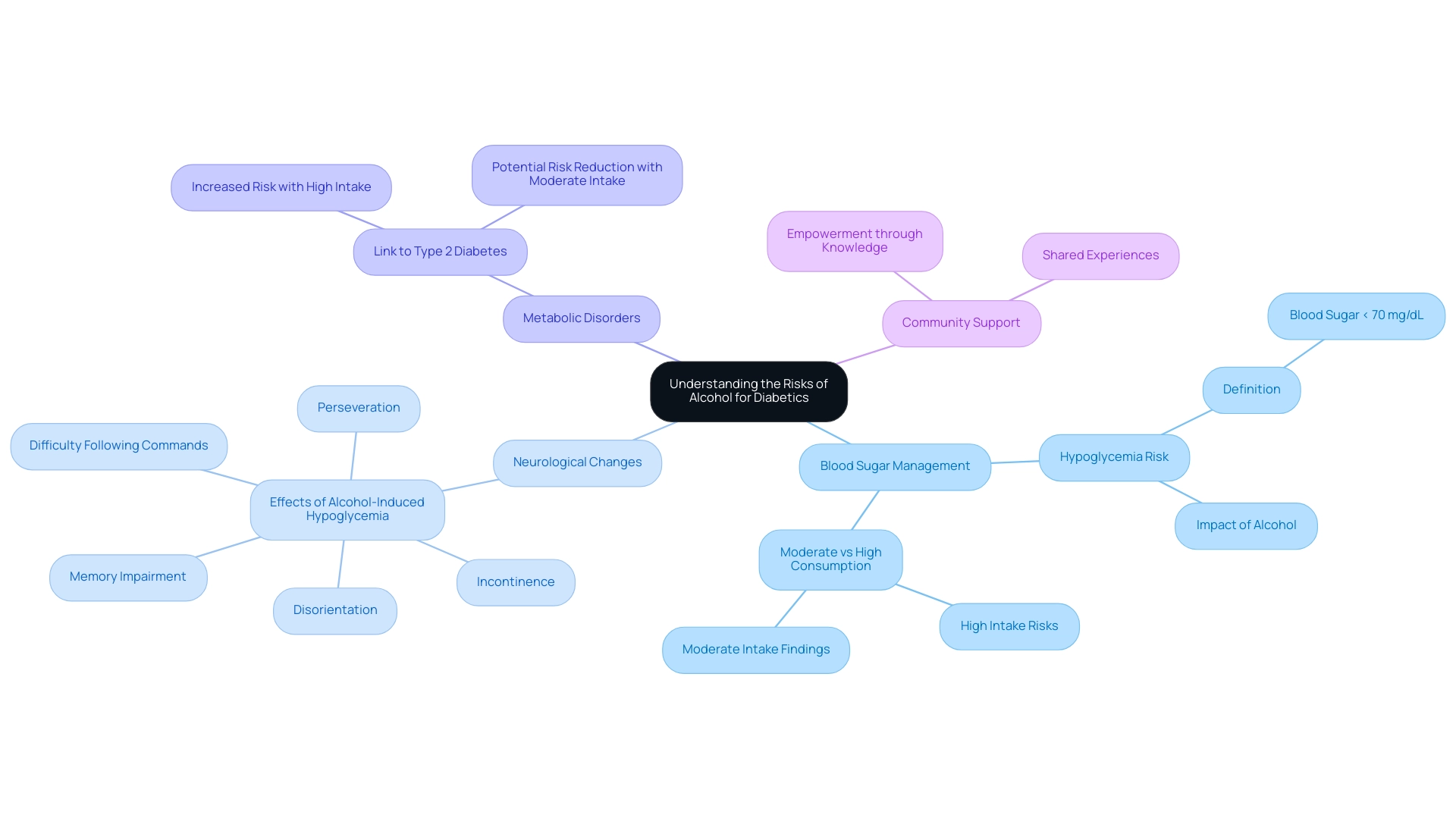
For individuals managing blood sugar issues, the intake of spirits can pose significant dangers. It’s important to understand the risks, especially when combined with insulin or other medications for blood sugar management. Alcohol can hinder the liver's ability to release glucose into the bloodstream, potentially leading to hypoglycemia—a condition where blood sugar drops below 70 mg/dL. This risk is heightened by the fact that beverage-induced hypoglycemia can lead to neurological changes, including:
- incontinence
- difficulty following simple commands
- perseveration
- disorientation
- recent memory impairment, as noted by Arky and colleagues.
