Overview
This article highlights best practices for using manual lancets to ensure safe and effective blood sampling. It's essential to understand the importance of proper technique, hygiene, and emotional support, as these factors significantly enhance your experience. By following the outlined steps for safe usage, you can feel more secure in your approach.
Advancements in lancet technology are designed to minimize discomfort, making the process easier for you. It's understandable to feel anxious about blood sampling, but there are emotional strategies available to help alleviate that anxiety. Ultimately, our goal is to improve diabetes management outcomes, and we want to support you every step of the way.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. We encourage you to share your experiences and connect with others who may feel the same way. Together, we can foster a community of support that makes a difference in managing diabetes.
Introduction
In the realm of diabetes management, the significance of manual lancets is truly profound. These precision instruments are essential for individuals who need to monitor their blood glucose levels regularly. Yet, many may not be aware of the different types and best practices associated with their use. As technology continues to advance, understanding how to choose the right lancet—one that minimizes discomfort and maximizes safety—becomes increasingly important.
This article explores the intricacies of manual lancets, focusing on their design features and proper usage techniques. Most importantly, we will highlight the critical role they play in enhancing your overall experience of diabetes care. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the choices available, but by addressing common misconceptions and emphasizing safety and emotional support, you can empower yourself to navigate your diabetes management journey with confidence and ease.
Remember, you're not alone in this journey. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Understanding Manual Lancets: An Overview
Manual lancets are precision tools designed to gently pierce the skin and collect samples, primarily from the fingertip. They play a vital role in managing blood sugar levels, enabling individuals to conduct regular glucose monitoring, which is essential for maintaining optimal health. Understanding the different kinds of manual lancet devices for blood sampling, along with their design characteristics and intended uses, is crucial for effective diabetes management.
Using manual lancet devices typically requires users to exert force to puncture the skin. Therefore, it is important to select the appropriate depth setting and method to minimize discomfort. Recent studies have shown that advancements in surgical instrument technology can significantly enhance the user experience. For instance, a randomized clinical trial conducted in Louisville, KY, and Indianapolis, IN, in 2007 assessed a new device with an exceptionally small needle (0.15 mm diameter and 0.75 mm length).
Participants reported no pain when using this innovative device, contrasting sharply with the average pain score of 1.702 associated with traditional lancets. This discovery highlights the potential for enhanced patient adherence with glucose monitoring through the use of nearly pain-free devices. As mentioned, "To reduce the psychological barrier for SMBG as much as possible, the medical personnel should recommend 'virtually pain-free' lancing devices to their patients with blood sugar management needs."
