Overview
This article delves into the intricate relationship between adrenaline and blood sugar levels, especially concerning diabetes management. It’s important to recognize how the release of adrenaline during stressful moments can lead to increased glucose levels. Understanding this connection is crucial for effective glucose regulation and management strategies, particularly during high-stress situations or intense physical activities.
If you’ve ever felt overwhelmed by the complexities of managing your diabetes, know that you’re not alone in this journey. We’re here to support you every step of the way. By grasping how adrenaline impacts your blood sugar, you can take proactive steps to manage your health more effectively.
Consider reaching out for support or resources that can help you navigate these challenges. Remember, it’s understandable to feel uncertain at times, but with the right knowledge and support, you can find a path that works for you.
Introduction
In the complex journey of diabetes management, understanding the relationship between adrenaline and blood sugar levels is essential. Adrenaline, a hormone released during stressful moments, initiates a series of physiological responses that raise blood glucose levels, providing the body with quick energy. However, for those living with diabetes, these adrenaline spikes can make blood sugar regulation more challenging, leading to unpredictable fluctuations that can disrupt carefully crafted management plans.
It's important to recognize that exploring this intricate relationship between stress hormones and glucose metabolism can empower you to navigate your health journey more effectively. By grasping the physiological mechanisms at play, you can implement proactive management techniques that acknowledge the influence of adrenaline. This understanding is crucial for achieving better blood sugar control and enhancing your overall well-being. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
The Connection Between Adrenaline and Blood Sugar Levels
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone that plays a vital role in how our bodies respond to stress and physical exertion. When released during stressful moments, adrenaline activates the fight-or-flight response, preparing us to react quickly to perceived threats. One of its key functions is to prompt the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream, which leads to increased glucose levels. This process is essential for providing immediate energy to our muscles during high-intensity activities.
For those managing diabetes, understanding the connection between adrenaline and blood sugar levels is crucial. Fluctuations in both adrenaline and blood sugar can lead to unpredictable changes in glucose, complicating management strategies. Recent studies have shown that during high-intensity exercise, there is a significant rise in both adrenaline and blood sugar levels, which correlates with increased glucose availability.
For instance, a study involving elite athletes revealed that glucose levels surged from an average of 6.1 mM before races to 11.2 mM during competition, before dropping to 6.7 mM post-race. This highlights the importance of tailored glucose management strategies, especially around competition times. Furthermore, the study collected samples to examine insulin, glucagon, adrenaline, and other metabolites, offering a comprehensive view of the metabolic changes occurring during these events.
Additionally, research suggests that the effects of adrenaline and blood sugar levels can vary depending on medication adherence. For example, local anesthesia with adrenaline was found not to significantly impact glycemic levels in patients who followed their medication regimen. In contrast, those who did not adhere experienced notable fluctuations. This underscores the importance of consistent medication management in mitigating the effects of adrenaline and blood sugar levels.
It's significant to note that a rise in the most prevalent non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) was observed, with a significance level below 0.01, further demonstrating the metabolic changes linked to adrenaline release.
In conclusion, the relationship between adrenaline and blood sugar levels is complex and multifaceted, particularly for individuals facing challenges with glucose regulation. By understanding how adrenaline and blood sugar levels interact, patients can better prepare for and manage their glucose levels during times of stress or vigorous physical activity. As noted by UP-B, a member of the editorial board of Diabetologia, grasping these dynamics is essential for effective diabetes management. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we are here to support you every step of the way.
How Stress Hormones Impact Blood Sugar Regulation
Stress hormones, particularly adrenaline and cortisol, play a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. When faced with pressure, our bodies release these hormones, leading to an increase in glucose production from the liver and a decrease in insulin sensitivity. This physiological response can be beneficial in acute situations, as it provides the energy needed for immediate physical demands.
However, persistent pressure can lead to prolonged elevated glucose levels, making health management more challenging for individuals.
At T2DSolutions, we understand how crucial it is to comprehend the effects of stress on blood sugar management. Our resource hub is designed to equip newly diagnosed patients with the tools and support they need to navigate these challenges. Research indicates that individuals with this condition who maintain stable cortisol levels often experience lower glucose levels, highlighting the intricate relationship between stress and glucose regulation.