Recent findings suggest that while high intake of spirits is linked to an increased risk of developing metabolic disorders, moderate consumption does not elevate this risk for either men or women. However, it’s crucial to recognize the complexities of how different beverages affect blood sugar management. A meta-analysis exploring the connection between beverage intake and Type 2 Diabetes indicated that earlier studies hinted at a possible risk reduction among moderate drinkers, but methodological limitations raised questions about the validity of these findings.
The new analysis sought to clarify the dose-response relationship between beverage intake and Type 2 conditions by testing various referent groups. The goal was to provide clearer associations between beverage consumption and the incidence of these conditions.
Real-life examples highlight the complications that can arise from beverage consumption among individuals with diabetes. Hypoglycemia resulting from beverage intake is not uncommon, underscoring the importance of closely monitoring blood sugar levels. As you navigate your condition, understanding the dangers of alcohol consumption is essential for your safety and well-being.
By fostering a community that shares experiences and knowledge, T2DSolutions empowers individuals to make informed choices about their health. Remember, managing health conditions is a shared journey toward better outcomes, especially regarding beverage choices. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Drinking Alcohol
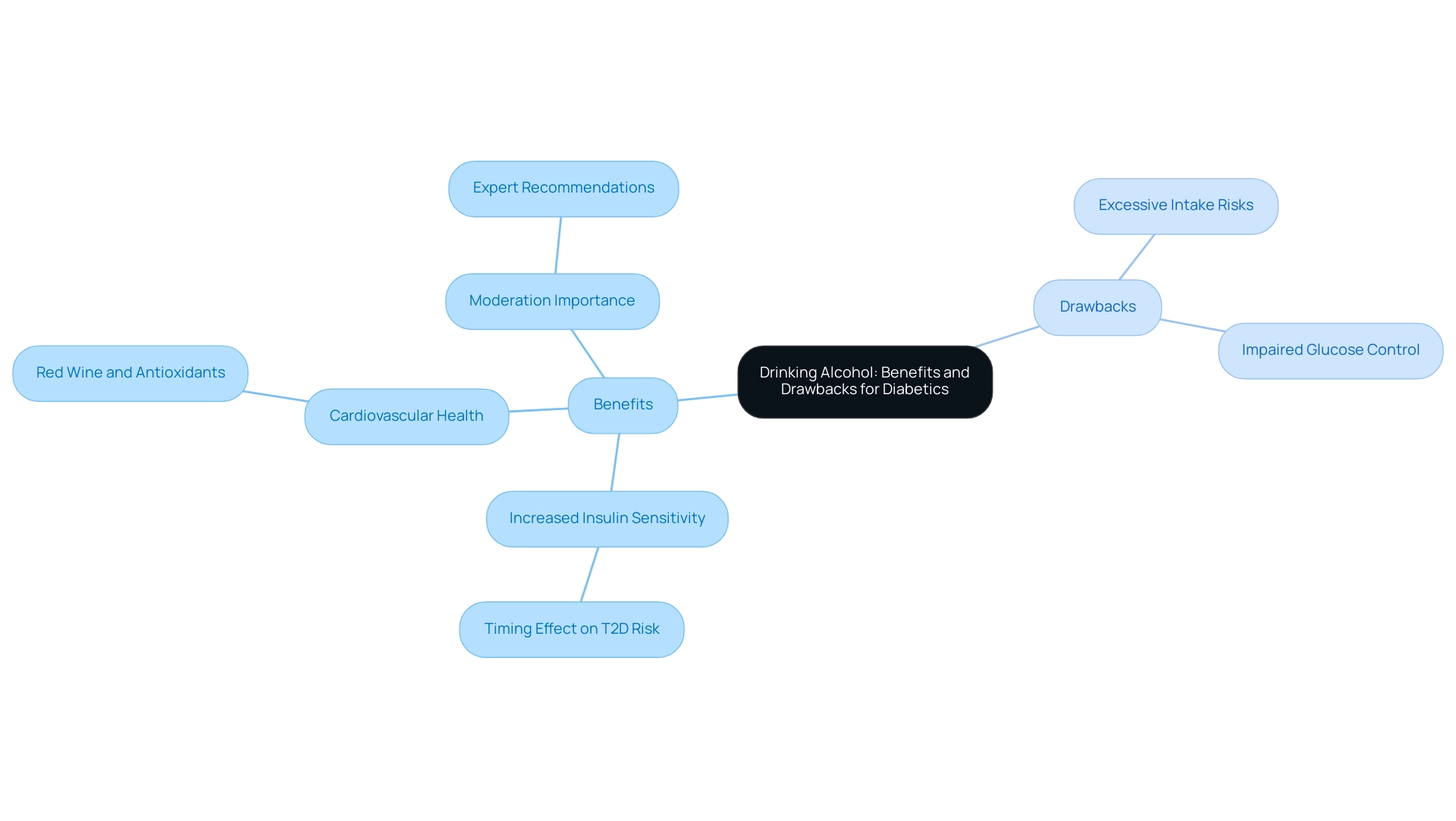
Moderate intake of beverages containing ethanol can be viewed as alcohol safe for diabetics, offering certain benefits for those managing blood sugar issues. This is particularly true when it comes to enhanced insulin sensitivity and heart health. Research indicates that moderate consumption of red wine, for instance, is linked to heart health benefits due to its rich antioxidant content, which may help reduce inflammation and improve blood vessel function. As we look ahead to 2025, studies continue to highlight the cardiovascular benefits of red wine, suggesting that its polyphenols can enhance endothelial function and promote better circulation.