Current statistics indicate that a notable segment of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions—80.6%—experience heightened systolic pressure. This emphasizes the significance of effective strategies for overseeing the condition, including regular monitoring. By utilizing a manual lancet that prioritizes user comfort, healthcare providers can help lower the psychological barriers associated with self-monitoring glucose levels (SMBG), ultimately fostering better health outcomes. Additionally, addressing the condition necessitates diverse strategies that engage policymakers, educators, and the healthcare community to ensure thorough assistance for individuals affected by this illness.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to offering educational materials and community support for managing this health issue. By linking improvements in needle technology to our mission, we strive to empower individuals with the knowledge and resources essential for effective diabetes management.
In summary, choosing the appropriate manual lancet is not merely about acquiring a sample; it is about enhancing the overall experience of managing diabetes. By understanding the various kinds of manual devices and their effectiveness, individuals can make informed choices that contribute to their health and well-being. You're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Safety First: Best Practices for Using Manual Lancets
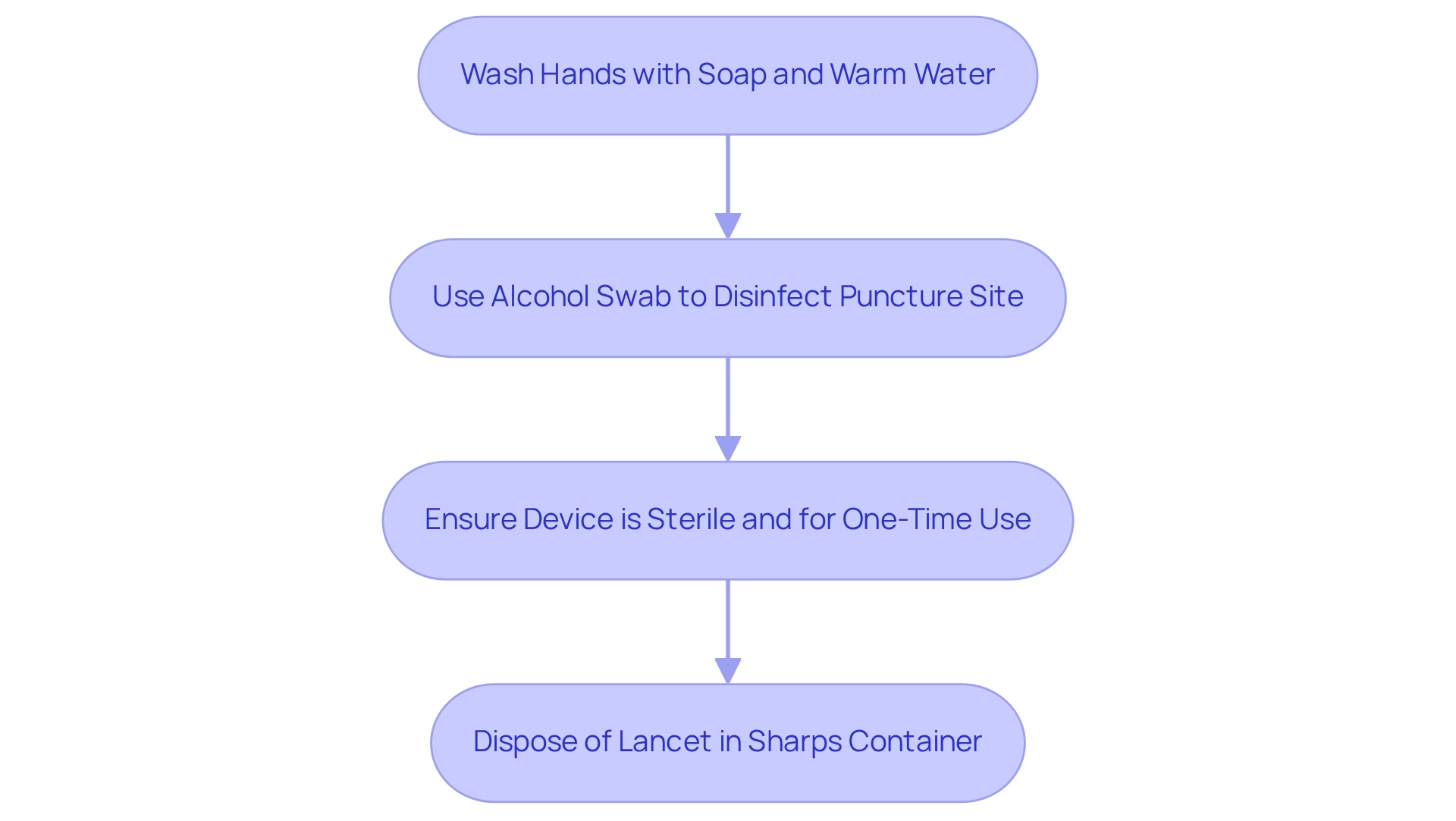
Prioritizing safety is crucial when using manual devices for blood sampling. It’s understandable to feel concerned about this process. Begin by thoroughly washing your hands with soap and warm water to eliminate any potential contaminants. Following this, use an alcohol swab to disinfect the puncture site, significantly reducing the risk of infection.
It is essential to ensure that the device is sterile and intended for one-time use only. Reusing such instruments can lead to complications, and we want to help you avoid that. After use, please dispose of the lancet in a designated sharps container to prevent accidental needle sticks and maintain a safe environment.
At T2DSolutions, we emphasize the importance of proper hand hygiene practices among individuals with blood sugar issues. Research indicates that these practices can dramatically lower the incidence of infections related to the use of a manual lancet. A study evaluating diabetes-related health evaluations highlighted gaps in management and awareness, emphasizing the need for comprehensive education on safe sampling techniques. We are here to support you every step of the way, offering resources and assistance to ensure you are knowledgeable about best practices.
Furthermore, consistent physical activity is linked to a 26 percent decrease in the likelihood of developing type 2 conditions. This highlights the significance of overall health alongside safe sampling practices. Educators at T2DSolutions also emphasize that increased strength and conditioning can enhance insulin function and sensitivity, which is crucial for effective management of the condition.