This connection emphasizes the importance of community support and collaboration in effectively managing diabetes. For instance, studies have shown that perceived discrimination and job-related stress can lead to a flatter diurnal cortisol slope, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities, potentially exacerbating glucose regulation issues. The case study titled "Work Stress, Discrimination, and Cortisol Levels" illustrates how these factors can influence cortisol regulation and, in turn, blood sugar levels.
Moreover, recent findings reveal that among multiethnic participants, men with the condition exhibited lower total area under the curve (AUC) cortisol compared to their non-affected counterparts, while women with the condition showed higher AUC cortisol levels. This disparity underscores the need for tailored stress management strategies, as a one-size-fits-all approach may not be effective.
Understanding the interplay between cortisol, adrenaline, and blood sugar levels is essential for patients, enabling them to anticipate and manage potential spikes during stressful times. As Katherine Marengo, LDN, R.D., notes, "This visual guide can assist in removing uncertainty from snacks when handling type 2 condition." By recognizing the long-term effects of stress on their situation, individuals can adopt proactive strategies to stabilize their glucose levels, ultimately enhancing their overall management of the condition and improving their quality of life.
At T2DSolutions, we are dedicated to fostering resilience and support within our community. We encourage individuals to share their experiences and strategies, enriching their diabetes management journey together.
Physiological Mechanisms of Adrenaline's Effect on Glucose Metabolism
Adrenaline plays a significant role in influencing blood sugar levels and glucose metabolism, especially during high-intensity exercise or stressful situations. One of the key effects of adrenaline is the stimulation of glycogenolysis, which is the breakdown of glycogen into glucose in both the liver and muscles. This process is crucial for quickly enhancing glucose availability, providing the energy needed to meet the body's heightened demands during challenging moments.
Additionally, adrenaline promotes gluconeogenesis, the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. This dual action helps ensure that glucose levels remain elevated, which is vital for sustaining energy during physical exertion or periods of tension. Importantly, adrenaline also suppresses insulin release, further contributing to increased sugar levels in acute stress situations.
Research shows that even mild elevations of epinephrine can lead to significant glucose intolerance. This highlights the need to understand these mechanisms for effective diabetes management. A study examining the effects of adrenaline on insulin-mediated regulation of glucose and fat metabolism found that adrenaline infusion raised blood glucose concentration by about 50%. However, insulin was able to normalize this hyperglycemia within 30 minutes, illustrating the complex interplay between these hormones.
As R. S. Sherwin noted, "Our findings suggest that epinephrine is an important contributor to stress-induced hyperglycemia and the susceptibility of diabetics to the adverse metabolic effects of stress."
For individuals managing their adrenaline and blood sugar levels, recognizing how adrenaline influences glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis is essential. It's important to carefully observe blood sugar levels during stressful circumstances or intense exercise, as these physiological reactions can lead to variations that may complicate management of the condition. By understanding these mechanisms, you can navigate your health journey more effectively, making informed decisions that support your overall well-being.
At T2DSolutions, we are here to offer resources and assistance for individuals facing diabetes-related challenges. We encourage you to sign up for our updates to stay informed about educational resources and community support that can help you in your health management journey.
