Overview
Understanding your blood sugar levels is crucial in managing Type 2 diabetes. A normal fasting blood sugar level is defined as less than 100 mg/dL. If your levels fall between 100 and 125 mg/dL, this indicates prediabetes, while levels of 126 mg/dL or higher confirm a diabetes diagnosis. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these numbers, but knowing them is the first step toward taking control of your health.
These benchmarks are not just numbers; they are vital tools for managing diabetes and preventing complications. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes can play a significant role in maintaining your glucose levels within the recommended range. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Many have walked this path and found ways to thrive.
Consider reaching out for support or resources that can help you navigate this journey. Sharing experiences with others can create a sense of community and understanding, reminding you that you are not alone. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Understanding fasting blood sugar levels is crucial for managing Type 2 diabetes. These measurements offer valuable insights into your metabolic health, empowering you to take proactive steps in monitoring your well-being. The American Diabetes Association defines normal fasting blood sugar levels as below 100 mg/dL. But what happens when those levels creep above this threshold? Or when lifestyle factors complicate glucose management? It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these concerns.
This article delves into the significance of fasting blood sugar levels and the implications of abnormal readings. We will explore essential strategies for maintaining optimal health. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Together, we can navigate the complexities of diabetes management and find the support you need.
Define Normal Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
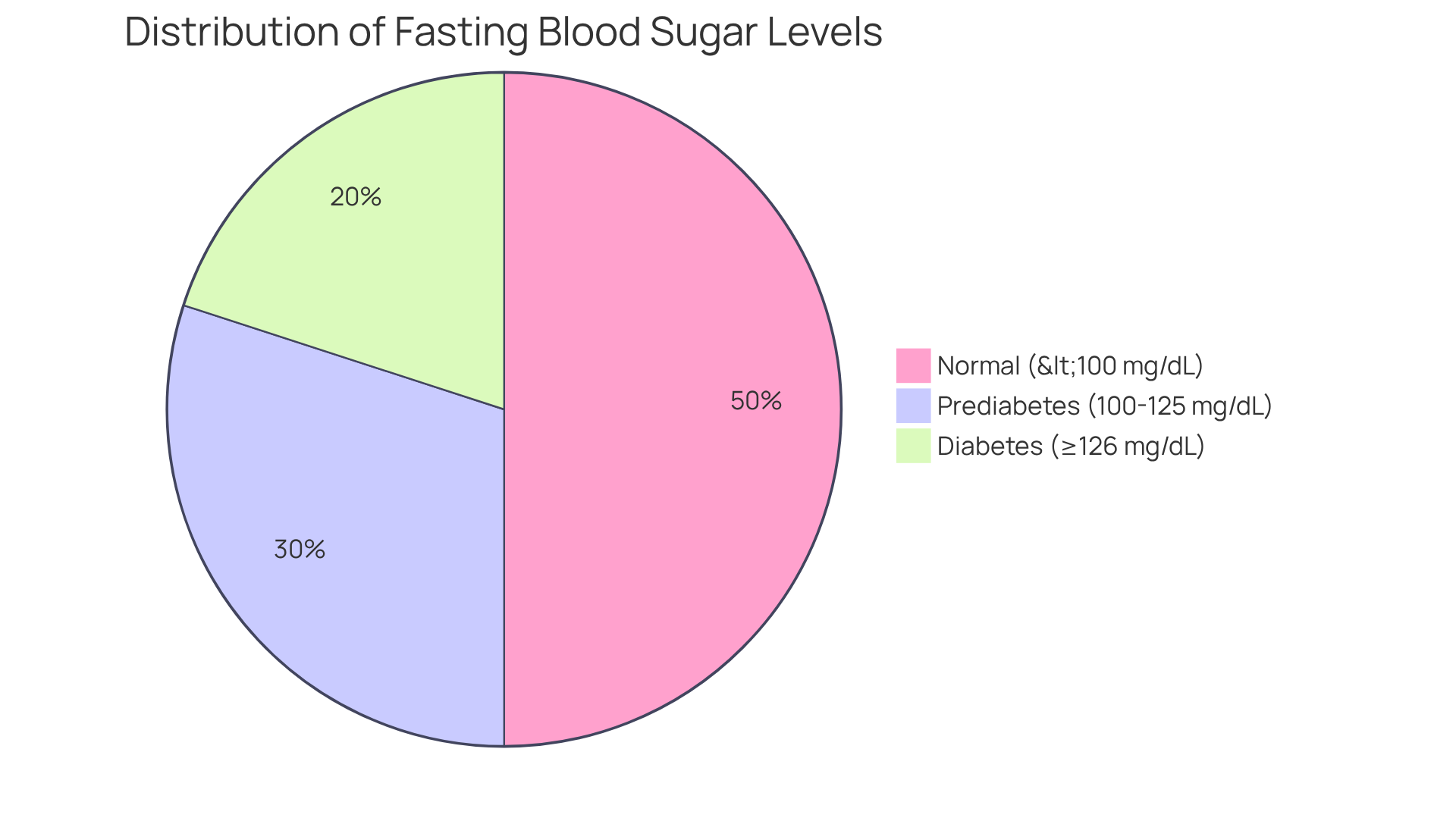
After an overnight abstinence from food, typically understood as not consuming anything for at least 8 hours, one can evaluate what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2 by assessing typical glucose concentrations in the circulation. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2 is defined as a standard glucose level below 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L). If your readings fall between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L), this may indicate prediabetes. A measurement of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or above, confirmed by two separate tests, verifies a diagnosis of diabetes. These values are essential benchmarks for understanding your metabolic health and the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Preparing for a glucose test involves abstaining from all food except water for eight to 12 hours beforehand. It's completely natural to feel anxious about this process; however, viewing it as a proactive step toward safeguarding your future health can help ease some of that worry. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in physical activity, are vital for determining what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2 and keeping your fasting glucose levels within the recommended range.