Real-life examples of infection prevention include individuals who consistently follow these safety practices, reporting fewer complications and better overall health outcomes. By following these best practices and using the resources available at T2DSolutions, you can greatly reduce the risks linked to sampling, ensuring a safer and more effective management experience. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Manual Lancets
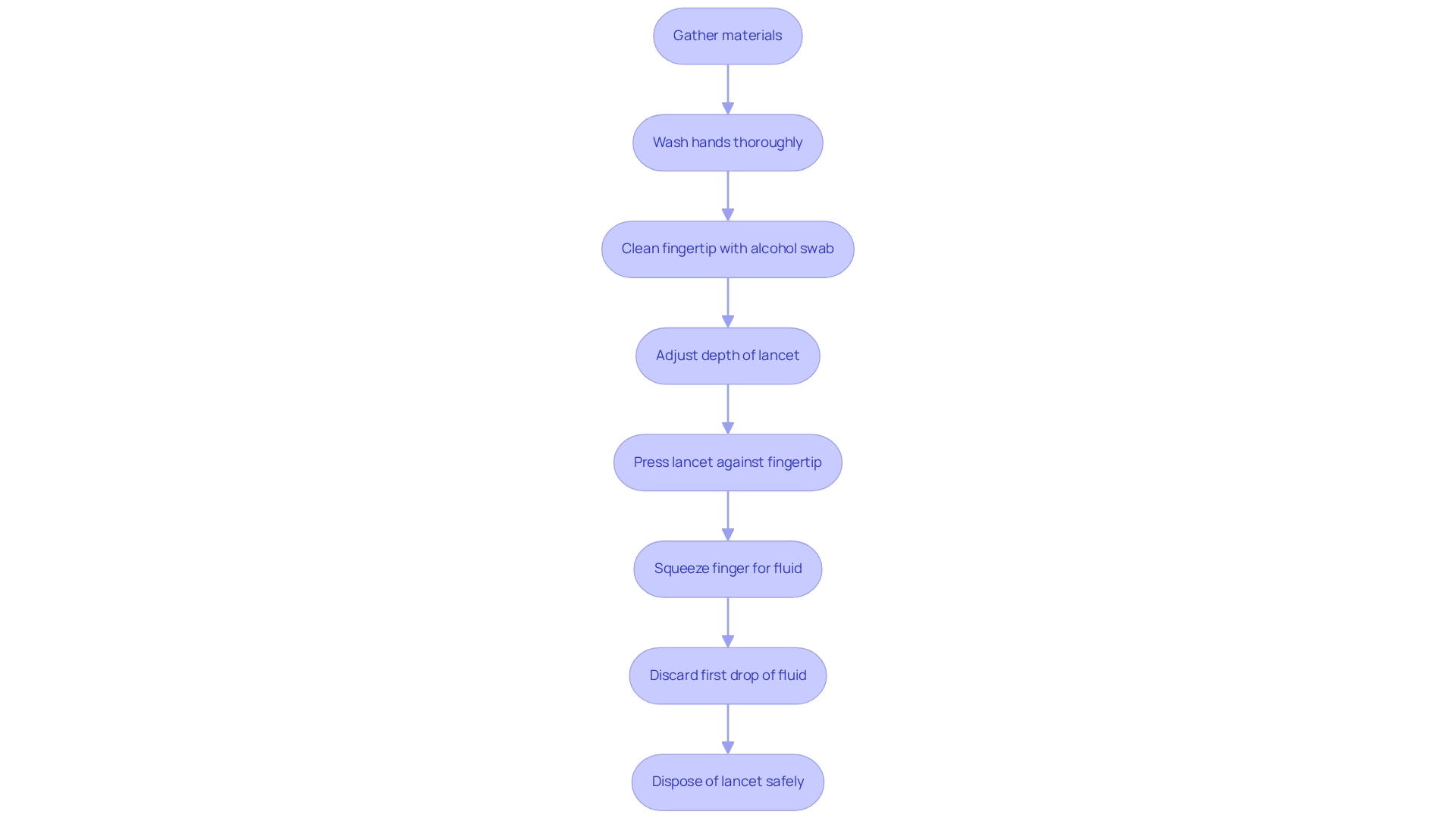
Welcome to T2 Solutions. As a new resource hub for diabetes education, T2 Solutions is dedicated to providing you with the best practices for managing your diabetes effectively. To start, gather your manual lancet, an alcohol swab, and a clean tissue, ensuring a sterile setting for sampling.
It's important to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water, making sure they are completely dry before proceeding. This simple step helps minimize the risk of infection.
Next, take an alcohol swab and clean the area on your fingertip where you will prick. Allow it to dry to ensure effective disinfection.
If your manual lancet has adjustable depth settings, select the appropriate depth based on your skin type. This ensures a clean puncture, which is crucial.
Hold the device firmly against the side of your fingertip, placing it slightly off-center. This positioning enables a more effective draw.
Now, press down firmly on the lancet to puncture the skin. A quick and decisive action minimizes discomfort.
Gently squeeze your finger to encourage a drop of fluid to form, ensuring you have enough for testing.
Remember to discard the initial drop of fluid, as it may contain tissue fluid that can affect test results. Use the second drop of fluid for testing, as this will provide a more accurate reading.
Afterward, immediately place the used lancet in a designated sharps container to ensure safe disposal and prevent injury.