Adrenaline Spikes: Implications for Diabetes Management
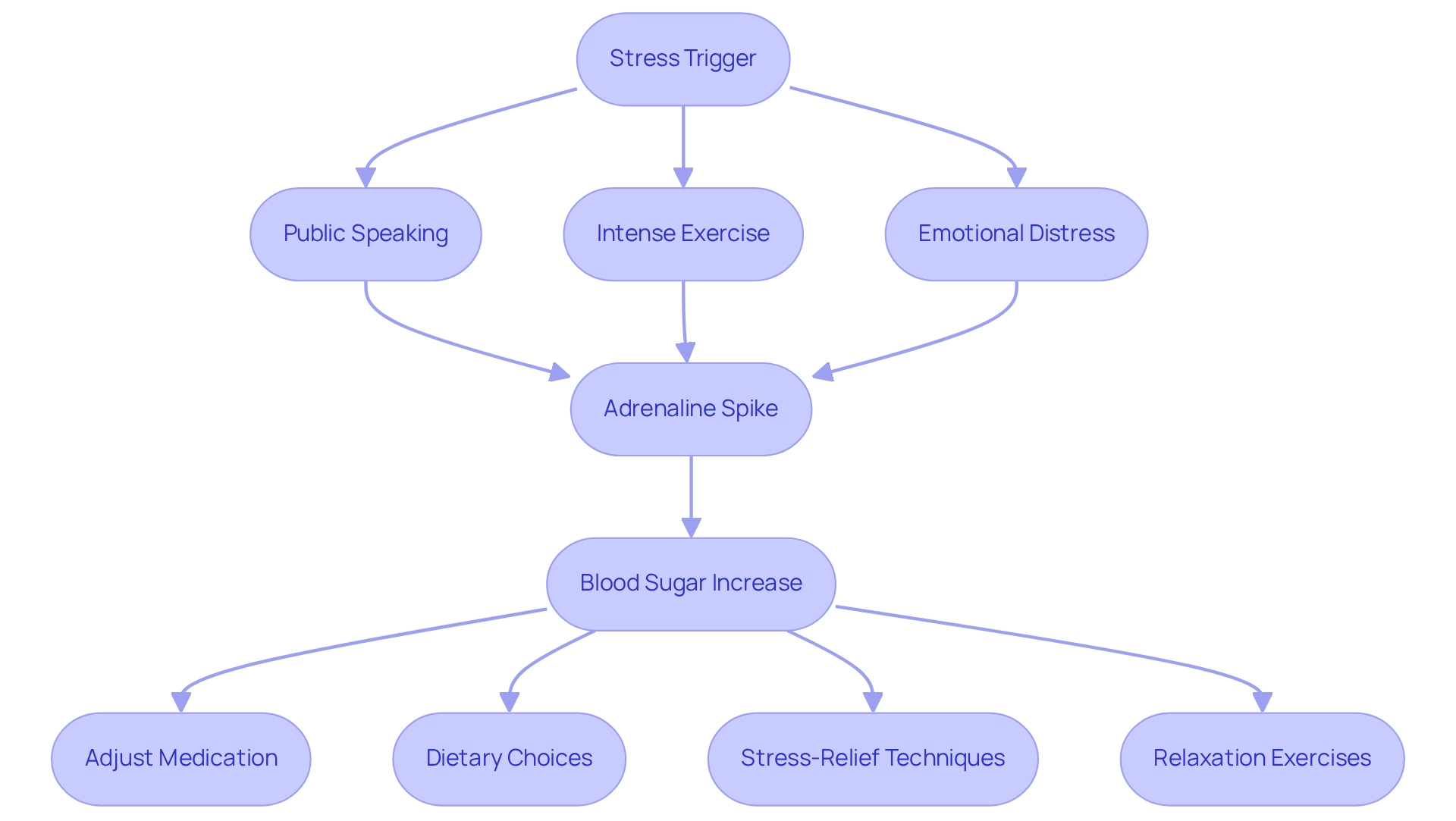
Adrenaline spikes can have a profound impact on both adrenaline and blood sugar levels in response to various stressors, such as public speaking, intense exercise, or emotional distress. For those managing diabetes, these spikes can lead to significant increases in adrenaline and blood sugar, complicating their management strategies. Research has shown that pressure is notably linked to elevated A1c values, especially among individuals with Type 2 Diabetes.
For instance, a study found that tension was significantly associated with A1c values exceeding 8.5% among Malaysian women with Type 2 Diabetes. This underscores the essential need for awareness and proactive management in navigating these challenges.
Understanding your personal stress triggers is vital for effective diabetes management. By closely tracking glucose levels during stressful situations, you can respond appropriately. Consider strategies such as:
- Adjusting medication in advance
- Making thoughtful dietary choices
- Incorporating stress-relief techniques to help mitigate the effects of adrenaline and blood sugar spikes
Engaging in relaxation exercises or practicing deep-breathing techniques before a stressful event can be particularly beneficial in lowering both adrenaline and blood sugar levels.
