Overview:
The GMI percentage, or Glucose Management Indicator, is a critical metric in diabetes management that reflects average blood sugar levels over time, derived from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data. The article emphasizes its importance by explaining how GMI provides real-time insights that allow for timely adjustments in treatment plans, distinguishing it from traditional measures like HbA1c, and highlighting its role in improving health outcomes through personalized care and lifestyle modifications.
Introduction
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) is reshaping the landscape of diabetes management by providing a more dynamic and immediate understanding of blood glucose levels. As healthcare continues to evolve, GMI stands out as a pivotal tool that empowers both patients and healthcare providers with real-time insights, enabling more tailored treatment strategies.
This article delves into the significance of GMI, contrasting it with traditional metrics like Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and explores its practical applications in everyday diabetes care.
By examining the accuracy, reliability, and future potential of GMI, it becomes evident how this innovative approach is enhancing the management of diabetes and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI)
Welcome to T2DSolutions, your new comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes education and community support. As we prepare to launch, we invite you to subscribe to stay updated on our latest content and resources. In our ongoing commitment to empower patients, we focus on essential metrics like the Blood Sugar Management Indicator (GMI), as understanding what is GMI percentage provides vital insights into average blood sugar levels over time.
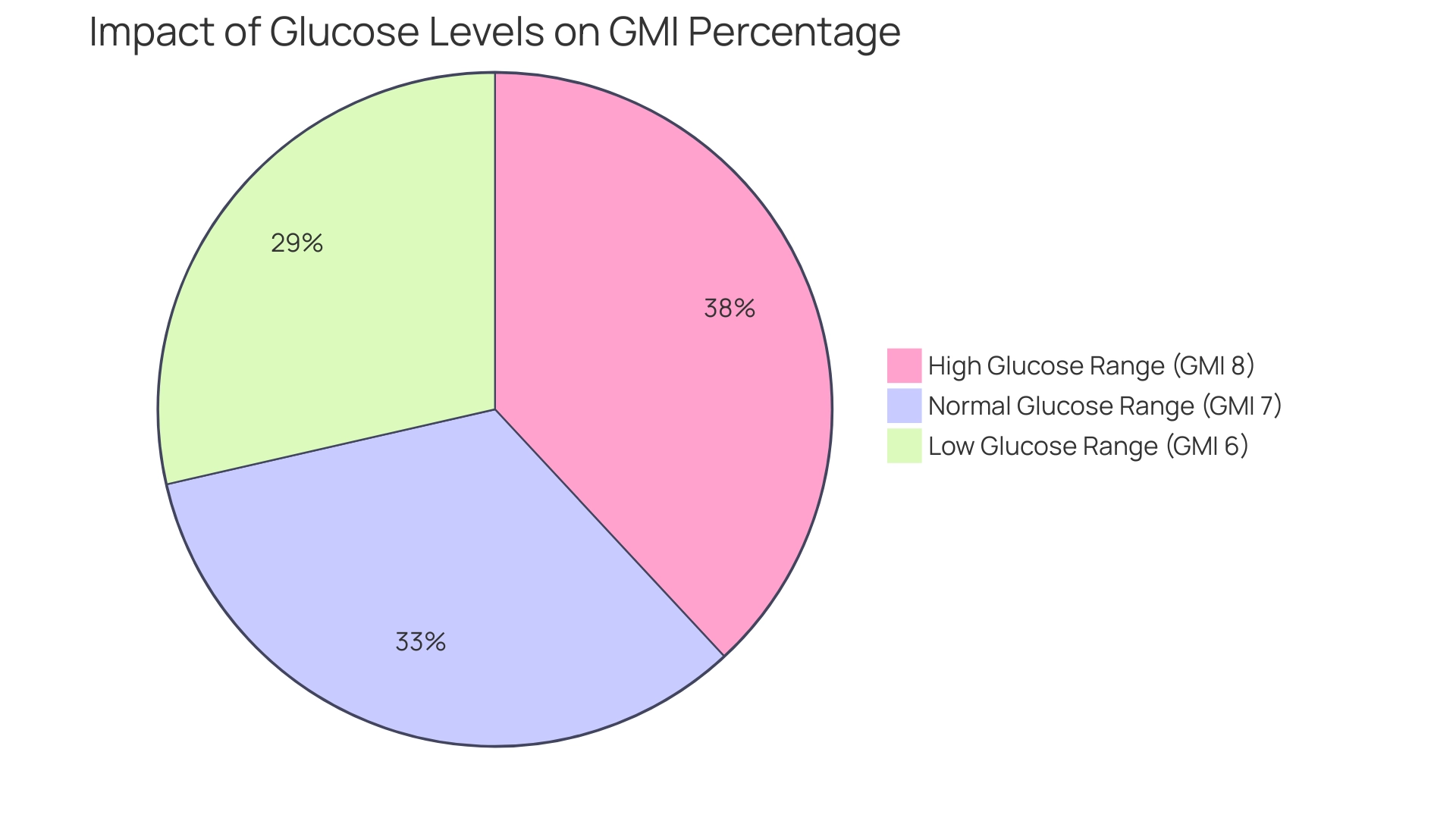