Incorporating proper sampling techniques is crucial for accurate diabetes management. Research shows that following these procedures significantly boosts sampling success rates, enhancing overall health outcomes. As Rajasekhar Ramakrishnan, Director of the Biomathematics Division in Pediatrics, emphasizes, 'All authors hold positions in the Department of Pediatrics, College of Physicians & Surgeons, Columbia University, New York, New York.' This underscores the importance of following these steps to ensure safety and effectiveness in sample collection.
Furthermore, the use of difference plots in method comparison studies illustrates how effective blood sampling techniques can lead to better measurement agreement and understanding of biases. This reinforces the need for precision in this process. By cultivating a community that exchanges knowledge and support, we can enhance health results for individuals managing this condition together. You're not alone in this journey. Explore more resources at T2 Solutions to enhance your diabetes management journey.
Choosing the Right Manual Lancet: Types and Features
Manual lancets are essential tools for blood sampling, and they come in various types, primarily categorized into standard and safety options. Standard surgical blades are typically more economical and easily accessible; however, they require cautious handling to avoid unintentional injuries. In contrast, safety devices are designed with a retractable needle mechanism that significantly decreases the risk of needle sticks after use, enhancing user safety.
When choosing a device, it's important to consider several factors to ensure optimal comfort and effectiveness. Key considerations include the needle gauge—thinner needles tend to cause less pain—and the availability of depth adjustment options, which allow users to customize the penetration depth based on their skin type and sensitivity. Ease of use is also crucial, especially for those who may have dexterity challenges.
Statistics suggest that patient preferences for types of blood sampling devices differ. Many individuals prefer safety options because of their improved safety characteristics. A study titled "Effects of Age, Sex, and Skin Type on Circulatory Volume and Pain Perception" found that older adults generally had higher circulatory volumes, while females reported slightly greater pain levels compared to males. This emphasizes the significance of selecting a device that reduces discomfort, particularly for individuals who might be more sensitive.
Expert insights indicate that when handling diabetes, the selection of the device can significantly affect the overall experience of blood sampling. Diabetes specialists stress the importance of choosing a device that suits personal requirements, especially regarding pain management and safety. Real-world comparisons between standard and safety manual devices reveal that while standard options may be cost-effective, safety alternatives provide a compelling advantage in terms of user safety and peace of mind.
Additionally, the FDA has altered the categorization for manual surgical instruments, distinguishing sampling devices under a new classification regulation. This change reflects ongoing efforts to enhance the safety and effectiveness of these devices. As Lauren K. Roth, Associate Commissioner for Policy, noted, the compliance timeframes for Unique Device Identification requirements provide sufficient time for manufacturers to comply, ensuring that users have access to safe and reliable products.