Moreover, T2DSolutions highlights the significance of community support and shared experiences in managing diabetes. By connecting with T2DSolutions, newly diagnosed patients can access invaluable educational resources and engage with others on similar journeys. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; together, we can take steps to improve your health and outcomes.
Contextualize Fasting Blood Sugar Levels in Type 2 Diabetes
Fasting glucose concentrations are crucial markers for understanding what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2 and effective glucose control for those living with the condition. These measures reveal how well the body metabolizes glucose, particularly in relation to insulin resistance—a condition where the body's cells struggle to respond to insulin, resulting in higher glucose levels. For instance, a glucose measurement of 126 mg/dL or above indicates diabetes, while readings between 100 to 125 mg/dL suggest impaired glucose tolerance, highlighting the importance of understanding what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2.
Tracking glucose levels is vital for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment strategies, dietary choices, and lifestyle changes. Regular assessments empower healthcare providers and patients to recognize trends and make necessary adjustments to their management plans. For example, a case study highlighted that individuals who embraced lifestyle modifications, such as increased physical activity and healthier eating habits, saw significant improvements in their glucose readings over time.
Understanding the role of insulin resistance in glucose levels during fasting is also essential. Insulin resistance can lead to elevated glucose readings, complicating the maintenance of optimal glucose management. This connection highlights the importance of improving insulin sensitivity through lifestyle changes, which can ultimately enhance overall diabetes management.
At T2DSolutions, we are committed to providing valuable resources and support for individuals navigating Type 2 diabetes. Our platform offers educational materials, tools, and community assistance to help newly diagnosed patients understand and monitor their glucose levels effectively.
In summary, regularly observing what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2 not only aids in managing Type 2 diabetes but also plays a critical role in preventing complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney failure. By focusing on these aspects, individuals can gain valuable insights into their glucose management and make informed health decisions. You're not alone in this journey; explore T2DSolutions for more information on managing your diabetes effectively.