To understand what is GMI percentage, it is calculated using data from continuous sugar monitoring (CGM) systems, providing a dynamic perspective that surpasses traditional measurement methods. Each 25 mg/dl increase in mean glucose correlates with a 0.7% increase in GMI, which raises the question of what is GMI percentage, highlighting how fluctuations in glucose levels can impact overall control. This tool is invaluable for both healthcare providers and individuals, fostering clearer understanding and facilitating necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
As we navigate the complexities of managing blood sugar levels, it is important to understand what is GMI percentage, as it reflects the critical influence of lifestyle choices and medication adherence on health outcomes. We also recognize the barriers some patients face, such as unjustified insurance coverage criteria limiting access to CGM technology. Furthermore, the advancements in CGM technology underscore what is GMI percentage in the context of modern glucose management.
Join us as we strive to enhance awareness and support for all individuals impacted by this condition, ensuring that personalized care is at the forefront of our mission.
GMI vs. HbA1c: Key Differences and Implications for Diabetes Care
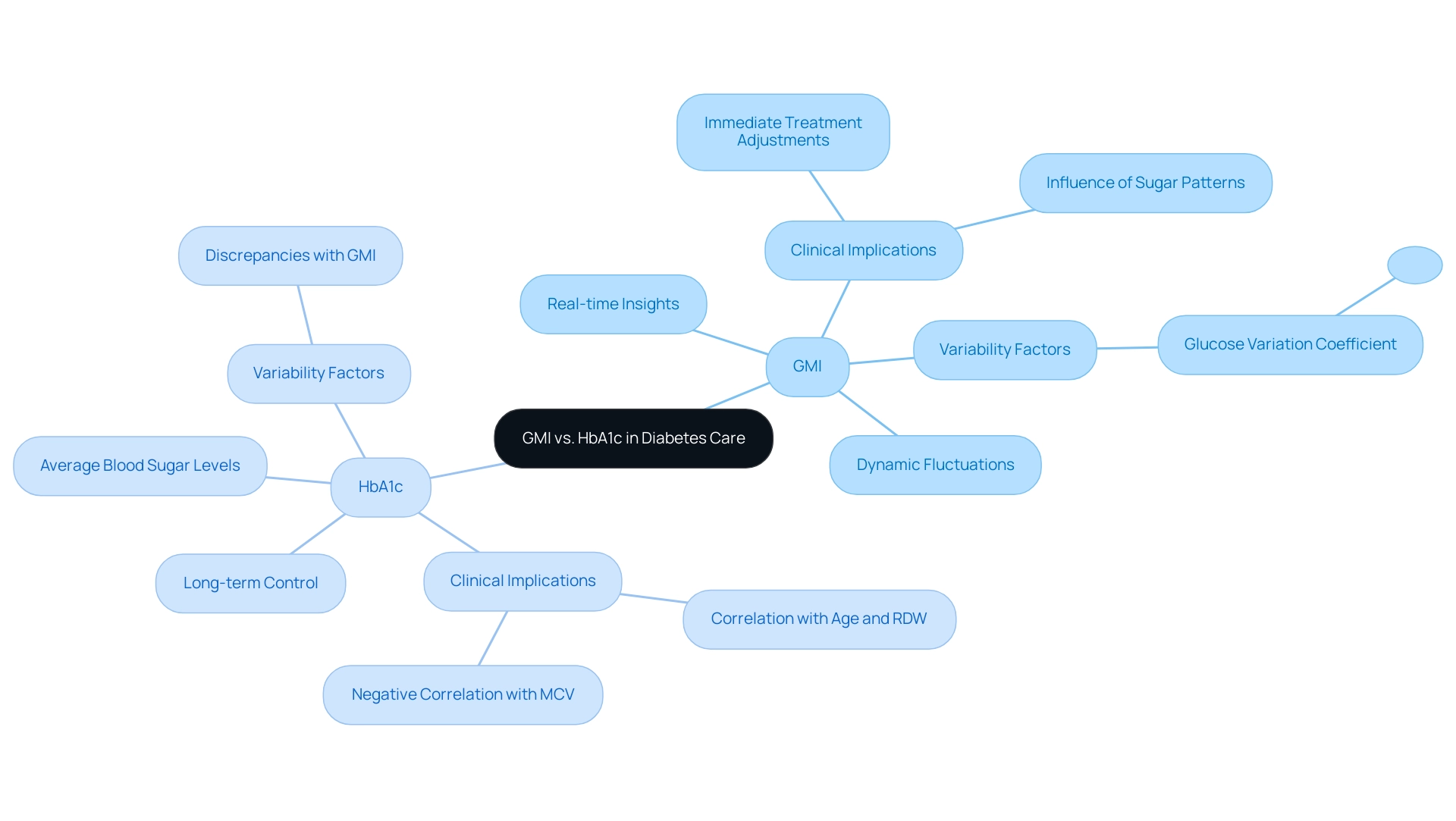
Understanding what is GMI percentage and how it differs from Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is crucial, as both serve as pivotal measures in diabetes management but exhibit significant differences in methodology and clinical implications. HbA1c reflects the average blood sugar levels over a period of two to three months, providing a comprehensive view of long-term sugar control. In contrast, GMI offers real-time insights derived from continuous glucose monitoring, which helps answer the question of what is gmi percentage by capturing the dynamic fluctuations and trends in glucose levels.
