Overview
The Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates is an important guideline that recommends 45% to 65% of your total daily caloric intake should come from carbohydrates. This is crucial for maintaining your energy levels and managing blood sugar, especially if you're navigating life with diabetes.
It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by dietary recommendations, but adhering to the AMDR can play a significant role in preventing chronic diseases and improving your overall health. Remember, the quality and quantity of carbohydrate sources in your diet matter just as much as the numbers themselves.
You're not alone in this journey. Many individuals find it helpful to seek support and resources that can guide them through making informed dietary choices. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Navigating the world of carbohydrates can feel overwhelming, especially for those managing diabetes. With dietary guidelines constantly changing and a wealth of information at your fingertips, understanding how to incorporate carbohydrates into your meals is crucial for maintaining your health and well-being. The Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) offers a supportive framework, outlining the recommended percentage of daily caloric intake from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This article will explore the importance of the AMDR, the impact of carbohydrate quality on your health, and provide practical strategies to personalize your carbohydrate intake.
It's understandable to feel confused by the numerous misconceptions surrounding carbohydrates. By shedding light on these misunderstandings and emphasizing the importance of informed dietary choices, we hope to empower you on your journey toward better diabetes management. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; together, we can navigate these challenges and find the right path for you.
Understanding the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR)
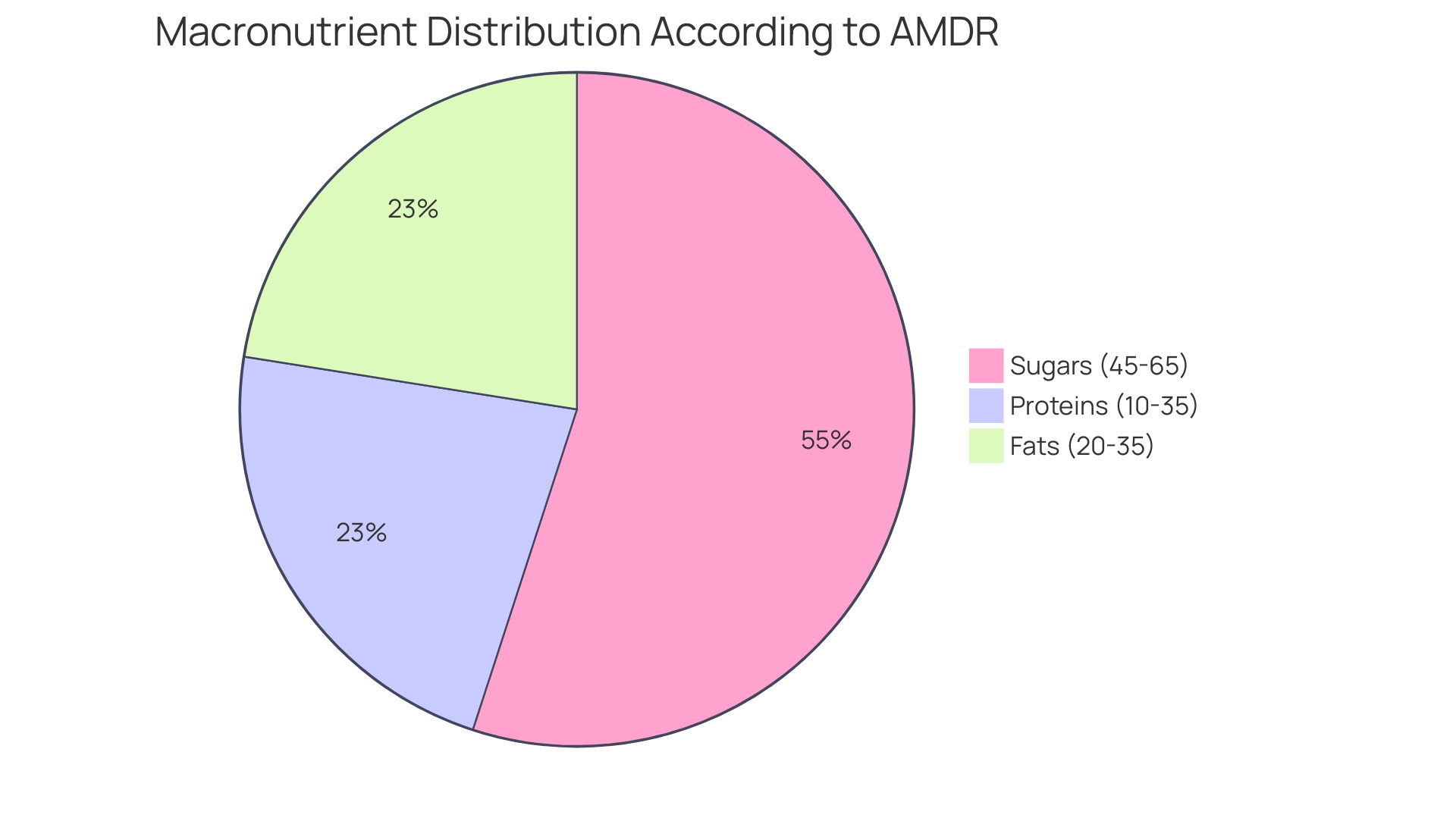
The Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) is an essential guideline that specifies the recommended percentage of total daily calories obtained from sugars, proteins, and fats. For sugars, the AMDR is set at 45% to 65% of total caloric consumption. This range is specifically designed to ensure adequate energy levels while reducing the risk of chronic diseases, a consideration that is particularly vital for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes.