In summary, understanding the characteristics of different types of manual lancets, including their safety features and user preferences, is crucial for effective management of the condition. By making informed choices, individuals can enhance their blood sampling experience, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. The path of managing this condition is a collective one, and by sharing experiences and insights within the community, individuals can support each other in achieving better health.
For additional details on blood sampling devices and resources for managing Type 2 and Type 3 conditions, visit T2DSolutions, your all-inclusive resource center for education and community assistance.
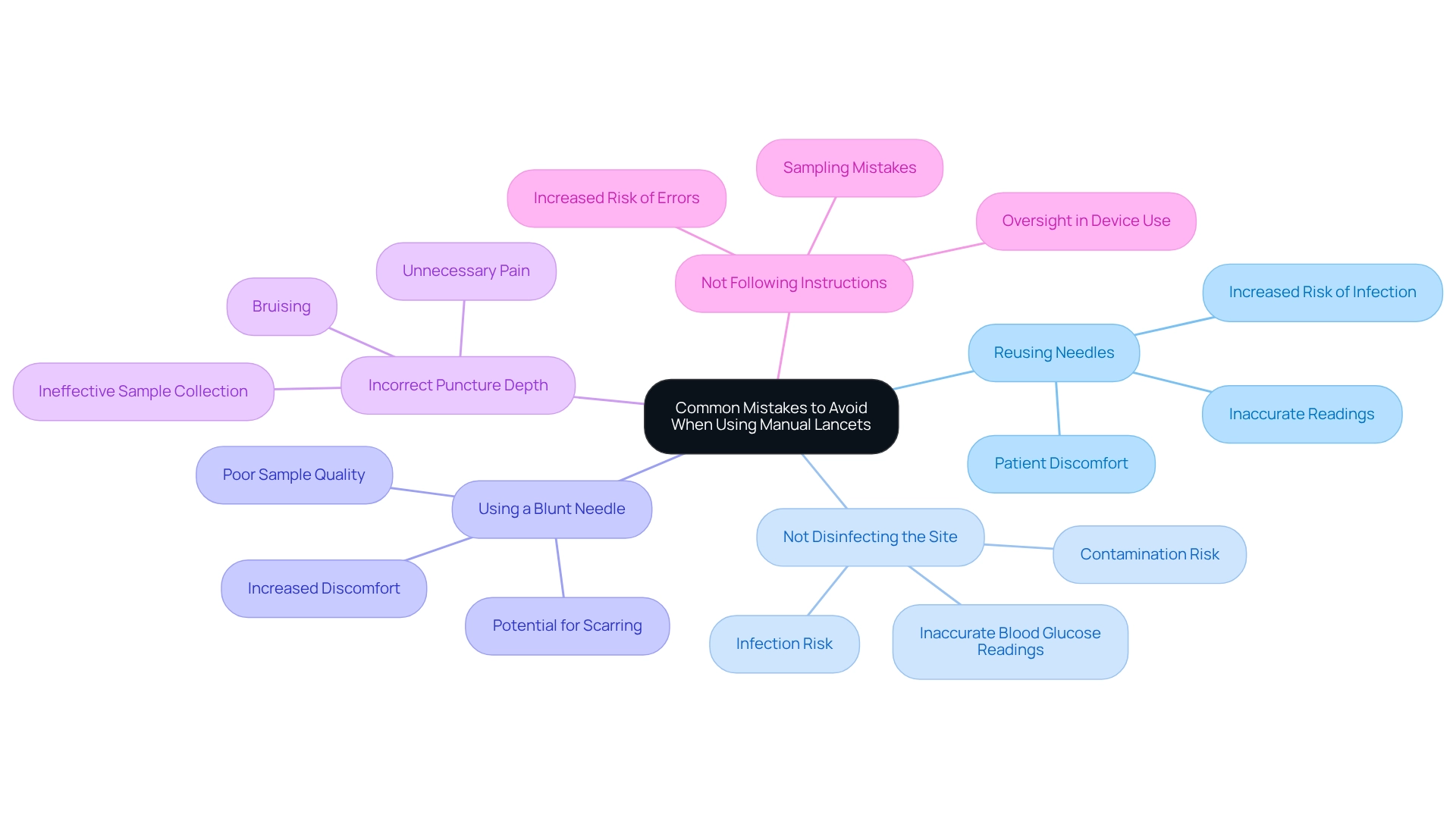
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Manual Lancets
- Reusing Needles: It's essential to use a new needle for each blood sample. Reusing needles can elevate the risk of infection and lead to inaccurate readings, complicating your blood sugar management. Many individuals with blood sugar concerns reuse a manual lancet, often due to discomfort or cost worries. However, this practice can have serious health implications. As Dirk Boecker notes, "The need for frequent lancing and associated discomfort and pain can be seen as a key hurdle for patients to comply with SMBG regimens." Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and there are ways to make it easier.
- Not Disinfecting the Site: Proper site disinfection is crucial before puncturing the skin. Neglecting to clean the puncture site can result in contamination, affecting the accuracy of your blood glucose readings and increasing the risk of infection. Many patients make the mistake of improper site preparation, leading to avoidable complications. Fortunately, resources for infusion site management and rotation are available through various diabetes organizations to assist you in this area.
- Using a Blunt Needle: Always replace your needle after each use. A blunt surgical instrument can lead to increased discomfort and may not extract enough fluid for an accurate sample. Healthcare professionals emphasize that using a sharp, new needle reduces discomfort and improves the quality of the blood sample. Dickinson has managed to prick many times a day for decades without forming scars or calluses, showcasing the effectiveness of proper needle use and care. You deserve a comfortable experience.
- Incorrect Puncture Depth: Adjusting the depth setting of your blood sampling device is vital. Setting the needle too deep can cause unnecessary pain and bruising. It’s recommended to tailor the depth based on your skin type and sensitivity, ensuring a balance between comfort and effective sample collection. It's understandable to feel uncertain, but with practice, you can find what works best for you.
- Not Following Instructions: Always adhere to the manufacturer's instructions for your specific lancet device. Each device may have unique features and recommendations that are crucial for safe and effective use. Neglecting these guidelines can lead to mistakes in sampling and oversight. Remember, taking these steps can make a significant difference in your blood sampling experience.