This real-time capability allows for more immediate adjustments in treatment and lifestyle. At T2DSolutions, your comprehensive resource for Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support, we recognize the importance of these metrics in managing your health. We provide a range of tools and resources, including personalized education plans and community forums, to assist you in managing your health journey.
Recent research indicates that the variation coefficient for HbA1c-GMI exceeds 0.374 in 37% of cases, underscoring the variability that can exist between these two metrics. A multilevel mixed model analysis of 646 records highlighted that clinical parameters such as age and red cell distribution width (RDW) positively correlate with HbA1c-GMI, while mean corpuscular volume (MCV) shows a negative correlation, emphasizing the complexity of these relationships. Understanding what is gmi percentage is vital for healthcare providers and patients alike, as it affects management strategies and can lead to improved care outcomes.
Consequently, discrepancies between HbA1c and GMI measurements are not uncommon. As noted by experts, 'In conclusion, discrepancies between HbA1c and GMI measurements are not uncommon,' reinforcing the necessity for clinicians to consider both metrics when tailoring treatment plans. Furthermore, it is essential to acknowledge how sugar patterns and other elements affect the connection between GMI and HbA1c, offering a more thorough perspective on management of the condition.
T2DSolutions is dedicated to assisting your journey with trustworthy information, community resources, and practical insights to empower you in managing your condition effectively.