Understanding the AMDR empowers you to make informed dietary choices that align with your health objectives. You're not alone in navigating these guidelines; many individuals are on a similar journey toward better health.
Recent research indicates that a proposed lower-carbohydrate dietary pattern can be both adequate and comparable in diet quality to the existing Dietary Guidelines for Americans. This change in dietary recommendations is backed by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data, which spans from 2005 to 2018, highlighting the evolving understanding of carbohydrate consumption in relation to health outcomes.
Experts emphasize the importance of regular monitoring of critical nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins A and E, folate, and iron, to ensure a balanced diet while adhering to the AMDR. As noted by M. A. S., 'Regular monitoring of critical nutrients might thus be advisable.' It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by this information, but remember that as the landscape of dietary recommendations continues to evolve, future research is expected to establish a standard definition of lower-carb diets in grams, utilizing biomarkers to assess the necessary level of restriction for optimal metabolic benefits.
Real-world examples illustrate the impact of adhering to the AMDR on Type 2 Diabetes patients. For instance, organizations like Diabetes UK have faced challenges in updating dietary advice due to fears of accountability, as highlighted in the case study titled 'High Stakes of Dietary Recommendations.' This fear of accountability can perpetuate outdated guidelines, reinforcing the need for ongoing education and adaptation in dietary practices to improve public health outcomes.
In summary, understanding the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) for carbohydrates in your diet is essential. It serves as a foundational element in managing blood sugar levels and guides you toward healthier eating patterns that support your overall well-being. By staying informed about the latest research and recommendations, you can navigate your dietary choices with confidence, fostering a proactive approach to your health journey. T2DSolutions aims to be a valuable resource in this journey, providing education and support for those managing Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Recommended Percentage of Carbohydrates in the AMDR
At T2D Solutions, we understand how crucial proper nutrition is in managing diabetes. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020-2025 offer valuable insights into the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) for carbohydrates. They recommend that sugars and starches make up 45% to 65% of total daily caloric intake. For those following a typical 2,000-calorie diet, this translates to approximately 225 to 325 grams of sugars each day.
This macronutrient range is vital for maintaining energy levels and supporting essential bodily functions. It’s particularly important for individuals managing their blood sugar levels, who need to grasp the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) for carbohydrates in their diet.
Focusing on the quality of starches is equally important. By emphasizing whole grains, fruits, and vegetables over refined sugars and processed foods, you can significantly improve your overall health and blood sugar management. The World Health Organization has recently updated its guidelines to stress the importance of dietary quality, aiming to reduce the risk of diet-related non-communicable diseases, including type 2 diabetes.
A recent case study highlights that both the amount and quality of sugars matter, suggesting specific consumption levels to foster healthier diets. Nutritionists advocate for a balanced approach to dietary intake, encouraging individuals to seek guidance from healthcare professionals before making significant dietary changes. As Hope Lynn Petersen wisely notes, "Eating the right types of carbs in the right amounts may seem easier said than done, but there are some simple guidelines you can follow to stay on the right track."
For example, a well-structured 2,000-calorie diet might allocate around 300 grams of sugars, distributed across meals to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. Real-life examples can illustrate how this distribution can be achieved. A typical daily meal plan could include:
- Oatmeal with berries for breakfast
- A quinoa salad with mixed vegetables for lunch
- A dinner featuring grilled chicken with sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli
These meals not only satisfy dietary recommendations but also provide essential nutrients that promote overall health.