Statistics reveal that moderate beverage consumption can positively influence insulin sensitivity. Findings show a significant interaction effect of timing relative to meals on Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) risk, indicating a nuanced relationship between intake and glucose metabolism. Specifically, moderate drinkers may experience improved insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for effective diabetes management. The interaction effect was noted to be significant at -0.017, underscoring the importance of timing in beverage consumption.
Moreover, expert opinions underscore the importance of moderation. Health professionals advocate for a balanced approach, emphasizing that while moderate alcohol consumption can be beneficial and is regarded as alcohol safe for diabetics, excessive intake poses serious risks, including impaired glucose control and heightened chances of diabetes-related complications. This perspective aligns with the holistic approach to managing chronic health conditions promoted by T2DSolutions, which encourages lifestyle changes and community support to foster resilience and better health outcomes.
As William C Knowler stated, community involvement is essential for achieving prevention goals. This highlights the collective effort needed in managing this condition, reminding us that we are not alone in this journey.
Real-world examples further illustrate these benefits. Individuals who include moderate red wine intake in their diets often report enhanced cardiovascular health indicators. This reinforces the notion that when enjoyed responsibly, alcohol safe for diabetics can indeed be part of a healthy lifestyle for those with blood sugar issues. T2DSolutions provides resources and community assistance to help people make informed choices regarding their beverage intake in relation to their diabetes management.
It is essential for individuals to consult healthcare providers to tailor their alcohol consumption to their specific health needs and circumstances. T2DSolutions' holistic approach emphasizes the importance of community engagement, ensuring that people have the support they need to make informed decisions about their health.