Case studies, such as "Interventions Targeting Stress and Glycemic Control," demonstrate that multi-component interventions focusing on stress management can lead to meaningful improvements in A1c levels. These interventions often highlight the importance of behavioral strategies and family involvement, suggesting that tailored approaches based on individual stressors can enhance the effectiveness of diabetes management plans.
Incorporating expert advice into your daily routine can further empower you to manage adrenaline and blood sugar levels during stress-induced spikes. For example, maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole foods and engaging in regular physical activity can build resilience against pressure. Additionally, T2DSolutions offers resources and newsletters that provide guidance on healthy eating and updates on management breakthroughs, ensuring you have access to the latest information and support.
As emphasized by Barbara J. Anderson and her collaborators, effective stress management is crucial for individuals with blood sugar concerns. By proactively addressing stress and understanding its effects on adrenaline and blood sugar levels, you can achieve better overall control and improve your quality of life. T2DSolutions is committed to assisting newly diagnosed patients by providing educational materials and community resources that address these challenges, helping you navigate your health journey more effectively.
Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar During Adrenaline Surges
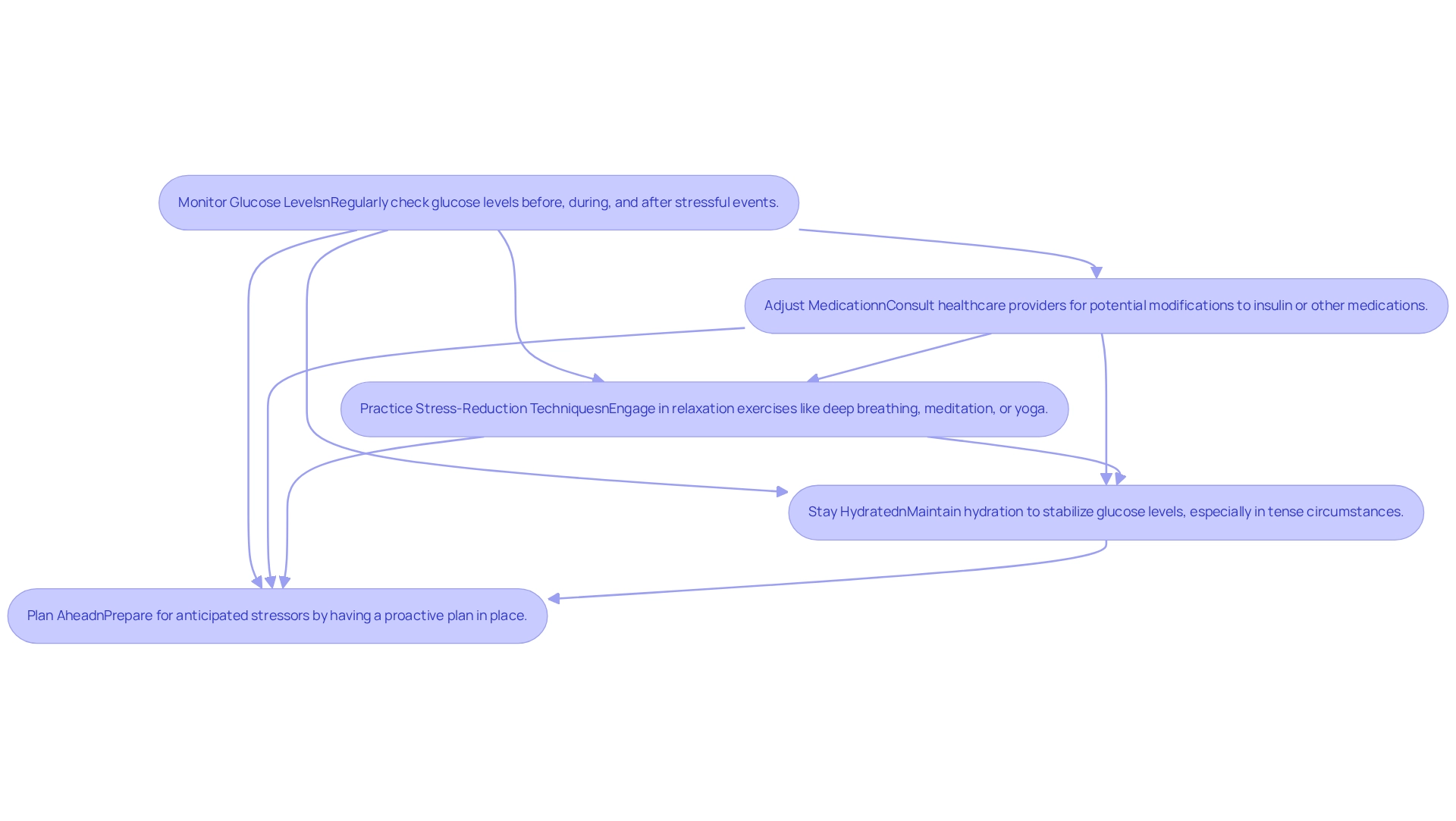
To effectively manage blood sugar during adrenaline surges, individuals with diabetes can adopt several key strategies, supported by T2DSolutions, a new resource hub for diabetes education and community support:
-
Monitor Glucose Levels: Regularly checking glucose levels before, during, and after stressful events is essential. This practice helps you understand how adrenaline and blood sugar levels influence your unique physiological responses, enabling timely adjustments. T2DSolutions offers tools and resources to assist in effective monitoring.