By understanding and implementing these best practices, you can significantly improve your blood sampling experience using a manual lancet, ensuring both safety and accuracy in your diabetes management. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Proper Disposal of Manual Lancets: Ensuring Safety and Compliance
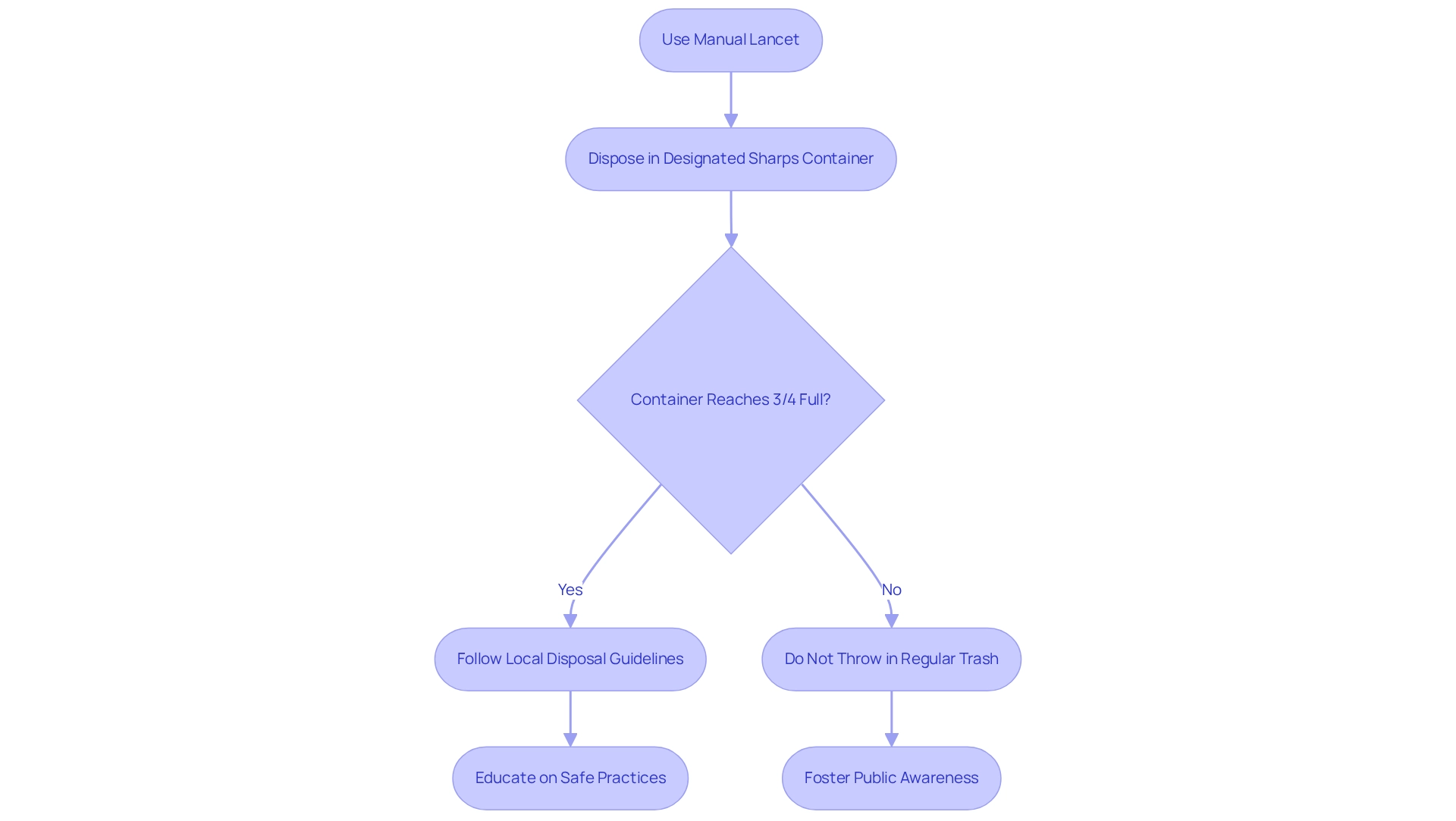
Used manual lancet devices must be disposed of in a designated sharps container immediately after use. These containers are specifically engineered to prevent needle sticks and securely contain biohazardous waste, ensuring safety for both users and the environment. It's understandable to feel concerned about the risks; thus, it is vital never to throw away used medical needles in regular trash or recycling bins, as this presents considerable health hazards.
When the sharps container reaches three-quarters full, please remember to adhere to local disposal guidelines. These may include taking the container to a designated drop-off location or utilizing a mail-back service for safe disposal. Compliance with these regulations is essential, as improper disposal can lead to injuries; approximately 385,000 needlesticks and other sharps-related injuries occur annually among hospital-based healthcare personnel.
Public awareness of appropriate needle disposal methods is critical. Recent data indicates that a significant portion of disposable syringe injuries—20% from 24/25 gauge needles and 18.3% from insulin needles—highlights the need for education on safe practices. Case studies from regions like Latin America show that as healthcare infrastructure improves, so does the awareness and implementation of sustainable sharps disposal methods.