As we move into 2025, understanding the suggested sugar intake and its effects on blood sugar control remains essential. The focus on both the quantity and quality of these nutrients is reinforced by recent case studies, showcasing the positive results linked to following these guidelines. By making informed decisions about sugar intake, you can enhance your blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. T2D Solutions is here to provide the resources and support you need as you navigate your path to better health.
The Impact of Carbohydrate Intake on Health
Carbohydrate intake is essential for maintaining overall health, especially for those managing diabetes. High-quality sugars, such as whole grains, legumes, and fiber-rich foods, play a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin sensitivity. On the other hand, a diet rich in simple sugars, particularly refined ones, can lead to significant spikes in blood glucose, increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
At T2DSolutions, we understand how important it is to know the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) for carbohydrates in your diet. This knowledge promotes metabolic health and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. Recent research underscores this, with a study identifying 3,903 articles in the initial search, highlighting the extensive research supporting the claims about nutrient consumption and diabetes management. For instance, findings suggest that a moderate starch diet can effectively improve glucose control in individuals with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) without increasing the likelihood of hypoglycemia or ketoacidosis.
As noted by ESF, who was responsible for the study's design and analysis, these insights are crucial for understanding effective dietary strategies.
The quality of the sugars you consume is equally important. Data indicates that contemporary starches differ significantly from those available in the early 20th century, with the current U.S. food supply increasingly reliant on highly refined sugars. This shift has important implications for blood sugar regulation and overall health outcomes.
Real-world examples illustrate the benefits of prioritizing the quality of sugars. A case study titled "Meal Planning for Diabetes Management" highlighted how structured meal planning, focusing on balanced meals and snacks, can lead to improved blood glucose control and enhance overall quality of life. By choosing high-quality carbs, you can better manage your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
At T2DSolutions, we emphasize that balanced consumption of sugars is crucial for effective blood sugar management, particularly concerning the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) for carbohydrates in your diet. As you navigate your dietary choices, remember that understanding the effect of food quality on your health is a key step in your journey toward improved blood sugar management. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to provide resources and support as you learn more about managing your diabetes effectively.
Types of Carbohydrates: Simple vs. Complex
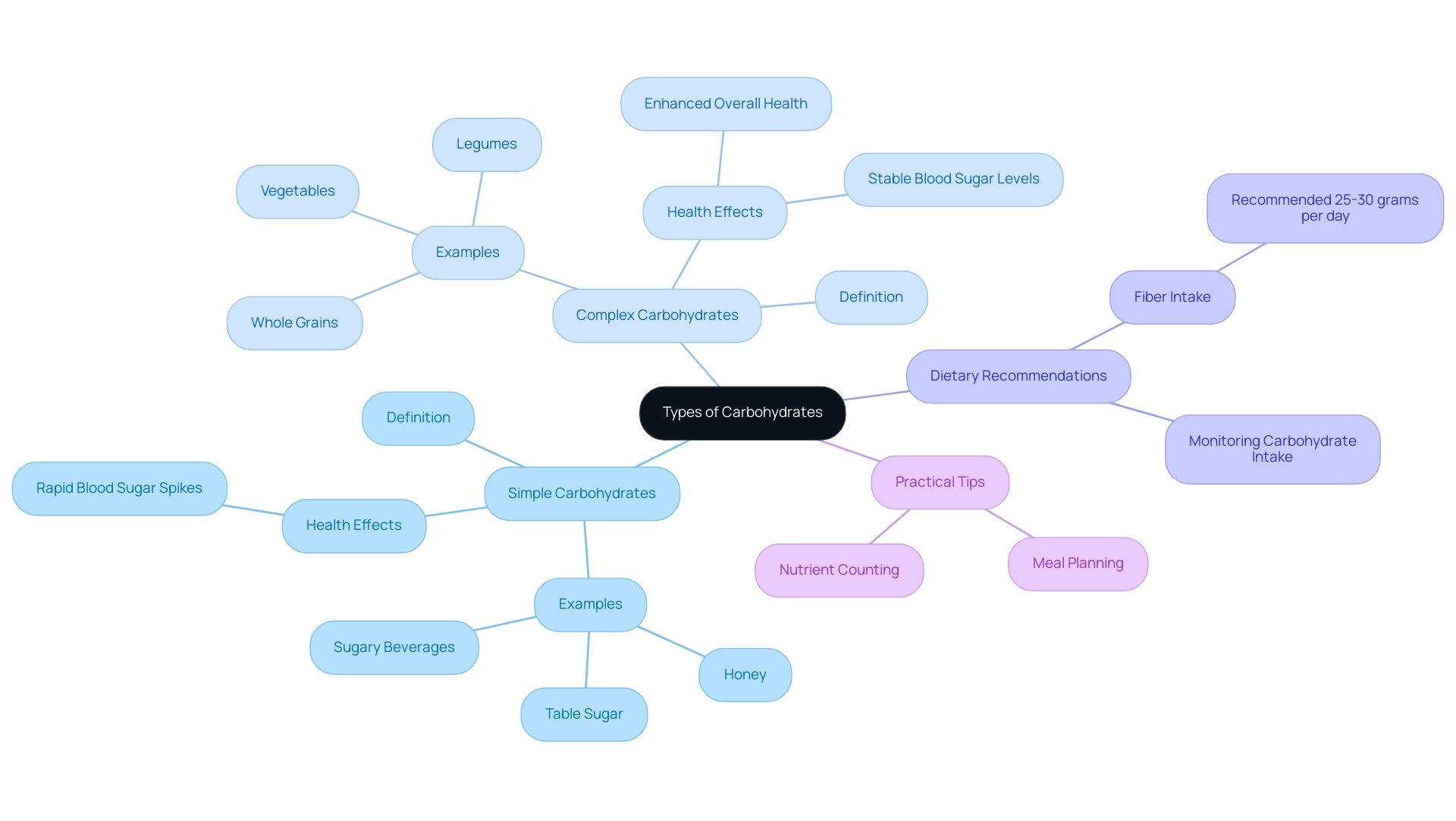
Carbohydrates are primarily classified into two categories: simple and complex. Simple sugars, which consist of one or two sugar molecules, are rapidly absorbed by the body, often resulting in swift spikes in blood sugar levels. Common examples include table sugar, honey, and sugary beverages. It's understandable to feel concerned about how these sugars affect your health.