Practical Applications of GMI in Diabetes Management
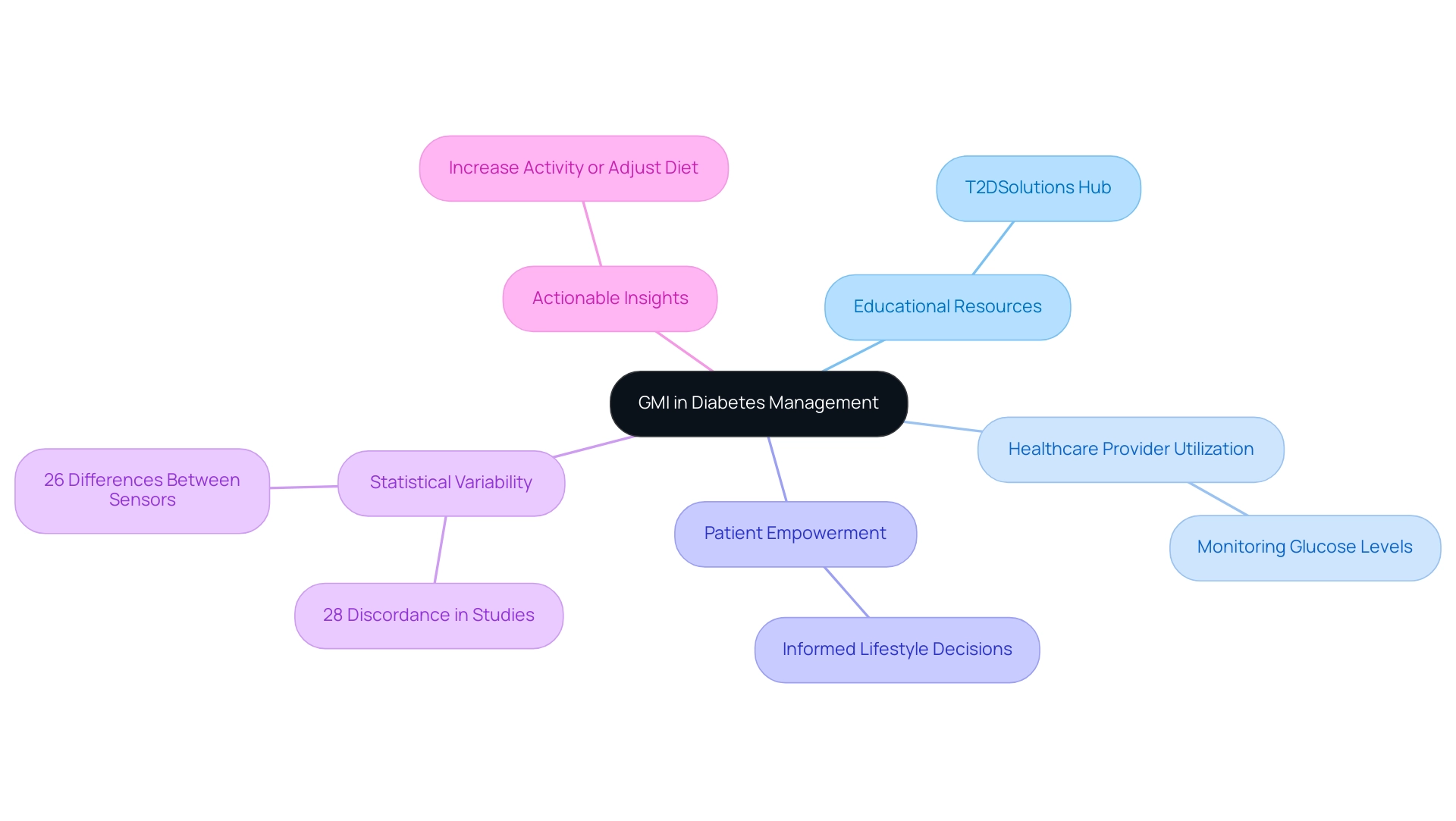
The management indicator for sugar serves as a crucial resource in numerous practical uses within blood sugar regulation, and it is important for individuals to comprehend its implications. T2DSolutions is launching as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 glucose management education, aiming to provide crucial information to newly diagnosed individuals. Healthcare providers can leverage GMI to closely monitor individuals’ glucose levels and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Richard M Bergenstal of the International Diabetes Center emphasizes the significance of this approach, stating,
With this diverse and thoughtful feedback, we accepted the term 'glucose management indicator'
This terminology reflects a shift toward a more empowering language in diabetes care, as highlighted by feedback from healthcare professionals and diabetes advocates. For individuals, understanding what is GMI percentage through resources provided by T2DSolutions can lead to informed lifestyle decisions regarding diet, exercise, and medication adherence.
For example, an individual noticing an upward trend in GMI might choose to increase physical activity or adjust carbohydrate consumption to attain improved blood sugar regulation. Furthermore, the variability noted in clinical studies, where 28% of participants exhibited clinically significant discordance (≥0.5 %-points) between GMI and laboratory HbA, underscores the importance of regular monitoring, as inaccuracies in CGM glucose can contribute to these discrepancies. Additionally, it is important to note that 26% of participants had differences of 0.5 %-points or more when comparing GMI from two sensors, reinforcing the need for consistent monitoring.