For instance, the expansion of healthcare services in Latin America has driven demand for better sharps disposal solutions, reflecting a growing commitment to safety and compliance.
To ensure compliance and safety, health authorities recommend that individuals familiarize themselves with local regulations regarding sharps disposal. Brian Moore, VP at NICCA USA, Inc., emphasizes, "The quality of research they have done for us has been excellent," underscoring the importance of expert insights in promoting safe disposal practices. By adhering to these guidelines, recently diagnosed patients can help create a safer environment and lessen the risk of injury linked to the improper disposal of used manual lancets. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way in promoting your overall health and condition management.
Managing Anxiety and Discomfort: Emotional Support for Blood Sampling
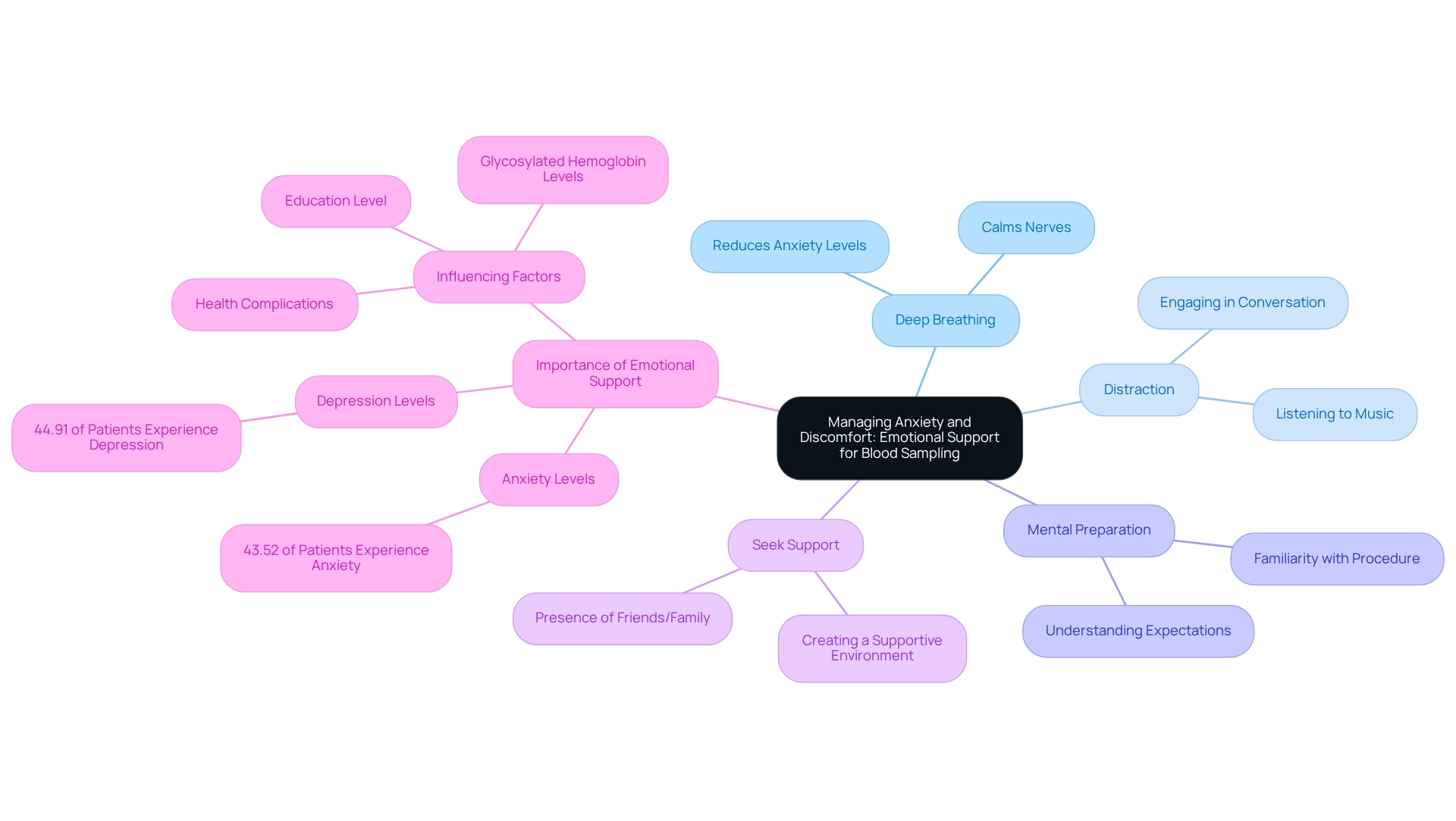
Blood sampling can evoke significant anxiety, especially for those newly diagnosed with diabetes. It’s completely understandable to feel this way. To help ease this discomfort, consider the following strategies:
- Practice Deep Breathing: Engaging in slow, deep breaths before and during the procedure can effectively calm your nerves and reduce anxiety levels.