In contrast, complex sugars are composed of longer chains of sugar molecules, leading to a slower digestion process and a more gradual release of energy. Foods like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables are rich in complex sugars and can be especially advantageous for individuals managing blood sugar levels, as they assist in maintaining stable glucose levels. Remember, making informed choices can empower you on your health journey.
Grasping the influence of these sugar categories is essential for effective blood sugar control. Research indicates that diets rich in complex sugars can enhance overall health and assist in blood sugar regulation. For instance, a case study titled "Nutritional Recommendations for Diabetes Management" highlights the importance of incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including healthy fats, proteins, and vegetables, to create a balanced diet that supports diabetes management. You're not alone in navigating these dietary choices; many have found success through similar paths.
Furthermore, tracking overall carb consumption is crucial, particularly when eating foods rich in fiber or sugar alcohols, since these can also affect blood glucose levels. The American Diabetes Association suggests a daily fiber consumption of 25 to 30 grams, as mentioned by Kristen Cherney, PhD. This can be accomplished by consuming complex sugars. Taking small steps can lead to significant improvements in your health.
This dietary approach not only enhances blood sugar control but also contributes to overall well-being. T2DSolutions offers practical advice and resources to help individuals manage their sugar intake effectively. By providing guidance on meal planning and nutrient counting, T2D Solutions aims to empower you to make informed dietary choices. Real-life examples demonstrate the differences in blood sugar responses to various types of sugars.
For instance, a meal made with whole grain pasta (complex) will typically lead to a more stable blood sugar level compared to a meal with white bread (simple). Expert opinions highlight the significance of selecting complex sugars for improved blood sugar management, as they offer sustained energy and assist in reducing the risk of glucose spikes. Current research continues to investigate the effects of simple sugars on blood sugar levels, reinforcing the need for informed dietary choices in your journey toward effective diabetes management. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Incorporating Carbohydrates into Your Daily Diet
Including starches in your daily diet can be effectively accomplished by prioritizing whole, nutrient-rich foods. Aiming to fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, such as leafy greens, broccoli, and bell peppers, is a wonderful strategy. These vegetables are not only low in calories but also high in fiber, which aids digestion and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Whole grains should also be a staple in your meals. Options like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread provide sustained energy and essential nutrients, making them excellent choices for a balanced diet. It's important to consider portion sizes; distributing nutrient intake evenly throughout the day can significantly contribute to better blood sugar control.
