Overview
An A1C level of 5.2 is considered good as it falls within the normal range of 4% to 5.6%, indicating effective blood sugar management and a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications. The article supports this by highlighting that maintaining an A1C below 7% significantly decreases the chances of serious health issues such as neuropathy and cardiovascular disease, thus underscoring the importance of achieving and sustaining optimal A1C values for overall health.
Introduction
Understanding A1C levels is vital for individuals managing diabetes, as it serves as a key indicator of blood glucose control over time. The A1C test measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, offering insights into long-term health and the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies. A level of 5.2 is particularly noteworthy, falling within the normal range for non-diabetic individuals and reflecting sound glucose management practices.
This article explores the significance of A1C levels, the health benefits of maintaining a level of 5.2, and the impact of lifestyle choices on glucose control. It also emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring and the role of healthcare professionals in guiding effective diabetes management, providing a comprehensive overview for those seeking to improve their health outcomes.
Understanding A1C Levels: What Does 5.2 Mean?
T2DSolutions is committed to offering vital resources for managing Type 2 and Type 3 diabetes, and comprehending A1C values is a key aspect of that journey. The A1C test serves as a vital tool in measuring the average blood glucose values over the preceding two to three months, presented as a percentage. An A1C measurement of 5.2 indicates that approximately 5.2% of hemoglobin in the blood is glycated, which raises the question: is 5.2 a good A1C for effective blood sugar control?
For individuals free from blood sugar issues, normal A1C values generally span from 4% to 5.6%, which raises the question: is 5.2 a good A1C, as it comfortably fits within this spectrum and indicates effective glucose management practices? Grasping A1C values is crucial for evaluating long-term blood sugar management and determining the potential hazards for complications linked to extended durations of uncontrolled glucose. Significantly, individuals with high blood sugar who have HbA1c readings exceeding 7% encounter a 59.1% occurrence of 30-day morbidity, in contrast to 19% for those with readings at or below 7% (p = 0.018).
This emphasizes the critical significance of maintaining A1C values within recommended thresholds. As Halis K. Akturk stated, "In summary, our results suggest that inequities in care still exist," underscoring the need for improved management strategies. Additionally, a recent case study titled "Clinical Significance of A1C Increase in Older Adults" explored how elevated A1C readings in older individuals without glucose intolerance may necessitate reconsideration of treatment targets, emphasizing the need for age-specific diagnostic criteria to avoid medication-related complications.
Such metrics are vital in guiding treatment decisions and improving health outcomes. Stay connected with T2D Solutions by subscribing for updates on new content and resources that can assist you in managing your condition effectively.
The Benefits of an A1C Level of 5.2: Why It’s Considered Good
Individuals managing diabetes often wonder, is 5.2 a good A1C, as achieving this measurement is associated with numerous health benefits. This stage signifies effective blood sugar control, which is essential for preventing serious complications, including:
- Neuropathy
- Retinopathy
- Cardiovascular disease
Research consistently shows that maintaining an A1C below 7% can significantly diminish the risk of diabetes-related complications.
In fact, a recent prospective study emphasized that HbA1c values are a critical predictor of higher risks associated with subclinical neuropathy in diabetic patients. Furthermore, it is 5.2 a good A1C, as it indicates a reduced likelihood of hypoglycemia, a prevalent concern for those using insulin or other glucose-lowering medications. Patients often experience enhanced overall well-being, with reports of improved energy levels and quality of life when their blood sugar is optimally managed.
Notably, 60% of the final sample in related studies were female, highlighting the importance of understanding gender dynamics in managing the condition. As T2D Solutions launches as a comprehensive resource hub for Type 2 and Type 3 conditions education, it will provide crucial insights and support for newly diagnosed patients navigating their health. T2DSolutions is presently in its initial phases, and while the site is forthcoming, it intends to provide educational resources and support networks specifically created to assist patients in managing their A1C values efficiently.
Additionally, as Patricia Platt, an independent contractor for HealthMetrics, noted, 'The authors would like to thank Patricia Platt for her editorial assistance in the writing and preparation of the manuscript.' It is also crucial to recognize that several medical conditions can falsely influence A1C results, including:
- Severe anemia
- Kidney failure
- Liver disease
- Specific medications
This is highlighted in the case study titled 'Factors Affecting A1C Accuracy.' Therefore, achieving and maintaining an A1C of 5.2 raises the question of whether is 5.2 a good A1C, as it not only reflects proficient control of the condition but also plays a vital role in fostering better long-term health outcomes.