This variability can spark more productive conversations between individuals and healthcare providers, fostering a collaborative approach that improves management outcomes. Consequently, understanding what is GMI percentage in the practical applications of GMI not only empowers patients but also supports healthcare providers in delivering tailored treatment adjustments. To remain informed about new content and resources from T2Solutions, we urge you to sign up for email notifications as we develop this invaluable tool for understanding and managing the condition effectively.
Evaluating the Accuracy and Reliability of GMI
The accuracy and reliability of the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI), or what is GMI percentage, remain critical topics in diabetes management research. Studies indicate that GMI demonstrates a strong correlation with traditional HbA1c measurements, providing healthcare providers with a more immediate and nuanced insight into sugar control. However, individual variability in glucose metabolism, along with the quality of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, can significantly influence the reliability of GMI readings.
J.E.P. highlights the significance of CGM metrics, stating,
It is especially crucial that endocrinologists view CGM metrics as an alternative evaluation of glycemic control during this time when acquiring formal laboratory testing could pose a risk to individuals with blood sugar issues.
Furthermore, guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus highlight the importance of comprehensive assessments that include both GMI and HbA1c.
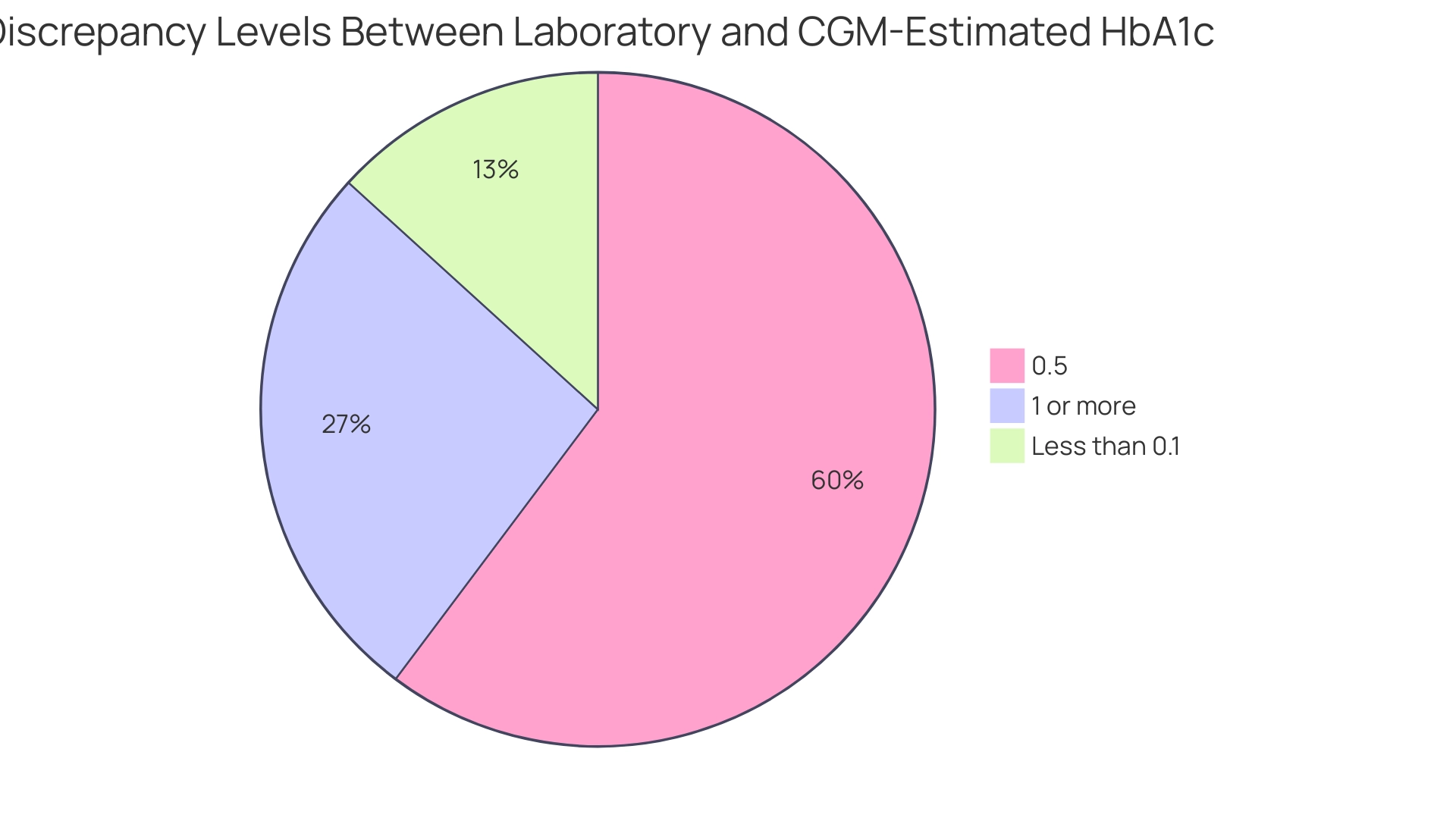
A study titled 'Discordance Between Laboratory and CGM-Estimated HbA1c,' conducted at the University of Washington Diabetes Care Center, revealed notable discordance between laboratory-measured HbA1c and CGM-estimated HbA1c, with only 11% of individuals showing a difference of less than 0.1%. In contrast, 50% and 22% exhibited discrepancies of 0.5% and 1% or more, respectively, particularly among those with advanced chronic kidney disease. Notably, the absolute mean discrepancy in individuals with eGFR ≤60 was 0.19% higher than in those with eGFR >60, underscoring the impact of kidney function on GMI readings.