Choosing Safer Alcoholic Beverages for Diabetes
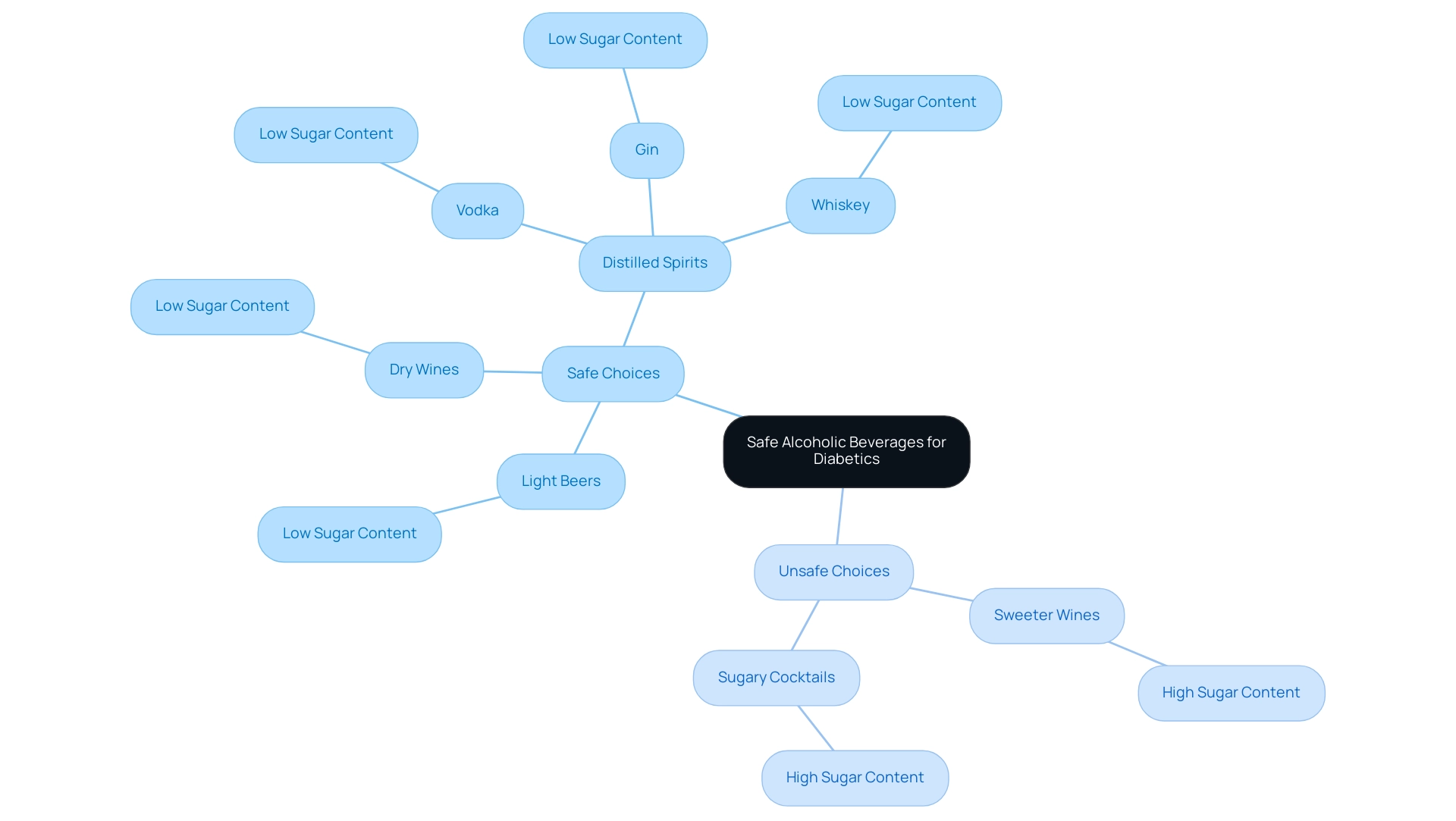
For individuals managing blood sugar issues, it’s essential to choose alcoholic drinks that are safe for diabetics, focusing on options with low sugar and carbohydrate content. Light beers, dry wines, and distilled spirits like vodka, gin, and whiskey are generally considered safe choices. These selections help minimize the risk of blood sugar spikes, making certain types of alcohol more appropriate for diabetics. In contrast, sweeter wines and sugary cocktails can lead to unwanted spikes.
Research shows that beverages with lower sugar content, which are safe for diabetics, can significantly reduce the likelihood of adverse effects on blood glucose levels. At T2DSolutions, we understand how important it is to make informed decisions about beverage intake as part of managing blood sugar levels. Many diabetics have successfully integrated low-sugar drinks into their social lives, opting for dry wines or spirits mixed with soda water instead of high-sugar cocktails. This approach not only allows them to enjoy social events but also aids in maintaining better control over their condition.
Statistics reveal that 20 articles were analyzed to determine the safest alcoholic options for diabetics, highlighting the growing body of research in this area. Expert recommendations consistently point to low-sugar and low-carbohydrate drinks as the best choices for those seeking alcohol that is safe for diabetics. As Ariane Lang, BSc, MBA, states, "The best kinds of beverages for individuals with high blood sugar are those that are safe for diabetics, characterized by low sugar or carb content."