-
Adjust Medication: It's important to consult healthcare providers regarding potential modifications to insulin or other medications during times of increased pressure. Customized modifications can assist in achieving ideal glucose regulation. T2DSolutions provides guidance on how to communicate these needs with healthcare professionals.
-
Practice Stress-Reduction Techniques: Engaging in relaxation exercises such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can significantly lower stress levels and reduce the release of adrenaline. These techniques not only promote your mental well-being but also support better metabolic outcomes. T2DSolutions offers workshops and resources to help you learn and practice these techniques.
-
Stay Hydrated: Maintaining hydration is vital for overall metabolic function. Consuming water can aid in stabilizing glucose levels, especially in tense circumstances. T2DSolutions emphasizes the importance of hydration through educational materials.
-
Plan Ahead: Preparing for anticipated stressors by having a proactive plan in place is beneficial. This involves bringing snacks or medications to efficiently handle possible glucose level increases. T2DSolutions encourages you to create personalized management plans with available resources.
Implementing these strategies can lead to better control of adrenaline and blood sugar levels during pressure, ultimately improving your quality of life. Real-life instances show that individuals who actively track their glucose levels and modify their management strategies during stressful periods frequently achieve improved results in controlling their adrenaline and blood sugar levels. For example, a case study named 'Management Strategies for Type 2 Diabetes' emphasized how individuals who employed anxiety management techniques along with medication adjustments reported fewer fluctuations in their blood sugar levels during high-pressure situations.
Current recommendations highlight the significance of these practices, reinforcing that effective management of the condition requires a comprehensive approach that includes both lifestyle modifications, medical guidance, and considerations for adrenaline and blood sugar levels. As researcher Mayur B Wanjari states, "Preventive measures such as anxiety management therapies should be utilized and promoted." This highlights the importance of incorporating stress management into the management of blood sugar conditions.
Moreover, cultivating a supportive community via T2DSolutions can improve health results through shared knowledge and teamwork, which is vital for individuals managing the intricacies of this condition.