These findings highlight the necessity for healthcare providers to consider these factors when interpreting GMI data and to inform individuals about the potential limitations of this metric. As ongoing validation studies progress, a deeper understanding of GMI's accuracy across diverse populations and clinical settings will emerge, ultimately enhancing management strategies for blood sugar. Understanding what is GMI percentage is vital for newly diagnosed patients, as it can help inform their management strategies and connect them to community resources offered by T2DSolutions.
The Future of GMI in Diabetes Management
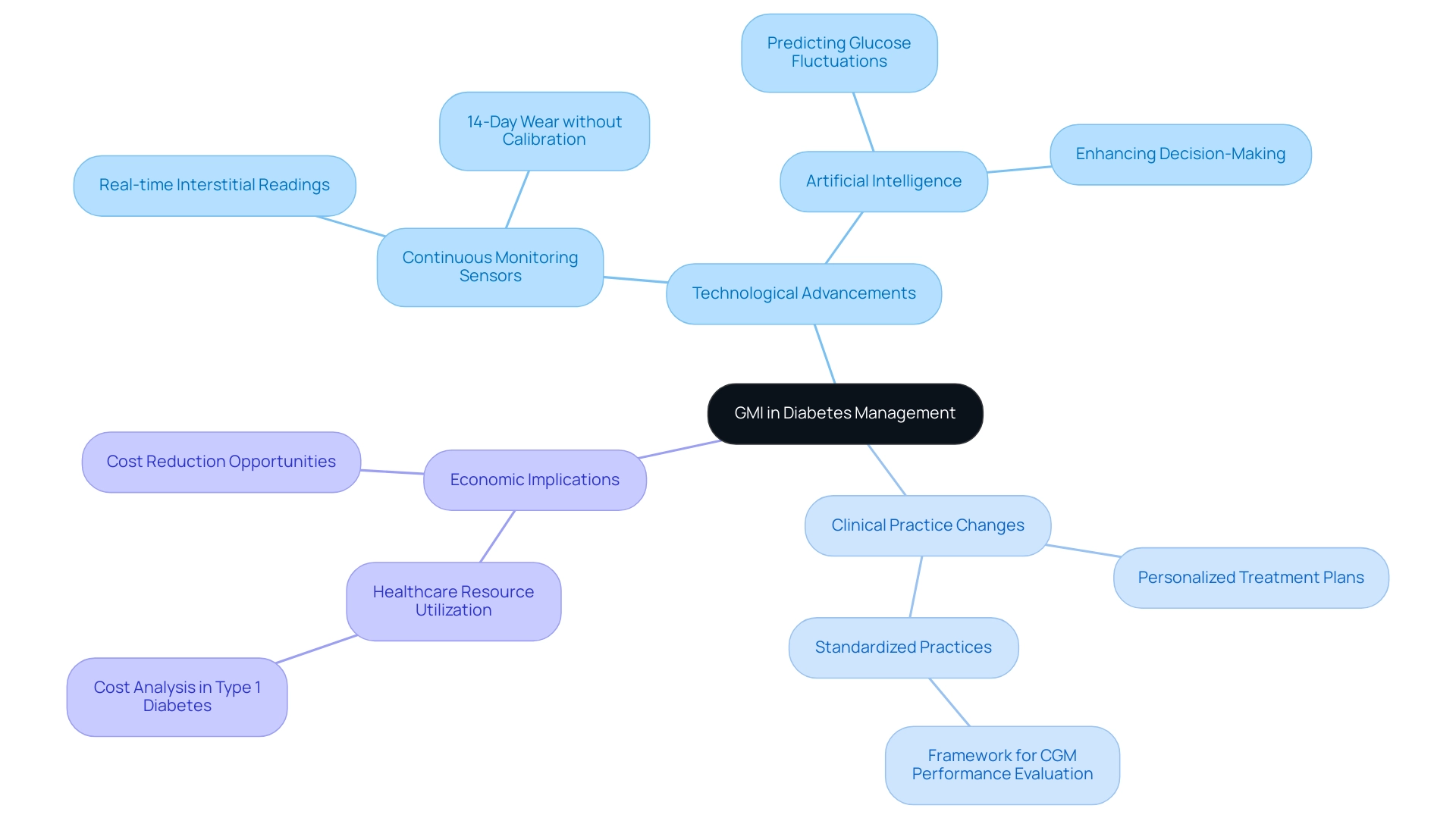
The future of managing blood sugar through the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) involves understanding what is GMI percentage, and it is set to be transformative, driven by continuous research and innovation aimed at refining its application and enhancing accuracy. As technology evolves, GMI is expected to be more seamlessly integrated into diabetes care protocols, paving the way for personalized treatment plans that leverage real-time data. Recent advancements in continuous monitoring sensors, which now deliver interstitial readings every minute for up to 14 days without the need for finger-stick calibration, signify a critical shift in how average levels correlate with HbA1c measurements.
This shift is supported by Frechman et al., who proposed a framework for reporting the design and results of clinical CGM performance evaluations, underscoring the importance of standardized practices in this evolving field. Additionally, the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) in analyzing CGM data offers promising avenues for predicting glucose fluctuations, thus enhancing outcomes for individuals. This technological integration not only boosts the accuracy of GMI but also supports healthcare providers in making more informed decisions.
Notably, the landscape of CGM claims has evolved from being predominantly durable medical equipment claims between 2010-2013 to a mix of durable medical equipment and pharmacy benefit claims from 2016-2019, highlighting the changing dynamics in managing blood sugar conditions and its implications for GMI. As awareness of what is GMI percentage grows among both healthcare providers and