- Distract Yourself: Engaging in conversation or listening to music during the test can serve as a helpful distraction, allowing you to focus less on the procedure itself.
- Prepare Mentally: Familiarizing yourself with the sampling procedure and understanding what to expect can significantly lessen the fear of the unknown, making the experience less intimidating.
- Seek Support: Having a friend or family member present can provide comfort and reassurance, creating a supportive environment during the blood sampling process.
Real-life examples illustrate the effectiveness of these strategies. Many patients report that practicing deep breathing techniques before testing has helped them feel more in control and less anxious. Additionally, a study involving 216 patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus revealed that a significant portion experienced anxiety (43.52%) and depression (44.91%). This highlights the importance of emotional support in managing these feelings.
The research also suggests that factors such as education level, health complications, and glycosylated hemoglobin levels significantly affect anxiety and depression scores. This underscores the necessity for thorough health education and support.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize how important emotional support is for individuals with diabetes-related conditions. Our platform serves as a resource center, providing educational materials and community assistance to help you navigate the challenges of managing your health. Remember, you are not alone—help is available!
This emphasizes the significance of a supportive network as you face the challenges of managing blood sugar levels. Furthermore, it’s noteworthy that 65.2% of patients used medications other than insulin, which may also impact their anxiety levels. By integrating these emotional support techniques and fostering a community of understanding through T2DSolutions, you can better manage your anxiety during blood sampling, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
Early intervention and support are essential to enhance adaptation and prevent complications, reinforcing the need for a holistic approach to diabetes management. We are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Selecting the right manual lancet is a pivotal step in effective diabetes management. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the choices available, but understanding the various types and their unique features empowers you to make informed decisions that prioritize comfort and safety. The advancements in lancet technology highlight the potential for virtually pain-free blood sampling, which can significantly improve your experience and compliance in managing diabetes.
Safety must always be at the forefront when using manual lancets. Best practices—such as proper hand hygiene, site disinfection, and correct disposal—are crucial to prevent infections and ensure accurate blood glucose readings. By adhering to these guidelines, you can mitigate risks and foster a safer environment for your diabetes care.
Moreover, addressing the emotional aspects of blood sampling is equally important. It's normal to experience anxiety and discomfort, but techniques to manage these feelings can transform the experience, making it less daunting. Support from healthcare providers, family, and community resources can create a nurturing environment that encourages you to engage actively in your diabetes management.
Ultimately, effective diabetes management is a multifaceted journey that combines knowledge, safety precautions, and emotional support. You're not alone in this journey; by leveraging the right tools and practices, you can navigate your diabetes care with confidence and ease, leading to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life. Remember, we are here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are manual lancets used for?
Manual lancets are precision tools designed to gently pierce the skin and collect blood samples, primarily from the fingertip. They are essential for managing blood sugar levels through regular glucose monitoring.
How do manual lancets minimize discomfort during use?
Users can select the appropriate depth setting and method when using manual lancets to minimize discomfort. Recent advancements in technology, such as devices with smaller needles, have been shown to significantly reduce pain during blood sampling.
What was the outcome of the clinical trial regarding new lancet technology?
A clinical trial conducted in 2007 found that participants using a new device with a very small needle (0.15 mm diameter) reported no pain, contrasting with the average pain score of 1.702 associated with traditional lancets.
Why is it important to choose the right manual lancet?
Choosing the appropriate manual lancet enhances the overall experience of managing diabetes, reduces psychological barriers to self-monitoring blood glucose levels, and fosters better health outcomes.
What safety precautions should be taken when using manual lancets?
It's crucial to wash hands thoroughly, disinfect the puncture site with an alcohol swab, ensure the device is sterile and intended for one-time use, and dispose of the lancet in a designated sharps container after use.
How can proper hand hygiene impact health for individuals using manual lancets?
Proper hand hygiene practices can significantly lower the incidence of infections related to the use of manual lancets, emphasizing the importance of education on safe sampling techniques.
What additional health practices are important for managing diabetes?
Consistent physical activity is linked to a decrease in the likelihood of developing type 2 conditions, and increased strength and conditioning can enhance insulin function and sensitivity, which are crucial for effective diabetes management.
How does T2DSolutions support individuals managing diabetes?
T2DSolutions offers educational materials and community support to empower individuals with knowledge and resources essential for effective diabetes management, including best practices for safe blood sampling.