Examine Factors Affecting Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting glucose concentrations can be influenced by various factors, including diet, exercise, stress, medications, and overall health. For instance, consuming a high-carbohydrate meal before fasting may lead to higher glucose levels the following morning. Conversely, regular physical activity is known to lower glucose concentrations, as exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes glucose absorption by muscles. It's understandable to feel concerned about stress, as it can disrupt this balance, often resulting in increased glucose levels due to the release of stress hormones like cortisol. Additionally, certain medications, particularly corticosteroids, can lead to elevated glucose concentrations.
A retrospective cohort study involving 500 individuals with Type 2 diabetes revealed significant links between lifestyle factors and fasting glucose (FBS) readings. The average FBS value decreased from 308 mg/dl to 163 mg/dl throughout the study, highlighting the positive effects of effective management strategies. Nutritionists emphasize that dietary choices play a crucial role in glucose regulation. For example, registered dietitian Nikki Doering notes that insulin resistance can hinder glucose transport into cells, resulting in higher glucose concentrations.
Understanding what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2 is essential for those managing Type 2 diabetes, as it empowers you to make informed choices about your diet and lifestyle. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way, helping you achieve better control of your condition.
Discuss Implications of Abnormal Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Irregular glucose concentrations during periods of not eating can lead to serious health concerns. When levels exceed 100 mg/dL, this may indicate prediabetes, affecting around 88 million adults in the United States. This condition significantly raises the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and its associated complications. It's important to understand that ongoing elevated glucose levels can result in long-term issues such as heart disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage. For instance, individuals with persistently high glucose may experience nerve damage, leading to pain or numbness in their extremities—common complications of diabetes.
Conversely, low glucose levels, known as hypoglycemia, can cause symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness. This duality underscores the importance of understanding what is normal fasting blood sugar level for diabetes type 2, as maintaining glucose readings within this normal range is essential for overall health and well-being, especially for those managing diabetes. Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments, including dietary plans and exercise routines, can greatly help mitigate these risks.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. T2DSolutions is here to provide resources and community support to help you manage your blood sugar levels effectively, fostering a healthier future. We encourage you to reach out and share your experiences, as together we can create a supportive environment for everyone navigating these challenges.
Conclusion
Understanding what constitutes normal fasting blood sugar levels is crucial for managing Type 2 diabetes effectively. Normal levels, defined as below 100 mg/dL, serve as a benchmark for assessing metabolic health and preventing complications. Recognizing these values can empower you to take proactive steps in monitoring your health and making informed lifestyle choices.
Throughout this article, we discussed key insights regarding the significance of fasting blood sugar levels. Factors such as diet, exercise, stress, and medications are influential elements that can affect glucose concentrations. Furthermore, we examined the implications of both high and low fasting blood sugar levels, emphasizing the potential health risks associated with abnormal readings. Regular monitoring, along with community support and educational resources, plays a vital role in managing diabetes and improving overall health outcomes.
In light of this information, it’s essential to remain vigilant about your fasting blood sugar levels. By understanding the factors that influence these levels and the potential implications of abnormal readings, you can take meaningful steps toward better health. Engaging with resources like T2DSolutions can provide the necessary support and information to navigate this journey effectively. Remember, taking control of fasting blood sugar management not only enhances your well-being but also fosters a supportive community for those facing similar challenges. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are normal fasting blood sugar levels for diabetes type 2?
Normal fasting blood sugar levels for diabetes type 2 are defined as a glucose level below 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L).
What does a fasting blood sugar level between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL indicate?
A fasting blood sugar level between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) may indicate prediabetes.
What fasting blood sugar level confirms a diagnosis of diabetes?
A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or above, confirmed by two separate tests, verifies a diagnosis of diabetes.
How should one prepare for a glucose test?
To prepare for a glucose test, one should abstain from all food except water for eight to 12 hours beforehand.
What lifestyle changes can help maintain normal fasting blood sugar levels?
Maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in physical activity are vital for determining normal fasting blood sugar levels and keeping glucose levels within the recommended range.
How can community support assist in managing diabetes?
Community support, such as that offered by T2DSolutions, provides educational resources and the opportunity to connect with others on similar journeys, which can be invaluable for newly diagnosed patients.