It’s also advisable to consume beverages containing ethanol alongside food, which can help reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, a common concern for those with high blood sugar. Looking ahead to 2025, the best alcoholic beverages for diabetics will prioritize health without sacrificing enjoyment. It’s crucial to avoid traditional cocktails and dessert wines, which are typically high in added sugars, and instead choose options that are safe for diabetics. Understanding situations like alcoholic ketoacidosis, which can arise from excessive beverage intake, further underscores the importance of making informed choices.
By being mindful of sugar levels and recognizing potential risks, individuals can manage their beverage intake safely while effectively controlling their blood sugar. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. T2DSolutions is here to provide ongoing support and resources to help you make the best choices for your health.
Moderation and Responsible Drinking Guidelines
At a2d Solutions, we understand the importance of grasping beverage intake and its effects on blood sugar management. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) offers clear guidelines for individuals with diabetes, suggesting that women limit their intake to one drink per day and men to two. A standard drink is defined as 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits.
Following these moderation guidelines is crucial, as it helps prevent blood sugar fluctuations and lowers the risk of complications associated with excessive drinking. It’s understandable to feel concerned about how your choices impact your health.
Research indicates that excessive drinking can significantly affect health, with studies showing an odds ratio of 3.04 for stage 2 hypertension among heavy users. This statistic highlights the importance of moderation, particularly for those with diabetes, as excessive intake can lead to serious health issues, including hypertension, which is prevalent in this population.
Real-world examples can illustrate the effectiveness of these guidelines. For instance, a case study titled 'Eating Before Drinking' underscores the necessity of consuming food prior to drinking. This practice not only stabilizes blood sugar levels but also reduces the likelihood of making poor dietary choices in social situations. By eating beforehand, individuals can better manage their blood sugar and avoid rapid drops that may occur with certain beverages.
Experts advocate for moderation in beverage intake, emphasizing that alcohol can be safely integrated into a diabetes management strategy. Hyacinth Irving, an expert in the field, states, "Beverage consumption is a risk factor for Type 2 Diabetes," reinforcing the need for careful consideration of intake. The ADA's 2025 guidelines strengthen this approach, urging individuals to be mindful of their drinking habits while enjoying social events.
Additionally, sensitivity analyses are being conducted to evaluate the impacts of moderate beverage intake on reported outcomes, emphasizing ongoing research in this area. You're not alone in navigating these challenges; support is available.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to providing resources and assistance for individuals managing their health, including information on beverage intake. By following these suggestions, those with blood sugar concerns can safely manage their drinking by choosing alcohol that is suitable for diabetics, fostering improved health outcomes and enhancing overall quality of life. We invite you to explore T2 Solutions for more information and community support related to managing blood sugar.
Tips for Safe Alcohol Consumption with Diabetes
For individuals overseeing blood sugar, enjoying beverages that are alcohol safe for diabetics requires careful monitoring of glucose levels before, during, and after intake. Research shows that consuming carbohydrates alongside beverages can significantly help stabilize blood sugar levels. Therefore, it’s essential to include a meal or snack rich in carbohydrates when drinking. This practice not only reduces the risk of hypoglycemia but also enhances overall safety during social occasions.
It's understandable to feel concerned about drinking alcohol safe for diabetics on an empty stomach, as this can lead to unpredictable fluctuations in blood sugar. Always having a source of fast-acting glucose, such as glucose tablets or juice, on hand is advisable to quickly address any potential hypoglycemic episodes.
Statistics indicate that excessive beverage intake is associated with a 77% heightened risk of developing diabetes. This emphasizes the importance of moderation in drink intake for individuals managing diabetes. A study titled "Clinical Implications of Blood Glucose in Alcohol Dependence" highlighted that elevated blood glucose levels could predict heavy drinking. Lorenzo Leggio, M.D., M.Sc., observed, "These results indicate that elevated glucose and heavy drinking may be influenced by a shared mechanism, and adjustments impacting glucose regulation may affect beverage intake."