For example, instead of ingesting a large quantity of starches in one meal, aim for smaller portions at each meal and snack. This approach can make a difference in how you feel.
Meal planning and preparation play a crucial role in ensuring that healthy food sources are readily available. By planning your meals ahead of time, you can make informed choices that align with your dietary needs. For instance, consider creating a weekly menu featuring a range of whole grains and vegetables. This can help you resist the lure of processed foods that are frequently high in refined sugars.
Statistics indicate that diets with a lower proportion of sugars can lead to a reduction in the need for pharmacological therapy among diabetic patients. This is essential for minimizing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and mortality. Therefore, understanding how to include healthy sugars in your diet is vital for effective diabetes management. As V.J.C.-S. noted, "Regarding physical health, sugar consumption can influence the development and outlook of metabolic disease, as an uncontrolled intake of refined sugars puts individuals at risk of developing metabolic syndrome and subsequently developing metabolic disease."
In 2025, nutritionists emphasize the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) for carbohydrate in the diet by highlighting the importance of selecting healthy carbohydrate sources, such as legumes, fruits, and whole grains. These not only provide energy but also contribute to overall health. By focusing on these nutrient-rich foods, you can create a diabetes-friendly diet that supports stable blood sugar levels and enhances your well-being.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey; community support and shared experiences can foster resilience and hope as you navigate the complexities of managing your condition. T2DSolutions encourages people to connect with others facing similar challenges, highlighting the importance of community in achieving better health outcomes.
Debunking Myths: Common Misconceptions About Carbohydrates
Myths about sugars often create confusion for individuals managing diabetes. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the information out there. A common misconception is that all types of carbs are unhealthy and should be entirely avoided. In truth, sugars are a vital macronutrient that provides essential energy and supports various bodily functions.
For instance, nutritious foods containing natural sugars, such as fruits and dairy, can be beneficial when included in a balanced diet. The FDA has considered certain artificial sweeteners, like saccharin, aspartame, and sucralose, safe to consume under specific conditions. This provides options for those regulating their intake of sugars. However, it's important to limit sugary foods that offer minimal nutritional value.
At T2DSolutions, we aim to empower newly diagnosed patients with precise information about sugars and diabetes management. Our resource hub offers valuable insights and support to help you navigate your dietary choices effectively.
Another prevalent myth is that eating sugars at night inevitably results in weight gain. However, research indicates that the timing of carbohydrate intake is less significant than the overall quality and quantity consumed throughout the day. This aligns with findings from a case study titled 'Understanding Risk Factors for Diabetes,' which debunked the myth that a lack of family history of the condition eliminates risk.
It highlighted that factors such as age, heart disease, high blood pressure, and obesity play crucial roles in diabetes risk, emphasizing the importance of healthy lifestyle choices.
By educating ourselves about these misconceptions, we empower ourselves to make informed dietary choices. A diabetes-friendly eating plan can be both healthy and enjoyable, allowing for the inclusion of beneficial sugars. As one expert noted, if your doctor recommended insulin therapy, ask about ways you can fit the taking of the medication into your life—instead of the other way around.
Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice is essential, as they can provide tailored guidance that considers your specific health needs. As we explore these myths together, it becomes evident that grasping the importance of sugars is a crucial step in effectively managing blood sugar levels. Remember, you're not alone in this journey—T2DSolutions is here to support you every step of the way.
Personalizing Your Carbohydrate Intake: A Tailored Approach
Customizing carbohydrate consumption is essential for effectively managing blood sugar. Personal requirements can differ greatly based on factors such as age, activity level, and specific health conditions. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by these differences. A recent study highlighted that participants who received tailored dietary recommendations showed a marked decrease in their consumption of unhealthy foods. This underscores the value of personalized nutrition advice. Notably, at week 26, 34 participants (100%) in the exploratory group did not progress to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), further emphasizing the effectiveness of personalized dietary interventions.
To develop a meal plan that aligns with your health goals, consider collaborating with healthcare professionals, including registered dietitians and certified diabetes educators. You're not alone in this journey; T2DSolutions can serve as a valuable resource, offering access to expert advice and educational materials that help customize your dietary intake effectively. This ensures it meets your unique requirements. Tracking your blood sugar levels is also crucial, as it provides important insights into how various food sources influence your personal reactions.