How Lifestyle Choices Affect A1C Levels
Lifestyle choices significantly influence hemoglobin A1C readings, making it essential for newly diagnosed patients to comprehend how various factors contribute to their overall health. T2DSolutions, a newly launched resource hub dedicated to Type 2 and Type 3 blood sugar management education and community support, emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet. Incorporating whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar.
Research shows that 87% of participants had untreated HbA1c readings below 6.5%, emphasizing the significance of dietary control in diabetes care. According to J.J., the guarantor of this work, 'I had full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.' Regular physical activity enhances glucose control by improving insulin sensitivity, further supporting optimal A1C levels.
Moreover, effectively managing stress through practices such as mindfulness or yoga can prevent harmful spikes in blood sugar. For those aiming for an A1C of 5.2, it is important to consider if 5.2 is a good A1C by embracing a holistic approach that incorporates dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques. This comprehensive strategy not only aids in achieving the desired A1C target but also promotes overall well-being.
T2DSolutions will provide a range of resources, including articles, videos, and community forums, to assist you in your health journey. For more resources and support, visit T2D Solutions and subscribe to stay updated on new content as it becomes available. For further reference, the ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier for the study is NCT03675360. Furthermore, the research employed a systematic method to determine Type 2 conditions, offering valuable insights into the lifestyle effects on diabetes care.
Monitoring and Managing A1C Levels Effectively
Frequent tracking of A1C readings is a fundamental aspect of efficient blood sugar control. The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes have their A1C tested at least twice a year, with more frequent testing advised for those who are not consistently meeting their targets. This proactive approach facilitates timely adjustments to treatment plans, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications.
For example, keeping a daily record of blood glucose readings can uncover patterns and triggers that affect A1C values, enabling individuals to make informed choices. Furthermore, engaging with healthcare professionals to develop personalized management strategies is essential. As noted by the American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee:
Insulin dosing adjustments should be based on meal composition
This highlights the importance of tailored advice.
By actively monitoring and managing A1C values, individuals can aim for a desirable target, as they may wonder if 5.2 is a good A1C, which can significantly enhance their overall health and quality of life. This diligence is particularly vital considering the rising occurrence of prediabetes among individuals of reproductive age and the distinct challenges encountered by specific groups, such as those living with HIV, who are at a greater risk for developing prediabetes, especially when undergoing certain antiretroviral treatments. It is important to note that the A1C test may not be reliable for diagnosis in this population, emphasizing the need for tailored screening protocols.
Furthermore, for young individuals with excess weight and type 2 sugar intolerance, a 7–10% reduction in additional weight is suggested to enhance A1C readings and general well-being. Moreover, several factors can influence A1C accuracy, including severe anemia, kidney failure, liver disease, certain blood disorders, specific medications, blood loss or transfusions, and pregnancy, further complicating the management of A1C readings.