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Adrenaline and Blood Sugar Levels
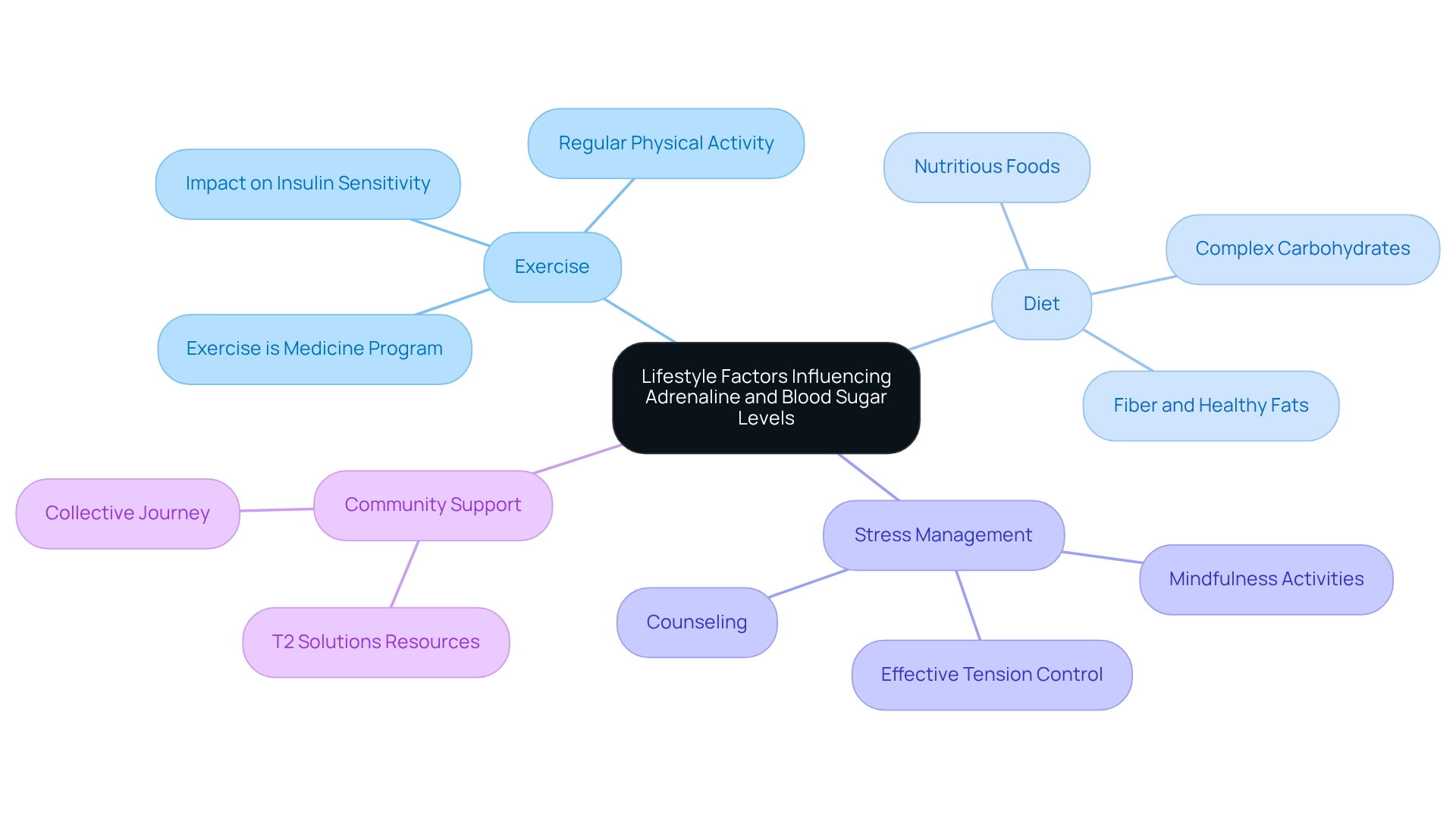
Lifestyle elements significantly influence adrenaline and blood sugar levels, playing a crucial role in diabetes control. It's understandable to feel overwhelmed by the complexities of managing diabetes, but participating in consistent physical exercise can be a powerful ally. Not only does it aid in reducing stress, but it also improves insulin sensitivity, which is essential for effective glucose management. For instance, the 'Exercise is Medicine Program' illustrates that integrating exercise into regular medical treatment can lead to enhanced diabetes-related habits, showcasing the practicality and efficacy of such lifestyle changes.
At T2DSolutions, we emphasize the significance of a nutritious diet, rich in whole foods, fiber, and healthy fats. This is crucial for stabilizing glucose levels and reducing spikes. Diets abundant in complex carbohydrates and low in processed sweeteners can help maintain steady glucose levels throughout the day. Moreover, sufficient rest and effective tension control methods—like mindfulness activities or counseling—are essential in reducing overall hormone levels, particularly adrenaline and blood sugar levels.
By embracing a comprehensive strategy that includes these lifestyle elements, individuals with glucose regulation issues can greatly enhance their metabolic management. The interaction among diet, exercise, and stress management not only helps in regulating glucose levels but also enhances overall well-being. As recent studies emphasize, the influence of physical activity on insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control is significant. This underscores the necessity for a thorough lifestyle approach in managing this condition.