This ongoing assessment allows for necessary adjustments to optimize your dietary choices for better health outcomes. Moreover, understanding the acceptable macronutrient distribution range (AMDR) for carbohydrates in the diet—typically recommended at 45-65% of total calorie intake—can guide you in making informed decisions. However, emerging research suggests that higher levels of starchy foods may be associated with elevated risks of Type 2 Diabetes, particularly in specific populations. Tauseef Ahmad Khan highlights that additional research, particularly in Asian nations, is necessary to examine the link between consumption levels exceeding the recommended dietary guidelines and the risk of T2D.
Therefore, it is vital to consider these factors when customizing your nutrient intake.
Real-world examples, such as the Food4Me trial, demonstrate the effectiveness of personalized dietary interventions. Participants in this multi-country study significantly improved their dietary choices by following tailored meal plans, which ultimately contributed to better health outcomes. The trial revealed significant differences in total energy consumption and saturated fat consumption in favor of personalized dietary approaches after adjustments.
By concentrating on personalized carbohydrate consumption, you can take proactive measures in managing your diabetes, leading to enhanced overall well-being. Remember, T2DSolutions is committed to supporting you on this journey by providing resources and guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion
Understanding how to effectively manage carbohydrate intake is essential for individuals navigating diabetes. The Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) provides a crucial framework, recommending that carbohydrates make up 45% to 65% of daily caloric intake. This guideline not only helps maintain energy levels but also plays a vital role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases, particularly for those managing Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes. By emphasizing the quality of carbohydrates—favoring whole grains, fruits, and vegetables over refined sugars—you can significantly enhance your health and metabolic control.
Personalizing carbohydrate intake based on your individual needs is paramount. It's important to consider factors such as age, activity level, and specific health conditions to develop a tailored dietary plan. Collaborating with healthcare professionals can ensure that your carbohydrate consumption aligns with your personal health goals, optimizing blood sugar management and overall well-being. Remember, the importance of ongoing monitoring and adjustment of dietary choices cannot be overstated; it empowers you to make informed decisions that positively impact your health.
Ultimately, debunking common myths about carbohydrates is essential for fostering a clearer understanding of their role in a balanced diet. Carbohydrates are not to be feared; instead, they should be embraced as a critical source of energy when chosen wisely. By focusing on informed dietary choices and the quality of food you consume, you can navigate your diabetes management journey with confidence and resilience. T2DSolutions stands ready to support you on this journey, providing vital resources and community connections to aid in achieving better health outcomes. You're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR)?
The AMDR is a guideline that specifies the recommended percentage of total daily calories obtained from sugars, proteins, and fats. For sugars, the AMDR is set at 45% to 65% of total caloric consumption.
Why is the AMDR for sugars important for individuals with diabetes?
The AMDR for sugars is vital for ensuring adequate energy levels while reducing the risk of chronic diseases, particularly for individuals managing Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes.
What does recent research say about carbohydrate consumption?
Recent research suggests that a proposed lower-carbohydrate dietary pattern can be adequate and comparable in diet quality to existing Dietary Guidelines for Americans, highlighting an evolving understanding of carbohydrate consumption in relation to health outcomes.
What nutrients should be regularly monitored when following the AMDR?
It is important to regularly monitor critical nutrients such as fiber, vitamins A and E, folate, and iron to ensure a balanced diet while adhering to the AMDR.
How can adhering to the AMDR impact Type 2 Diabetes patients?
Adhering to the AMDR can help manage blood sugar levels, and real-world examples show that organizations have faced challenges in updating dietary advice, which underscores the need for ongoing education and adaptation in dietary practices.
What is the recommended sugar intake for a typical 2,000-calorie diet?
For a typical 2,000-calorie diet, the AMDR recommends that sugars and starches make up approximately 225 to 325 grams of sugars each day.
What types of carbohydrates should be emphasized in the diet?
It is important to focus on the quality of carbohydrates by emphasizing whole grains, fruits, and vegetables over refined sugars and processed foods.
Can you provide an example of a daily meal plan that aligns with the AMDR?
A typical daily meal plan could include oatmeal with berries for breakfast, a quinoa salad with mixed vegetables for lunch, and grilled chicken with sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli for dinner.
What role does T2D Solutions play in managing diabetes through nutrition?
T2D Solutions aims to provide education and support for those managing Type 2 and Type 3 Diabetes, helping individuals navigate dietary choices and guidelines effectively.