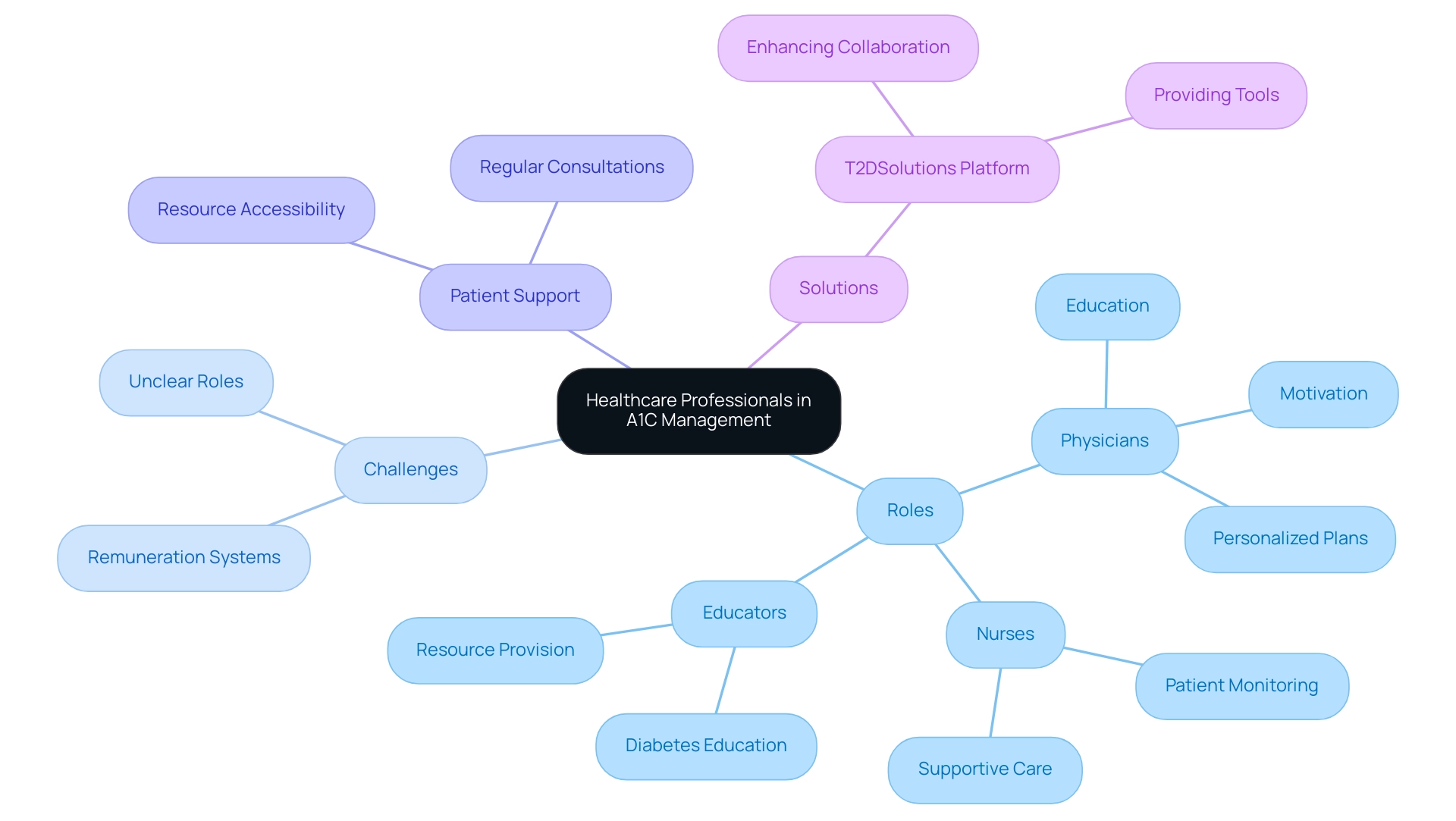
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in A1C Management
Healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurses, and educators, play a crucial role in helping individuals effectively manage their A1C levels. At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of these professionals in providing essential education about diabetes, treatment options, and personalized lifestyle modifications. Our resource hub will enhance their efforts by providing accessible information and tools that empower patients to interpret their A1C results accurately, set achievable health goals, and create comprehensive plans tailored to their unique needs.
Regular consultations with these professionals, supported by the resources available through T2DSolutions, foster patient motivation, which is essential for maintaining an A1C level while considering if 5.2 is a good A1C. This cooperative method not only boosts patients' understanding and resources but also greatly enhances the results of blood sugar care. Moreover, evidence suggests that continuous enhancement in information systems supporting chronic illness management can alleviate workloads for healthcare providers, allowing them to focus more on motivating and educating patients effectively.
This is especially crucial considering the increasing occurrence of the condition, as emphasized by recent data from the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study, which revealed that in 2017-2018, there were 5,293 newly diagnosed cases of type 2 and 18,169 instances of type 1. Such statistics highlight the urgent requirement for effective healthcare support systems in managing blood sugar conditions. Additionally, the case study titled 'Institutional Barriers to Team-Based Care' illustrates that structural challenges, such as remuneration systems and unclear roles, can hinder effective collaboration among healthcare professionals, preventing the realization of the benefits associated with multi-professional diabetes care.
T2DSolutions aims to address these challenges by providing a platform that facilitates collaboration and enhances the support network for both patients and healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Achieving and maintaining an A1C level of 5.2 is a significant milestone for individuals managing diabetes. This level not only indicates effective blood sugar control but also correlates with a lower risk of serious complications such as neuropathy and cardiovascular disease. The importance of regular monitoring and proactive management of A1C levels cannot be overstated, as consistent tracking enables timely adjustments to treatment plans and lifestyle choices.
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in influencing A1C levels. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and effective stress management are foundational elements that contribute to optimal glucose control. By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses these factors, individuals can work towards achieving their health goals while enhancing their overall well-being.
The role of healthcare professionals is equally vital in guiding patients through their diabetes management journey. By providing personalized education and support, these professionals empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health. Collaborative efforts between patients and healthcare providers, supplemented by resources like those offered by T2DSolutions, create a robust support system aimed at improving health outcomes.
In summary, understanding and managing A1C levels is essential for anyone living with diabetes. By prioritizing regular monitoring, making informed lifestyle choices, and leveraging professional support, individuals can achieve better health and a higher quality of life.