Furthermore, addressing this issue is a shared journey, and assistance from community resources like T2 Solutions can improve this process. As Adam Felman pointed out, 'Similar to certain chronic conditions, depression is manageable,' highlighting that effective treatment is achievable. In summary, integrating regular exercise, a nutritious diet, and stress reduction techniques can empower individuals with diabetes to better manage their condition and reduce the impact of adrenaline and blood sugar levels on their health.
Identifying signs like heightened appetite, frequent urination, and thirst is vital for grasping the significance of controlling glucose levels efficiently. Moreover, understanding how adrenaline and blood sugar levels vary during high-intensity workouts can further educate individuals on how to customize their activities for optimal glucose regulation. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
The Psychological Impact of Stress on Blood Sugar Control
The psychological influence of pressure on adrenaline and blood sugar levels is significant and should not be overlooked. It’s understandable to feel overwhelmed by persistent pressure, which often manifests as anxiety and depression, complicating diabetes management. Many individuals under significant pressure may find themselves neglecting vital self-care routines, such as regular glucose monitoring and adhering to medication schedules.
Moreover, tension can lead to unhealthy coping methods, like overeating or skipping meals, which can contribute to erratic adrenaline and blood sugar levels. Research indicates that chronic tension can result in lean body mass loss and an increase in visceral fat, both of which negatively impact metabolic health. In 2025, data continues to show a strong correlation between psychological distress and poor health outcomes related to metabolic conditions. This underscores the urgent need for effective stress management strategies.
Participating in online support groups, such as Diabetic Connect and Diabetes Sisters, can offer individuals valuable coping strategies and a sense of community—crucial elements for managing their condition and improving overall well-being. Addressing mental health is essential for those dealing with blood sugar issues. Recognizing stress triggers and practicing stress-reduction techniques can lead to better management of adrenaline and blood sugar levels, ultimately enhancing quality of life.
As emphasized by Mark Davies, "Significant psychological ill-health is more likely among individuals with the condition, and psychological distress negatively affects self-care, resulting in worse biomedical outcomes, heightened complications, healthcare expenses, reduced productivity, and increased mortality."
Thus, prioritizing mental health is not only beneficial but essential for effective management of the condition. Despite guidelines stressing the necessity for enhanced access to psychological assistance for individuals with diabetes-related issues, advancements in services have been limited, highlighting ongoing challenges in obtaining mental health resources.
At T2DSolutions, we recognize the importance of mental health in managing diabetes-related conditions. As a new resource center for Type 2 and Type 3 education and community support, we strive to provide individuals with access to valuable resources and support networks to help navigate the psychological challenges associated with their condition. By fostering a sense of community and offering educational resources, T2D Solutions is dedicated to improving the overall well-being of individuals impacted by this condition.
Key Takeaways for Better Blood Sugar Management
To effectively manage blood sugar levels in relation to adrenaline surges, individuals with diabetes can benefit from a compassionate, multifaceted approach. This includes strategies supported by T2DSolutions, a valuable resource hub for diabetes education and community support.
Firstly, it's crucial to understand the connection between stress and glucose levels. Recognizing how stress triggers the release of adrenaline, which can elevate blood sugar, is essential for effective management. Notably, the ideal glucose level for ICU patients remains uncertain, highlighting the complexities of glucose regulation under pressure.
Next, monitoring glucose levels closely during challenging situations is vital. By keeping a vigilant eye on these levels, individuals can make timely adjustments to their treatment plans. T2DSolutions provides helpful tools and resources to assist in this important monitoring process.
Adrenaline and blood sugar levels significantly influence the body's response to stress. Engaging in mindfulness practices, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can greatly reduce both adrenaline and blood sugar levels. T2DSolutions offers access to guided sessions and community support for these beneficial practices.
Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine is essential. A nutritious diet, paired with consistent physical activity, supports overall health and helps mitigate the effects of stress on blood sugar. T2DSolutions provides meal planning resources and exercise advice tailored for individuals managing their blood sugar.