Real-life examples show that many diabetics successfully manage their alcohol consumption by following these guidelines. By being proactive and informed, you can enjoy social settings without compromising your health. Experts suggest that individuals with diabetes participate in regular blood sugar monitoring, especially before and after consuming alcohol safe for diabetics, to ensure their levels stay within a safe range.
At T2DSolutions, we are here to support you through these challenges. Our platform provides educational resources, community discussions, and expert insights on managing beverage habits while living with blood sugar issues. We encourage you to enroll for notifications on new material related to managing blood sugar levels, including beverage strategies.
In summary, ensuring that beverage consumption is alcohol safe for diabetics involves a combination of strategic planning, carbohydrate intake, and vigilant monitoring of blood sugar levels. By adhering to these practices and utilizing the resources available at T2 Solutions, you can navigate your social life while maintaining control over your blood sugar management. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider About Alcohol
Before enjoying beverages that contain ethanol, it’s crucial for individuals with blood sugar concerns to consult with their healthcare provider. This step ensures that they understand which options are safe for diabetics. Factors such as current medications, overall health status, and specific diabetes management goals are essential in determining whether alcohol is advisable. Healthcare providers can offer personalized recommendations that cater to each patient’s unique needs, ensuring that their drinking practices are safe.
As Mary West notes, "Most importantly, if individuals wish to engage in moderate drinking, they should first discuss what is alcohol safe for diabetics with their doctor."
Research shows that a significant portion of U.S. adults with diabetes—70.8%—experience elevated blood pressure levels, which can complicate the decision to drink. This statistic underscores the importance of professional guidance, as certain substances can interact with medications and exacerbate health issues. For instance, some medications for blood sugar management may increase the risk of hypoglycemia when combined with spirits. Therefore, it’s vital for patients to understand these interactions.
Unfortunately, consultation rates with healthcare providers regarding beverage consumption among diabetics remain low. This highlights a gap in communication that needs to be addressed. There is a pressing need for further investigation into the effectiveness of brief substance use interventions for individuals with blood sugar issues, emphasizing the importance of fostering open conversations. By engaging in these discussions, healthcare professionals can provide invaluable insights and recommendations tailored to individual health profiles.
For example, a healthcare provider might suggest specific types of beverages that are safe for diabetics or advise on moderation strategies.
Real-world examples illustrate the positive impact of personalized beverage advice. In one instance, a patient was encouraged to limit their beverage consumption to special occasions and to closely monitor their blood sugar levels when consuming drinks. This customized approach not only allowed the patient to enjoy social situations but also supported effective health management.
As T2DSolutions launches as a new resource center for education and community support, it aims to provide essential information on beverage intake and its effects on blood sugar management. By visiting T2DSolutions, newly diagnosed patients can access resources that help them navigate their health journey safely, including discussions about beverage intake with healthcare providers.
Expert opinions stress the importance of these consultations. As healthcare experts highlight, discussing drink intake is essential for individuals with blood sugar issues to manage their health journey safely. By engaging in these conversations, patients can make informed decisions that align with their health goals, ultimately leading to improved management of their condition.

Key Takeaways on Alcohol and Diabetes
People with high blood sugar can enjoy drinks in moderation, but it's essential to make informed decisions about both the kind and amount of beverages consumed. It's understandable to feel uncertain about this, as studies suggest that the connection between beverage intake and glucose-related risk is complex. For example, a study emphasized that women may encounter a notable decrease in diabetes risk at lower amounts of beverage intake, while men exhibit a slight rise in risk even with very low intake levels. This highlights the significance of comprehending personal reactions to spirits.
Statistics reveal that high-risk drinkers face an increased likelihood of developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), with an odds ratio of 1.289, indicating a notable risk associated with excessive consumption. Therefore, moderation is key. The American Diabetes Association has recognized a U-shaped connection between average daily beverage consumption and the risk of developing blood sugar issues, indicating that light to moderate drinking may not present the same dangers as excessive drinking.
Jürgen Rehm, PhD, noted, "Our meta-analysis confirms the U-shaped relationships between average amount of beverages consumed per day and risk of incident type 2 diabetes among men and women."