individuals, its adoption in clinical practice is expected to increase, thereby strengthening its crucial role in the effective management of the condition. Insights from recent case studies, such as the analysis of healthcare resource utilization and costs among patients with type 1 diabetes, underscore the economic burden of managing diabetes and the role of GMI in identifying areas for potential cost reduction while enhancing patient care.
Conclusion
The Glucose Management Indicator (GMI) represents a significant advancement in diabetes management, offering real-time insights that enhance the understanding of blood glucose levels. Unlike traditional metrics such as Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), which provide a retrospective view of glucose control, GMI allows for immediate adjustments to treatment plans based on current data. This capability is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike, facilitating more personalized and effective management strategies.
The practical applications of GMI extend beyond mere monitoring; they empower patients to make informed lifestyle decisions that can lead to better health outcomes. By recognizing trends in their GMI readings, individuals can proactively adjust their diets, exercise regimens, and medication adherence. Furthermore, the importance of understanding the discrepancies between GMI and HbA1c measurements cannot be overstated, as these differences highlight the complexity of diabetes management and the need for comprehensive assessments.
Looking ahead, the future of GMI in diabetes care is promising, driven by continuous advancements in technology and ongoing research. As GMI becomes more integrated into clinical practice, its role in shaping personalized treatment plans is expected to grow. The incorporation of artificial intelligence in analyzing CGM data further enhances the potential for predicting glucose fluctuations, ultimately improving patient outcomes and optimizing healthcare resources.
In summary, GMI is not just a tool; it is a transformative element in diabetes management that empowers patients and providers alike. By embracing its capabilities, the diabetes community can enhance care, improve health outcomes, and navigate the complexities of this chronic condition more effectively.