It's also important to address mental health concerns. Seeking support for mental health is vital, as emotional well-being directly impacts diabetes management. As Dhatariya K. notes, "in individuals who are unwell or incapacitated, the systems must be switched from automatic to 'manual' mode to enable the teams to assist in managing the condition."
By integrating these strategies into daily routines, individuals can achieve better blood sugar control. For example, a case study on impaired glucose tolerance highlights that early intervention can prevent progression to type 2 conditions, underscoring the importance of proactive management. Moreover, statistics reveal that 8.0% of U.S. adults with diagnosed conditions have concerning non-HDL cholesterol levels, indicating the need for comprehensive health strategies.
As diabetes management evolves, staying informed about current best practices and expert insights through T2DSolutions empowers individuals to navigate their health journey effectively. Remember, you're not alone in this journey—we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between adrenaline and blood sugar levels is vital for effective diabetes management. It's important to recognize that adrenaline plays a significant role in raising blood glucose levels during stress. This can complicate management strategies for individuals living with diabetes. By acknowledging how stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol influence glucose metabolism, you can anticipate and better control blood sugar fluctuations that may arise during stressful situations or high-intensity activities.
Implementing proactive management techniques—such as regular blood sugar monitoring, stress-reduction strategies, and personalized medication adjustments—can empower you to navigate your diabetes journey more effectively. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity not only supports your overall health but also enhances insulin sensitivity, ultimately aiding in blood sugar control.
It's also crucial to address the psychological aspects of stress for achieving better health outcomes. Chronic stress can lead to neglect in self-care practices, further complicating diabetes management. By fostering a supportive community and prioritizing your mental health, you can develop effective coping strategies that enhance your quality of life.
Incorporating these insights and strategies into your daily routine can lead to improved blood sugar control and overall well-being. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. By staying informed and utilizing resources like T2DSolutions, you can take charge of your diabetes management and work towards a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is adrenaline and what role does it play in the body?
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone that helps the body respond to stress and physical exertion by activating the fight-or-flight response. It prepares the body to react quickly to perceived threats and prompts the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream for immediate energy.
How does adrenaline affect blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes?
Adrenaline can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which is particularly important for those managing diabetes. During high-intensity exercise, both adrenaline and blood sugar levels can rise significantly, affecting glucose availability and complicating management strategies.
What did recent studies reveal about glucose levels in athletes during competition?
A study found that glucose levels in elite athletes surged from an average of 6.1 mM before races to 11.2 mM during competition, and then dropped to 6.7 mM post-race, indicating the need for tailored glucose management strategies around competition times.
How does medication adherence impact the effects of adrenaline and blood sugar levels?
Medication adherence can significantly influence the effects of adrenaline and blood sugar levels. For instance, patients who followed their medication regimen experienced fewer fluctuations in glycemic levels compared to those who did not adhere to their medications.
What other metabolic changes are associated with adrenaline release?
Research has shown a significant rise in non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) linked to adrenaline release, indicating broader metabolic changes during stress and physical exertion.
Why is understanding the relationship between adrenaline and blood sugar levels important for diabetes management?
Understanding how adrenaline and blood sugar levels interact can help individuals better prepare for and manage their glucose levels during stress or vigorous physical activity, ultimately improving their diabetes management.
What role do stress hormones like cortisol play in regulating blood sugar levels?
Stress hormones, particularly cortisol and adrenaline, increase glucose production from the liver and decrease insulin sensitivity in response to pressure, which can be beneficial in acute situations but may lead to prolonged elevated glucose levels with chronic stress.
How does community support influence diabetes management?
Community support and collaboration are crucial in managing diabetes, as stable cortisol levels have been linked to lower glucose levels, and shared experiences can help individuals navigate the challenges of the condition.
What disparities in cortisol levels have been observed among individuals with diabetes?
Studies show that among multiethnic participants, men with diabetes exhibited lower total area under the curve (AUC) cortisol compared to non-affected men, while women with diabetes showed higher AUC cortisol levels, highlighting the need for tailored stress management strategies.
How can individuals manage potential spikes in blood sugar during stressful times?
By understanding the interplay between cortisol, adrenaline, and blood sugar levels, individuals can anticipate and manage potential spikes, adopt proactive strategies, and improve their overall diabetes management and quality of life.