To navigate alcohol consumption safely, diabetics should consider the following guidelines:
- Choose Safer Beverages: Opt for drinks with lower sugar content, such as dry wines or spirits mixed with calorie-free mixers.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Alcohol can affect blood sugar levels, so it's essential to check levels before and after drinking.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Discuss beverage consumption with healthcare professionals to customize advice to personal health needs.
Real-life examples demonstrate that many diabetics can enjoy beverages responsibly. For instance, people have shared experiences of attending social gatherings while adhering to their dietary plans, choosing low-sugar options, and maintaining their health without feeling deprived. You're not alone in this journey.
In summary, while beverages containing ethanol can be part of a diabetic's lifestyle, it is vital to approach the consumption of alcohol safe for diabetics with caution and awareness. By adhering to established guidelines and understanding personal health conditions, individuals can partake in social occasions without compromising their condition management. Furthermore, it is crucial to take into account possible publication bias in the studies related to substances and blood sugar regulation, as this can affect the understanding of results.
The case study titled "Sex-Specific Analysis of Beverage Intake and Health Risk" further illustrates the distinct patterns of beverage use and health risk for men and women, emphasizing the need for personalized approaches to beverage use in health management.
For more information and support on managing diabetes, including alcohol consumption, visit T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of alcohol consumption for individuals managing diabetes is both crucial and challenging. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the relationship between alcohol and diabetes, so let's explore it together. Throughout this article, we've examined the potential risks and benefits of alcohol, emphasizing that moderation and informed choices are paramount. Alcohol can lead to unpredictable fluctuations in blood sugar levels, posing risks of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, especially when consumed in excess or without proper food intake.
The evidence suggests that while excessive alcohol intake significantly increases the risk of developing diabetes, moderate consumption may offer certain cardiovascular benefits and improved insulin sensitivity. It's important to remember that the type of alcohol consumed plays a vital role, with lower-sugar options being safer choices for maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Real-life strategies shared by individuals with diabetes highlight the importance of:
- Monitoring blood sugar before and after drinking
- Selecting lower-sugar beverages
- Consulting healthcare providers for personalized guidance
In conclusion, you're not alone in this journey. Individuals with diabetes can enjoy alcohol responsibly by adhering to established guidelines, understanding their unique health profiles, and making informed choices. By prioritizing safety and moderation, it is possible to navigate social situations while effectively managing diabetes. Ongoing support and resources, such as those provided by T2DSolutions, are invaluable in empowering you to take charge of your health and enjoy life to the fullest, without compromising your well-being. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does alcohol intake affect individuals managing diabetes?
Alcohol intake can significantly impact blood sugar regulation in individuals with diabetes, potentially leading to both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
What types of alcohol are safe for diabetics?
Diabetics should choose lower-sugar options and consider the carbohydrate content in alcoholic drinks. Spirits mixed with calorie-free mixers are generally safer than sweet wines and cocktails, which can lead to higher blood sugar spikes.
What strategies can diabetics use to manage alcohol consumption?
Diabetics can manage their alcohol consumption by choosing lower-sugar options, monitoring blood glucose levels before and after drinking, and consuming food alongside alcoholic beverages to mitigate risks.
What are the risks of consuming spirits for individuals with diabetes?
Consuming spirits can hinder the liver's ability to release glucose, leading to hypoglycemia, particularly when combined with insulin or other blood sugar medications. This can result in neurological changes and other complications.
Is there a difference between moderate and excessive alcohol consumption for diabetics?
While excessive intake of spirits is linked to an increased risk of developing metabolic disorders, moderate consumption does not elevate this risk for men or women. However, the effects of different beverages on blood sugar management can vary.
What should individuals with diabetes be aware of regarding hypoglycemia from alcohol?
Hypoglycemia from alcohol consumption can lead to serious neurological changes, such as disorientation and memory impairment, highlighting the importance of monitoring blood sugar levels closely.
How can research inform safe alcohol consumption for diabetics?
Research has explored the relationship between beverage intake and blood sugar disorders, revealing that careful consideration of alcohol types and moderation can aid in diabetes management.
Where can individuals find more information about managing blood sugar issues related to alcohol?
For additional details on handling blood sugar issues, including methods concerning beverage intake, individuals can visit T2D Solutions, a resource for diabetes education and community support.
